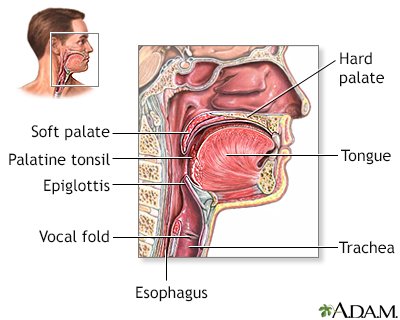
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation (swelling) of the tonsils.
Tonsillitis - Animation
If your child often has a sore throat, trouble swallowing, and ear pain, she may have a problem with her tonsils. So, what causes tonsillitis? The tonsils are small, dimpled, golf ball-like nodes on either side of the back of your child's throat. They normally help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body. If the tonsils become so overwhelmed with bacteria from strep throat or a viral infection, they can swell and become inflamed, causing tonsillitis. Your child's doctor will look in your child's mouth and throat for swollen tonsils. The tonsils will probably be red and may have white spots on them. The lymph nodes in your child's jaw and neck may be swollen and tender to the touch. The doctor may test your child's blood for infection. If bacteria are the cause, your child will probably need to take antibiotics, either in a shot or in pill form. If your child needs to take antibiotic pills, make sure she takes all of the medicine. To comfort your child, give her cold liquids and popsicles. Gargling with salt water can help. She can also take over-the-counter medicine like acetaminophen or ibuprofen for her pain and fever. Tonsillitis usually improves two or three days after treatment starts. The infection usually goes away too, but some people may need to take antibiotics for longer. If your child has a great many repeated infections, surgery may be recommended to remove her tonsils, but this is no longer a common reason to have the tonsils out.
Causes
The tonsils are lymph nodes in the back of the mouth and top of the throat. They help to filter out bacteria and other germs to prevent infection in the body.
A bacterial or viral infection can cause tonsillitis. Strep throat is a common cause.
Strep throat
Strep throat is a disease that causes a sore throat (pharyngitis). It is an infection with a bacteria called group A streptococcus.
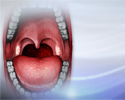

Strep throat
Strep throat is the most common bacterial cause of sore throat. Because strep throat can occasionally lead to rheumatic fever, antibiotics are given. Strep throat often includes a fever (greater than 101 degrees Fahrenheit or 38.3 degrees Centigrade), white draining patches on the throat, and swollen or tender lymph glands in the neck. Children may have headache and stomach pain.
The infection may also be seen in other parts of the throat. One such infection is called pharyngitis.
Pharyngitis.
Pharyngitis, or sore throat, is discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow.
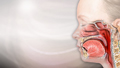
Tonsillitis is very common in children.
Symptoms
Common symptoms may be:
- Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty swallowing
Painful swallowing is any pain or discomfort while swallowing. You may feel it high in the neck or lower down behind the breastbone. Most often, th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ear pain
Ear pain
An earache is a sharp, dull, or burning pain in one or both ears. The pain may last a short time or be ongoing. Related conditions include:Otitis m...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever and chills
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleChills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sore throat, which lasts longer than 48 hours and may be severe
- Tenderness of the jaw and throat
Other problems or symptoms that may occur are:
- Problems breathing, if the tonsils are very large
- Problems eating or drinking
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will look in the mouth and throat.
- The tonsils may be red and may have white spots on them.
- The lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may be swollen and tender to the touch.
A rapid strep test can be done in most providers' offices. However, this test may be normal, and you can still have strep. Your provider may send the throat swab to a laboratory for a strep culture. Culture results can take a few days.
Rapid strep test
A streptococcal screen is a test to detect group A streptococcus. This type of bacteria is the most common cause of strep throat.

Strep culture
A throat swab culture is a laboratory test that is done to identify germs that may cause infection in the throat. It is most often used to diagnose ...

Treatment
Swollen tonsils that are not painful or do not cause other problems do not need to be treated. Your provider may not give you an antibiotic. You may be asked to come back for a checkup later to assess your progress.
If tests show you do have strep, your provider will give you an antibiotic. It is important to finish all of your antibiotic doses as directed, even if you feel better. If you do not take them all, the infection can return.
The following tips may help your throat feel better:
- Drink cold liquids or suck on fruit-flavored frozen bars.
- Drink fluids, and mostly warm (not hot), bland fluids.
- Gargle with warm salt water.
- Suck on lozenges (containing benzocaine or similar ingredients) to reduce pain (these should not be used in young children because of the choking risk).
- Take over-the-counter (OTC) medicines, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen to reduce pain and fever. DO NOT give a child aspirin. Aspirin has been linked to Reye syndrome in children.
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some people who have repeated infections may need surgery to remove the tonsils (tonsillectomy).
Tonsillectomy
Tonsillectomy is a surgery to remove the tonsils. The tonsils are glands at the back of your throat. The tonsils are often removed along with the ad...

Outlook (Prognosis)
Tonsillitis symptoms due to strep will often get better within 2 or 3 days after you start the antibiotics.
Children with strep throat should be kept home from school or day care until they have been on antibiotics for 24 hours. This helps reduce the spread of illness.
Possible Complications
Complications from strep throat may be severe. They may include:
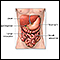
- Abscess in the area around the tonsils
Abscess in the area around the tonsils
Peritonsillar abscess is a collection of infected material in the area around the tonsils.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney disease caused by strep
- Rheumatic fever and other heart problems
Rheumatic fever
Rheumatic fever is a disease that may develop after an infection with group A streptococcus bacteria (such as strep throat or scarlet fever). It can...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if there is:
- Excess drooling in a young child
- Fever, particularly 101°F (38.3°C) or higher
- Pus in the back of the throat
- Red rash that feels rough, and increased redness in the skin folds
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe problems swallowing or breathing
- Tender or swollen lymph glands in the neck
Reviewed By
Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Chi DH, Tobey A. Otolaryngology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.
Mitchell RB, Archer SM, Ishman SL, et al. Clinical practice guideline: tonsillectomy in children (update) - executive summary. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;160(2):187-205. PMID: 30921525 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30921525/.
Zur KB. Tonsils and adenoids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 431.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.