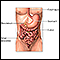
Duodenal atresia
Duodenal atresia is a condition in which the first part of the small bowel (the duodenum) has not developed properly. It is not open and does not allow the passage of stomach contents.
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine. It is located between the stomach and the middle part of the small intestine, or jejunum. Aft...
Causes
The cause of duodenal atresia is not known. It is thought to result from problems during an embryo's development. The duodenum does not change from a solid to a tube-like structure, as it normally would.
Many infants with duodenal atresia also have Down syndrome. Duodenal atresia is often associated with other birth defects.
Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which a person has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSymptoms
Symptoms of duodenal atresia include:
- Upper abdominal swelling (sometimes)
- Early vomiting of large amounts, which may be greenish (containing bile)
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Continued vomiting even when infant has not been fed for several hours
- No bowel movements after first few meconium stools
Exams and Tests
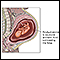
A fetal ultrasound may show high amounts of amniotic fluid in the womb (polyhydramnios). It may also show swelling of the baby's stomach and part of the duodenum.
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac....

Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios occurs when too much amniotic fluid builds up during pregnancy. It is also called amniotic fluid disorder, or hydramnios.
An abdominal x-ray may show air in the stomach and first part of duodenum, with no air beyond that. This is known as the double-bubble sign.
Abdominal x-ray
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. Wh...

Treatment
A tube is placed to decompress the stomach. Dehydration and electrolyte imbalances are corrected by providing fluids through an intravenous tube (IV, into a vein). Checking for other congenital anomalies should be done.
Surgery to correct the duodenal blockage is necessary, but not an emergency. The exact surgery will depend on the nature of the abnormality. Other problems (such as those related to Down syndrome) must be treated as appropriate.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Recovery from the duodenal atresia is expected after treatment. If not treated, the condition is deadly.
Possible Complications
These complications may occur:
- Other birth defects
- Dehydration
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
After surgery, there may be complications such as:
- Swelling of the first part of the small bowel
- Problems with movement through the intestines
- Gastroesophageal reflux
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if your newborn is:
- Feeding poorly or not at all
- Vomiting (not simply spitting up) or if the vomit is green
- Not urinating or having bowel movements
Prevention
There is no known prevention.
Reviewed By
Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Dingeldein M. Selected gastrointestinal anomalies in the neonate. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 84.
Maqbool A, Bales C, Liacouras CA. Intestinal atresia, stenosis, and malrotation. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 356.
Semrin MG. Anatomy, histology, and developmental anomalies of the stomach and duodenum. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 49.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.