Angioedema
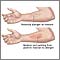
Angioneurotic edema; Welts; Allergic reaction - angioedema; Hives - angioedemaAngioedema is swelling that is similar to hives, but the swelling is under the skin instead of on the surface.
Hives
Hives are raised, often itchy, red bumps (welts) on the surface of the skin. They can be an allergic reaction to food or medicine. They can also ap...

Hives are often called welts. They are a surface swelling. It is possible to have angioedema without hives, and many times angioedema can come with hives.
Causes
Angioedema may be caused by an allergic reaction. Angioedema typically is not itchy while hives are very itchy. During the reaction, histamine and other chemicals are released into the bloodstream. The body releases histamine when the immune system detects a foreign substance called an allergen.
Allergic reaction
Allergic reactions are sensitivities to substances called allergens that come into contact with the skin, nose, eyes, respiratory tract, and gastroin...

Allergen
An allergen is a substance that can cause an allergic reaction. In some people, the immune system recognizes allergens as foreign or dangerous. As ...
However, in most cases, the cause of angioedema is never found.
The following may cause angioedema:
- Allergies due to animal dander (scales of shed skin), foods, insect bites or pollen
Scales
Scales are a visible peeling or flaking of outer skin layers. These layers are called the stratum corneum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Exposure to water, sunlight, cold or heat
- Medicines (drug allergy) such as antibiotics (penicillin and sulfa drugs), nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and certain blood pressure medicines (ACE inhibitors)
Drug allergy
Drug allergies are a group of symptoms caused by an allergic reaction to a drug (medicine).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune diseases such as lupus
Hives and angioedema may also occur after infections. Angioedema may occur alone or with other illnesses (including autoimmune disorders such as lupus, leukemia, and lymphoma).
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...

A rare form of angioedema runs in families and has different triggers, complications, and treatments. This is called hereditary angioedema.
Hereditary angioedema
Hereditary angioedema is a rare but serious problem with the immune system. The problem is passed down through families. It causes swelling, partic...
Symptoms
The main symptom is sudden swelling below the skin surface. Welts or swelling on the surface of the skin can also develop.
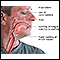
The swelling usually occurs around the eyes and lips. It may also be found on the hands, feet, and throat. The swelling may form a line or be more spread out.
The welts are painful and may be itchy. This is known as hives (urticaria). They turn pale and swell if irritated. The deeper swelling of angioedema may also be painful.
Other symptoms may include:
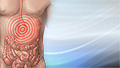
- Abdominal cramping
Abdominal cramping
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen eyes and mouth
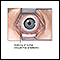
- Swollen lining of the eyes (chemosis)
Chemosis
Chemosis is swelling of the tissue that lines the eyelids and surface of the eye (conjunctiva).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
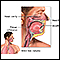
The health care provider will look at your skin and ask if you have been exposed to any irritating substances. If your throat is affected, a physical exam might reveal abnormal sounds (stridor) when you breathe in.
Stridor
Stridor is an abnormal, high-pitched, musical breathing sound. It is caused by a blockage in the throat or voice box (larynx). It is most often hea...
Blood tests or allergy testing may be ordered, but often no cause of the swelling or hives is found.
Allergy testing
Allergy skin tests are used to find out which substances cause a person to have an allergic reaction. These substances are called allergens....

Treatment
Mild symptoms may not need treatment. Moderate to severe symptoms may need to be treated. Breathing difficulty is an emergency condition.
People with angioedema should:
- Avoid any known allergen or trigger that causes their symptoms.
- Avoid any medicines, herbs, or supplements that are not prescribed by a provider.
Cool compresses or soaks can relieve pain.
Medicines used to treat angioedema include:
- Antihistamines
Antihistamines
An allergy is an immune response, or reaction, to substances (allergens) that are usually not harmful. In someone with allergies, the immune respons...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Anti-inflammatory medicines (corticosteroids)
- Epinephrine injectors (people with a history of severe symptoms may need to carry these with them in case of a severe reaction)
- Inhaler medicines that help open up the airways
If the person has trouble breathing, seek medical help right away. A severe, life-threatening airway blockage may occur if the throat swells.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Angioedema that does not affect the breathing may be uncomfortable. It is usually harmless and goes away in a few days.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Angioedema does not respond to treatment
- It is severe
- You have never had angioedema before
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if there are any of the following symptoms:
- Abnormal breathing sounds
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Fainting
References
Barksdale AN, Ross W. Allergy, anaphylaxis, and angioedema. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 106.
Dinulos JGH. Urticaria, angioedema, and pruritus. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 6.
Saini SS. Urticaria and angioedema. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 232.
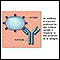
Histamine is released - illustration
Mast cells release histamine when an allergen is encountered. The histamine response can produce sneezing, itching, hives and watery eyes.
Histamine is released
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Deborah Pedersen, MD, MS, Allergy & Asthma Care, PC, Taunton, MA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


