Aneurysm
An aneurysm is an abnormal widening or ballooning of a part of an artery due to weakness in the wall of the blood vessel.
Aneurysm description - Animation
An aneurysm is a fluid-filled pouch that forms as a result of a separation in the wall of a blood vessel. It usually occurs in a weak area of an artery’s wall where the blood pressure forces the weakened area to bulge outward. An aneurysm can rupture resulting in internal bleeding. A large rupture may be rapidly fatal. A small one, sometimes termed a leak, may produce warning symptoms that allow people to seek medical care.
Causes
It is often not clear exactly what causes aneurysms. Some aneurysms are present at birth (congenital). Defects in some parts of the artery wall may be a cause.
Common locations for aneurysms include:
- Major artery from the heart such as the thoracic or abdominal aorta
Aorta
The aorta is the main blood vessel that supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs. An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) occurs when an area of t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain (cerebral aneurysm)
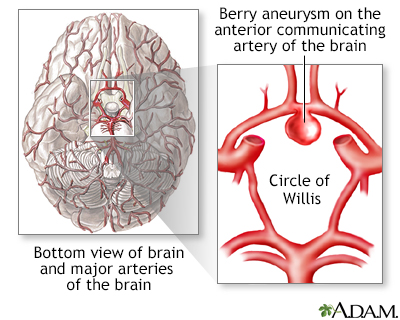
Cerebral aneurysm
An aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel that causes the blood vessel to bulge or balloon out. When an aneurysm occurs in a blood ve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Behind the knee (popliteal artery aneurysm)
- Intestine (mesenteric artery aneurysm)
- Artery in the spleen (splenic artery aneurysm)
Certain factors or conditions may increase the risk for aneurysms including:
- High blood pressure (thoracic, abdominal and cerebral aneurysms)
- High cholesterol
- Cigarette smoking
- Illicit drug use (cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamine)
- Pregnancy (often linked to splenic artery aneurysms)
- Family history (sibling, parent, or child)
Inherited disorders that may increase the risk include:
- Fibromuscular dysplasia (abnormal cell growth in artery walls)
- Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome is a disorder of connective tissue. This is the tissue that strengthens the body's structures. Disorders of connective tissue affect...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a kidney disorder passed down through families. In this disease, many cysts form in the kidneys, causing them to ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Coarctation of the aorta
Coarctation of the aorta
The aorta is a larger artery that carries blood from the heart to the vessels that supply the rest of the body with blood. If part of the aorta is n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
Cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AV...
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
The symptoms depend on where the aneurysm is located. If the aneurysm occurs near the body's surface, pain and swelling with a throbbing lump is often seen.
Aneurysms in the body or brain often cause no symptoms. Aneurysms in the brain may expand without breaking open (rupturing). The expanded aneurysm may press on nerves and cause double vision, dizziness, or headaches. Some aneurysms may cause ringing in the ears.
If an aneurysm ruptures, pain, low blood pressure, a rapid heart rate, and lightheadedness may occur. When a brain aneurysm ruptures, there is a sudden severe headache that some people say is the "worst headache of my life." The risk of neurologic injury, coma, or death after a rupture is high.
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness from whi...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleExams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam.
Tests used to diagnose an aneurysm include:
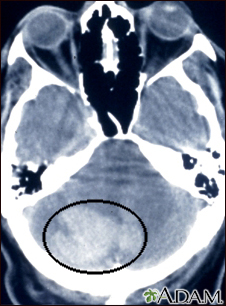
- CT scan
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT angiogram
- MRI
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
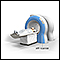 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRA (magnetic resonance angiogram)
Magnetic resonance angiogram
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an MRI exam of the blood vessels. Unlike traditional angiography that involves placing a tube (catheter) int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
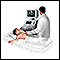 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Angiogram
Angiogram
An arteriogram is an imaging test that uses x-rays and a special dye to see inside the arteries. It can be used to view arteries in the heart, brain...
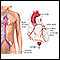 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the size and location of the aneurysm. Your provider may only recommend regular checkups to see if the aneurysm is growing.
Surgery may be done. The type of surgery that is done and when you need it depend on your symptoms and the size and type of aneurysm.
Surgery may involve a large (open) surgical cut. Many times, a procedure called endovascular embolization is done. Coils or stents of metal are inserted into a brain aneurysm to make the aneurysm clot. This reduces the risk for rupture while keeping the artery open. Other brain aneurysms may need to have a clip placed on them to close them off and prevent a rupture.
Endovascular embolization
Endovascular embolization is a procedure to treat abnormal blood vessels in the brain and other parts of the body. It is an alternative to open surg...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleAneurysms of the aorta may be reinforced with surgery to strengthen the blood vessel wall.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop a lump on your body, whether or not it is painful and throbbing.
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have:
- Pain in your belly or back that is very bad or does not go away
- A sudden loss of consciousness (fainting) or severe headache, especially if you also have nausea, vomiting, seizures, or any other nervous system symptom
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSeizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If you are diagnosed with an aneurysm that has not bled, you will need to have regular testing to detect if it increases in size. In some cases, your provider will suggest early treatment because the aneurysm is large enough.
Prevention
Controlling high blood pressure may help prevent many aneurysms. Follow a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and keep your cholesterol at a healthy level to help prevent aneurysms or their complications.
Do not smoke. If you do smoke, quitting will lower your risk for an aneurysm.
Smoke, quitting
There are many ways to quit smoking. There are also resources to help you. Family members, friends, and co-workers may be supportive. But to be su...
Reviewed By
Luc Jasmin, MD, Ph.D., FRCS (C), FACS, Department of Neuroscience, Guam Regional Medical City, Guam; Department of Surgery, Johnson City Medical Center, TN; Department of Maxillofacial Surgery at UCSF, San Francisco, CA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Hemphill K, Tierney S, Tirschwell D, Davis AP. A review of methamphetamine use and stroke in the young. Front Neurol. 2024;15:1397677. PMID: 38721123 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38721123/.
Lawrence PF, Rigberg DA. Arterial aneurysms: etiology, epidemiology, and natural history. In: Sidawy AN, Perler BA, eds. Rutherford's Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 71.
Lee JJ, Mambelli DD, Britz GW. Surgical approaches to intracranial aneurysms. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 435.
Mills JL, Zachary Sr, Pallister S. Peripheral arterial disease. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 63.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.