CSF leak
Intracranial hypotension; Cerebrospinal fluid leakA CSF leak is an escape of the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is called the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
Causes
Any tear or hole in the membrane that surrounds the brain and spinal cord (dura) can allow the fluid that surrounds those organs to leak. When it leaks out, the pressure around the brain and spinal cord drops.
Causes of leakage through the dura include:
- Certain head, brain, or spinal surgeries
- Head or spine injury
- Placement of tubes for epidural anesthesia or pain medicines
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Sometimes, no cause can be found. This is called a spontaneous CSF leak.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- A headache that is worse when you sit up and improves when you lie down. It may be associated with light sensitivity, nausea, and neck stiffness.
- Drainage of CSF from the ear (rarely).
- Drainage of CSF from the nose (rarely).
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. Tests may include:
- CT scan of the head with contrast dye
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT myelogram of the spine
- MRI of the head or spine
MRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radioisotope test of the CSF to track the leakage
Treatment
Depending on the cause of the leak, many symptoms improve on their own after a few days. Complete bed rest for several days is usually recommended. Drinking more fluids, especially drinks with caffeine, can help slow or stop the leak and may help with headache pain.
Your headache may be treated with pain relievers and fluids. If your headache lasts longer than a week after a lumbar puncture, a procedure may be done to block the hole that may be leaking fluid. This is called a blood patch, because a blood clot can be used to seal the leak. In most cases, this makes symptoms go away. In rare cases, surgery is needed to repair the tear in the dura and stop your headache.
If symptoms of infection (fever, chills, change in mental status) are present, treatment with antibiotics will likely be needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook is usually good depending on the cause. Most cases heal by themselves with no lasting symptoms.
If the CSF leak keeps coming back, high pressure of the CSF (hydrocephalus) might be the cause and should be treated.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
Possible Complications
Complications may occur if the cause is surgery or trauma. Infections after surgery or trauma can lead to meningitis and serious complications, such as swelling of the brain, and need to be treated right away.
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have a headache that gets worse when you sit up, especially if you have recently had a head injury, surgery, or childbirth involving epidural anesthesia.
- You have a moderate head injury, and then develop a headache that is worse when you sit up, or you have a thin, clear fluid draining from your nose or ear.
Prevention
Most CSF leaks are a complication of a spinal tap or surgery. The provider should use the smallest needle possible when doing a spinal tap.
References
Maslak JP, Casper DS, Pelle D. Neurologic complications of common spine operations. In: Steinmetz MP, Benzel EC, eds. Benzel's Spine Surgery. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 91.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
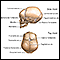
Cerebrospinal fluid leak - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid is the fluid found in and around the central nervous system (CNS) organs, the brain and spinal cord. It protects the brain and spinal cord by acting like a liquid cushion. The fluid allows the organs to be buoyant protecting them from blows or other trauma. Inside the skull the cerebrospinal fluid is contained by the dura which covers the brain. Any trauma or tear in the dura can allow the fluid to leak out creating an emergency situation.
Cerebrospinal fluid leak
illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid leak - illustration
Cerebrospinal fluid is the fluid found in and around the central nervous system (CNS) organs, the brain and spinal cord. It protects the brain and spinal cord by acting like a liquid cushion. The fluid allows the organs to be buoyant protecting them from blows or other trauma. Inside the skull the cerebrospinal fluid is contained by the dura which covers the brain. Any trauma or tear in the dura can allow the fluid to leak out creating an emergency situation.
Cerebrospinal fluid leak
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


