Mononeuropathy
Mononeuropathy is damage to a single nerve, which results in loss of movement, sensation, or other function of that nerve.
Loss of movement
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.
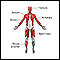
Causes
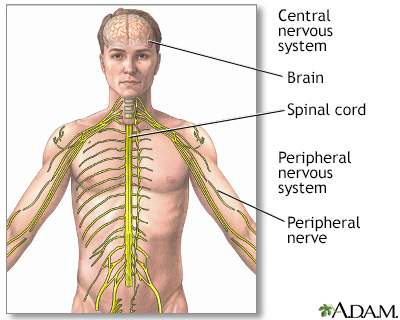
Mononeuropathy is due to damage to a nerve outside the brain and spinal cord (peripheral neuropathy).
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral nerves carry information to and from the brain. They also carry signals in both directions between the spinal cord and the rest of the bo...
Mononeuropathy is most often caused by injury. Diseases affecting the entire body (systemic disorders) can also cause isolated nerve damage.
Systemic
Systemic means affecting the entire body, rather than a single organ or body part. For example, systemic disorders, such as high blood pressure, or s...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleLong-term pressure on a nerve due to swelling or injury can result in mononeuropathy. The covering of the nerve (myelin sheath) or part of the nerve cell (the axon) may be damaged. This damage slows or prevents signals from traveling through the damaged nerves.
Myelin
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty ...

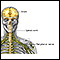
Mononeuropathy may involve any part of the body. Some common forms of mononeuropathy include:
- Axillary nerve dysfunction (loss of movement or sensation in the shoulder)
Axillary nerve dysfunction
Axillary nerve dysfunction is nerve damage that can lead to a loss of movement or sensation in the shoulder.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Common peroneal nerve dysfunction (loss of movement or sensation in the foot and leg)
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction is due to damage to the peroneal nerve leading to loss of movement or sensation in the foot and leg. This conditio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
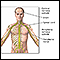
Cranial mononeuropathy III, IV, compression or diabetic type
Compression
Cranial mononeuropathy III is a nerve disorder. It affects the function of the third cranial nerve. As a result, the person may have double vision ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDiabetic
This diabetic type of cranial mononeuropathy III is a complication of diabetes. It causes double vision and eyelid drooping.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cranial mononeuropathy VI (double vision)
Cranial mononeuropathy VI
Cranial mononeuropathy VI is a nerve disorder. It affects the function of the sixth cranial (skull) nerve. As a result, the person may have double ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cranial mononeuropathy VII (facial paralysis)
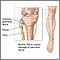
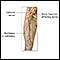
- Femoral nerve dysfunction (loss of movement or sensation in part of the leg)
Femoral nerve dysfunction
Femoral nerve dysfunction is a loss of movement or sensation in parts of the legs due to damage to the femoral nerve.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Median nerve dysfunction (carpal tunnel syndrome -- including numbness, tingling, weakness, or muscle damage in the hand and fingers)
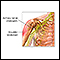
- Radial nerve dysfunction (problems with movement in the arm and wrist and with sensation in the back of the arm or hand)
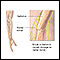
Radial nerve dysfunction
Radial nerve dysfunction is a problem with the radial nerve. This is the nerve that travels from the armpit down the back of the arm to the hand. I...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sciatic nerve dysfunction (problem with the muscles of the back of the knee and lower leg, and sensation to the back of the thigh, part of the lower leg, and sole of the foot)
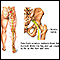
Sciatic nerve dysfunction
Sciatica refers to pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg. It is caused by injury to or pressure on the sciatic nerve. Sciatica is a symp...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ulnar nerve dysfunction (cubital tunnel syndrome -- including numbness, tingling, weakness of outer and underside of arm, palm, ring and little fingers)
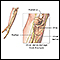
Ulnar nerve dysfunction
Ulnar nerve dysfunction is a problem with one of the nerves that travel from the shoulder to the hand, called the ulnar nerve. It helps you move you...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the specific nerve affected, and may include:
- Loss of sensation
- Paralysis
Paralysis
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tingling, burning, pain, abnormal sensations
Tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and focus on the affected area. A detailed medical history is needed to determine the possible cause of the disorder.
Tests that may be done include:
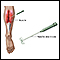
- Electromyogram (EMG) to check the electrical activity in the muscles
Electromyogram
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
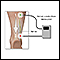
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve conduction tests (NCV) to check the speed of electrical activity in the nerves
Nerve conduction tests
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve ultrasound to view the nerves
- X-ray, MRI or CT scan to get an overall view of the affected area
X-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
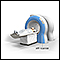
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests
- Nerve biopsy (in case of mononeuropathy due to vasculitis)
Nerve biopsy
A nerve biopsy is the removal of a small piece of a nerve for examination.
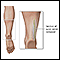 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CSF examination
CSF examination
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is a group of laboratory tests that measure chemicals in the cerebrospinal fluid. CSF is a clear fluid that surro...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skin biopsy
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
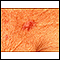 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to allow you to use the affected body part as much as possible.
Some medical conditions make nerves more prone to injury. For example, high blood pressure and diabetes can injure an artery, which can often affect a single nerve. So, the underlying condition should be treated.
Treatment options may include any of the following:
- Over the counter painkillers, such as anti-inflammatory medicines for mild pain
- Antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and similar medicines for chronic pain
- Injections of steroid medicines to reduce swelling and pressure on the nerve
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Surgery to relieve pressure on the nerve
- Physical therapy exercises to maintain muscle strength
- Braces, splints, or other devices to help with movement
Splints
A splint is a device used to hold a part of the body stable to decrease pain and prevent further injury.
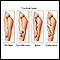 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to improve nerve pain associated with diabetes
Outlook (Prognosis)
Mononeuropathy may be disabling and painful. If the cause of the nerve dysfunction can be found and successfully treated, a full recovery is possible in some cases.
Nerve pain may be uncomfortable and last for a long time.
Nerve pain
Neuralgia is a sharp, shocking pain that follows the path of a nerve and is due to irritation or damage to the nerve. Common neuralgias include:Posth...

Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Deformity, loss of tissue mass
- Medicine side effects
- Repeated or unnoticed injury to the affected area due to lack of sensation
Prevention
Avoiding pressure or traumatic injury may prevent many forms of mononeuropathy. Treating conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes also decreases the risk of developing the condition.
Reviewed By
Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier;2022:chap 106.
National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke website. Peripheral neuropathy. www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/peripheral-neuropathy. Updated August 7, 2024. Accessed September 30, 2024.
Smith G, Shy ME. Peripheral neuropathies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 388.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.