Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a condition in which the lens of the eye loses its ability to focus. This makes it hard to see objects up close.
Causes
The lens of the eye needs to change shape to focus on objects that are close. The ability of the lens to change shape is because of the elasticity of the lens. This elasticity decreases slowly as people age. The result is a slow loss in the ability of the eye to focus on nearby objects.
People most often begin to notice the condition at around age 45, when they realize that they need to hold reading materials farther away in order to focus on them. Presbyopia is a natural part of the aging process and it affects everyone.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Decreased focusing ability for near objects
- Eyestrain
- Headache
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a general eye exam. This will include measurements to determine a prescription for glasses or contact lenses.
Tests may include:
- Exam of the retina
- Muscle integrity test
- Refraction test
Refraction test
A refraction is an eye exam that measures a person's prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Slit-lamp test
Slit-lamp
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Visual acuity
Visual acuity
The visual acuity test is used to determine the smallest letters you can read on a standardized chart (Snellen chart) or a card held 20 feet (6 meter...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
There is no cure for presbyopia. In early presbyopia, you may find that holding reading materials farther away or using larger print or more light for reading may be enough. As presbyopia worsens, you will need glasses or contact lenses to read. In some cases, adding bifocals to an existing lens prescription is the best solution. The reading glasses or bifocal prescription will need to be strengthened as you get older and lose more ability to focus up close.
By the age of 65, most of the lens elasticity is lost so that the reading glasses prescription won't continue to get stronger.
People who do not need glasses for distance vision may only need half glasses or reading glasses.
People who are nearsighted may be able to take off their distance glasses to read.
With the use of contact lenses, some people choose to correct one eye for near vision and one eye for far vision. This is called "monovision." The technique eliminates the need for bifocals or reading glasses, but it can affect depth perception.
Sometimes, monovision can be produced through laser vision correction. There are also bifocal contact lenses that can correct for both near and far vision in both eyes.
New surgical procedures are being evaluated that can also provide solutions for people who do not want to wear glasses or contacts for reading. Research is ongoing.
There are two new classes of eye drops being researched that may be able to help people with presbyopia.
- One type makes the pupil smaller, which increases the depth of focus, similar to a pinhole camera.
- The other type of drops works by softening the natural lens. The long-term effects of these drops are unknown.
People who are having cataract surgery can choose to have a special type of lens implant that allows them to see clearly in the distance and up close.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Vision can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or surgery.
Possible Complications
Vision difficulty that gets worse over time and is not corrected can cause problems with driving, lifestyle, or work.
Vision difficulty
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or ophthalmologist if you have eye strain or have trouble focusing on close objects.
Prevention
There is no proven prevention for presbyopia.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Could eyedrops replace reading glasses? www.aao.org/eye-health/news/could-eyedrops-replace-glasses-presbyopia. Updated January 6, 2022. Accessed January 18, 2024.
Crouch ER, Crouch ER, Grant TR. Ophthalmology. In: Rakel RE, Rakel DP, eds. Textbook of Family Medicine. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 17.
Reilly CD. Decision-making in refractive surgery. In: Mannis MJ, Holland EJ, eds. Cornea. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 172.
Schallhorn JM. Surgical treatment of presbyopia. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 3.9.
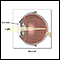
Presbyopia - illustration
Presbyopia is a condition in which the lens of the eye loses its elasticity and its ability to focus. In the normal eye, the lens changes shape so that light rays from a near object are focused clearly on the retina. In presbyopia, the lens hardens and can't change shape, so the light rays are focused behind the retina. The image that lands on the retina is blurry and out of focus.
Presbyopia
illustration
Presbyopia - illustration
Presbyopia is a condition in which the lens of the eye loses its elasticity and its ability to focus. In the normal eye, the lens changes shape so that light rays from a near object are focused clearly on the retina. In presbyopia, the lens hardens and can't change shape, so the light rays are focused behind the retina. The image that lands on the retina is blurry and out of focus.
Presbyopia
illustration
Review Date: 1/29/2024
Reviewed By: Audrey Tai, DO, MS, Athena Eye Care, Mission Viejo, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


