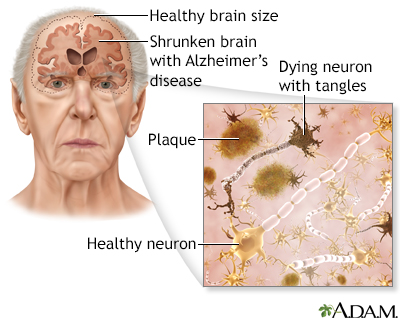
Alzheimer disease
Senile dementia - Alzheimer type (SDAT); SDAT; Dementia - Alzheimer; Alzheimer's diseaseDementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
Dementia
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects one or more brain functions such as memory, thinking, language, j...

Dementia may also be referred to as major neurocognitive disorder.
Neurocognitive disorder
Neurocognitive disorder is a general term that describes decreased mental function due to a medical disease other than a psychiatric illness. Neuroco...

Causes
The exact cause of Alzheimer disease is not known. Research shows that certain changes in the brain are associated with Alzheimer disease. This leads to structures called neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Most experts believe that this is the cause of Alzheimer disease but why this happens to some people is not known.
You are more likely to develop Alzheimer disease if you:
- Are older -- Developing Alzheimer disease is not a part of normal aging.
- Have a close relative, such as a brother, sister, or parent with Alzheimer disease.
- Have certain genes linked to Alzheimer disease.
The following may also increase the risk:
- Being female
- Having heart and blood vessel problems due to high cholesterol
- History of head trauma
There are two types of Alzheimer disease:
- Early onset Alzheimer disease -- Symptoms appear before age 60. This type is much less common than late onset. It tends to get worse quickly. Early onset disease can run in families. Several genes have been identified.
- Late onset Alzheimer disease -- This is the most common type. It occurs in people age 60 and older. It may run in some families, but the role of genes is less clear.
Symptoms
Alzheimer disease symptoms include difficulty with many areas of mental function, including:
- Emotional behavior or personality
- Language
- Memory
- Perception
- Thinking and judgment (cognitive skills)
Alzheimer disease usually first appears as forgetfulness.
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is a condition in which a person has more memory and thinking problems than other people their age. People with MCI have mild problems with thinking and memory that do not interfere with daily activities. They are often aware of the forgetfulness. Not everyone with MCI develops Alzheimer disease.
Symptoms of MCI include:
- Difficulty doing more than one task at a time
- Difficulty solving problems or making decisions
- Forgetting names of familiar people, recent events, or conversations
- Taking longer to do more difficult mental activities
Early symptoms of Alzheimer disease can include:
- Difficulty performing tasks that take some thought, but used to come easily, such as balancing a checkbook, playing complex games (bridge), and learning new information or routines
- Getting lost on familiar routes
- Language problems, such as trouble remembering the names of familiar objects
- Losing interest in things previously enjoyed and being in a flat mood
- Misplacing items
- Personality changes and loss of social skills
- Mood changes leading to aggressive behavior
- Poor performance of job duties
As Alzheimer disease becomes worse, symptoms are more obvious and interfere with the ability to take care of oneself. Symptoms may include:
- Change in sleep patterns, often waking up at night
- Delusions, depression, and agitation
Depression
Depression may be described as feeling sad, blue, unhappy, miserable, or down in the dumps. Most of us feel this way at one time or another for shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty doing basic tasks, such as preparing meals, choosing proper clothing, and driving
- Difficulty reading or writing
- Forgetting details about current events
- Forgetting events in one's life history and losing self-awareness
-
Hallucinations, arguments, striking out, and violent behavior
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Poor judgment and loss of ability to recognize danger
- Using the wrong word, mispronouncing words, or speaking in confusing sentences
- Withdrawing from social contact
People with severe Alzheimer disease can no longer:
- Recognize family members
- Perform basic activities of daily living, such as eating, dressing, and bathing
- Understand language
Other symptoms that may occur with Alzheimer disease:
-
Problems controlling bowel movements or urine
Urine
Urinary (or bladder) incontinence occurs when you are not able to keep urine from leaking out of your urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swallowing problems
Swallowing problems
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A diagnosis of Alzheimer disease is made when certain symptoms are present, and by making sure other causes of dementia are not present.
A skilled health care provider can often diagnose Alzheimer disease with the following steps:
- Performing a complete physical exam, including a nervous system exam.
- Asking about the person's medical history and symptoms.
- Mental function tests (mental status examination).
- Neuropsychological testing.
-
PET scan and lumbar puncture (spinal tap) are sometimes needed to confirm Alzheimer disease.
PET scan
A brain positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test of the brain. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleLumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests may be done to rule out other possible causes of dementia, including:
-
Anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Brain tumor
Brain tumor
A primary brain tumor is a group (mass) of abnormal cells that start in the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Long-term (chronic) infection
- Intoxication from medicines
- Severe depression
-
Increased fluid on the brain (normal pressure hydrocephalus)
Increased fluid on the brain
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of spinal fluid inside the fluid chambers of the brain. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "Normal pressure hydroce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid disease
- Vitamin deficiency
CT or MRI of the brain may be done to look for other causes of dementia, such as a brain tumor or stroke.
CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.

MRI
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...

The only way to know for certain that someone has Alzheimer disease is to examine a sample of their brain tissue after death.
Treatment
There is no cure for Alzheimer disease. The goals of treatment are:
- Slow the progression of the disease (although this is difficult to do)
- Manage symptoms, such as behavior problems, confusion, and sleep problems
- Change the home environment to make daily activities easier
- Support family members and other caregivers
Medicines are used to:
- Slow the rate at which symptoms worsen, though the benefit from using these medicines may be small
- Lower the amount of beta amyloid protein in the brain
- Control problems with behavior, such as loss of judgment or confusion
Before using these medicines, ask your provider:
- What are the side effects? Is the medicine worth the risk?
- When is the best time, if any, to use these medicines?
- Do medicines for other health problems need to be changed or stopped?
Someone with Alzheimer disease will need support in the home as the disease gets worse. Family members or other caregivers can help by helping the person cope with memory loss and behavior and sleep problems. It is important to make sure the home of a person who has Alzheimer disease is safe for them.
Support in the home
Dementia is a loss of cognitive function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
Memory loss
People who have dementia may have trouble with: Language and communicationEatingHandling their own personal care
Behavior and sleep problems
People with dementia often have certain problems when it gets dark at the end of the day and into the night. This problem is called sundowning. The...

Safe for them
It is important to make sure the homes of people who have dementia are safe for them.

Support Groups
Having Alzheimer disease or caring for a person with the condition may be a challenge. You can ease the stress of illness by seeking support through Alzheimer disease resources. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Alzheimer disease resources
The following organizations are good resources for information on Alzheimer disease:Alzheimer's Association -- www. alz. orgAlzheimers. gov -- www. a...
Outlook (Prognosis)
How quickly Alzheimer disease gets worse is different for each person. If Alzheimer disease develops quickly, it is more likely to worsen quickly.
People with Alzheimer disease often die earlier than normal, although a person may live anywhere from 3 to 20 years after diagnosis.
Families will likely need to plan for their loved one's future care.
Future care.
Dementia is a loss of cognitive function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects memory, thinking, and behavior.
The final phase of the disease may last from a few months to several years. During that time, the person becomes totally disabled. Death usually occurs from an infection or organ failure.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- Alzheimer disease symptoms develop or a person has a sudden change in mental status
- The condition of a person with Alzheimer disease gets worse
- You are unable to care for a person with Alzheimer disease at home
Prevention
Although there is no proven way to prevent Alzheimer disease, there are some measures that may help prevent or slow the onset of Alzheimer disease:
- Stay on a low-fat diet and eat foods high in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Get plenty of exercise.
- Stay mentally and socially active.
- Wear a helmet during risky activities to prevent brain injury.
References
Alzheimer's Association website. First practice guidelines for clinical evaluation of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias for primary and specialty care. [press release] July 22, 2018. aaic.alz.org/releases_2018/AAIC18-Sun-clinical-practice-guidelines.asp. Accessed May 8, 2024.
Budson AE, Solomon PR. Alzheimer's disease. In: Budson AE, Solomon PR, eds. Memory Loss, Alzheimer's Disease, and Dementia. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 4.
Knopman DS. Cognitive impairment and dementia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 371.
Peterson RC, Graff-Radford J. Alzheimer disease and other dementias. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 95.
Wilamowska K, Knoefel J. Alzheimer's disease. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, Heidelbaugh JJ, Lee EM, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2024. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2024:741-748.
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.