Metastatic brain tumor
A metastatic brain tumor is cancer that started in another part of the body and has spread to the brain.
Causes
Many tumor or cancer types can spread to the brain. The most common are:
- Lung cancer
Lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It spreads much more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two typ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer:Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (du...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Melanoma
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous type of skin cancer. It is also the rarest. It is the leading cause of death from skin disease. Other common types o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney cancer
Kidney cancer
Renal cell carcinoma is a type of kidney cancer that starts in the lining of very small tubes (tubules) in the kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some types of cancer rarely spread to the brain, such as prostate and colon cancer. In some cases, a tumor can spread to the brain from an unknown location. This is called cancer of unknown primary (CUP).
Growing brain tumors can place pressure on nearby parts of the brain. Brain swelling due to these tumors also causes increased pressure within the skull.
Pressure within the skull
Increased intracranial pressure is a rise in the pressure inside the skull that can result from or cause brain injury.
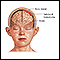
Brain tumors that spread are classified based on the location of the tumor in the brain, the type of tissue involved, and the original location of the tumor.
Metastatic brain tumors occur in about one fourth (25%) of all cancers that spread through the body. They are much more common than primary brain tumors (tumors that start in the brain).
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Decreased coordination, clumsiness, falls
Decreased coordination
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General ill feeling or fatigue
General ill feeling
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache, new or more severe than usual
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Memory loss, poor judgment, difficulty solving problems
- Numbness, tingling, pain, and other changes in sensation
- Personality changes
- Rapid emotional changes or strange behaviors
- Seizures that are new
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Problems with speech
- Vision changes, double vision, decreased vision
Vision changes
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vomiting, with or without nausea
- Weakness of a body area
Specific symptoms vary. Common symptoms of most types of metastatic brain tumors are caused by increased pressure in the brain.
Exams and Tests
An exam can show brain and nervous system changes based on where the tumor is in the brain. Signs of increased pressure in the skull are also common. Some tumors may not show signs until they are very large. Then, they can cause a very quick decline in nervous system function.
The original (primary) tumor may be found by examining tumor tissues from the brain.
Tests may include:
- Mammogram, CT scans of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to find the original tumor site
Mammogram
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to evaluate some breast symptoms and to find breast cancer in women with no symptoms (cal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scans
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
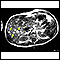
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan or MRI of the brain to confirm the diagnosis and identify the tumor location (MRI is usually more sensitive for finding tumors in the brain)
MRI of the brain
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Examination of tissue removed from the tumor during surgery or CT scan- or MRI-guided biopsy to confirm the type of tumor
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on:
- The size and type of the tumor
- Location in the body from where it spread
- The person's general health
The goals of treatment may be to relieve symptoms, improve functioning, or provide comfort.
Whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) is often used to treat tumors that have spread to the brain, especially if there are many tumors, and surgery is not a good option.
Surgery may be used when there is a single tumor. Some tumors may be completely removed. Tumors that are deep or that extend into brain tissue may be reduced in size (debulked).
Surgery may reduce pressure and relieve symptoms in cases when the tumor cannot be removed.
Chemotherapy for metastatic brain tumors is usually not as helpful as surgery or radiation. Some types of tumors, though, do respond to chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) may also be used. This form of radiation therapy focuses high-power x-rays on a small area of the brain. It is used when there are only a few, small, metastatic tumors.
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS)
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a form of radiation therapy that focuses high-power energy on a small area of the body. Despite its name, radiosu...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleMedicines for brain tumor symptoms include:
- Anticonvulsants such as phenytoin or levetiracetam to reduce or prevent seizures
- Corticosteroids such as dexamethasone to reduce brain swelling
- Pain medicines
When the cancer has spread, treatment may focus on relieving pain and other symptoms. This is called palliative or supportive care.
Palliative
Palliative care helps people with serious illnesses feel better by preventing or treating symptoms and side effects of disease and treatment....
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleComfort measures, safety measures, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and other treatments may improve the patient's quality of life. Some people may want to seek legal advice to help them create an advance directive and power of attorney for health care.
Advance directive
When you are very ill or injured, you may not be able to make health care choices for yourself. If you are unable to speak for yourself, your health...

Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
For many people with metastatic brain tumors, the cancer is not curable. Prognosis depends on the type of tumor and how it responds to treatment.
Possible Complications
Health problems that may result include:
- Brain herniation (fatal)
- Loss of ability to function or care for self
- Loss of ability to interact
- Permanent, severe loss of nervous system function that gets worse over time
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you develop a persistent headache that is new or different for you.
Call your provider or go to the emergency room if you or someone you know suddenly becomes sluggish or has vision changes, or speech impairment, or has seizures that are new or different.
Reviewed By
Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Dorsey JF, Salinas RD, Dang M, et al. Cancer of the central nervous system. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 63.
Elder JB, Nahed BV, Linskey ME, Olson JJ. Congress of Neurological Surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines on the role of emerging and investigational therapies for the treatment of adults with metastatic brain tumors. Neurosurgery. 2019;84(3):E201-E203. PMID: 30629215 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30629215/.
National Cancer Institute website. Adult central nervous system tumors treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/brain/hp/adult-brain-treatment-pdq. Updated March 6, 2024. Accessed May 14, 2024.
Olson JJ, Kalkanis SN, Ryken TC. Congress of neurological surgeons systematic review and evidence-based guidelines for the treatment of adults with metastatic brain tumors: executive summary. Neurosurgery. 2019;84(3):550-552. PMID: 30629218 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30629218/.
Traylor JI, Rao G. Metastatic brain tumors. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 169.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.