Trigeminal neuralgia
Tic douloureux; Cranial neuralgia; Facial pain - trigeminal; Facial neuralgia; Trifacial neuralgia; Chronic pain - trigeminal; Microvascular decompression - trigeminalTrigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a nerve disorder. It causes a stabbing or electric shock-like pain in parts of the face.
Causes
The pain of TN comes from the trigeminal nerve. This nerve carries the sensations of touch and pain from the face, eyes, sinuses, and mouth to the brain.
TN may be caused by:
- Multiple sclerosis (MS) or other diseases that damage the protective covering myelin of the nerves
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMyelin
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pressure on the trigeminal nerve from a swollen blood vessel or tumor
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Injury to the trigeminal nerve, such as from trauma to the face or from oral or sinus surgery
Often, no exact cause is found. TN usually affects adults above age 50 years, but it can occur at any age. Women are affected more often than men. When TN affects people younger than 40, it is often due to MS or a tumor.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Very painful, sharp electric-like spasms that are usually brief. The spasms may occur close together such that it feels like they last from several seconds to minutes. Pain can become constant.
- Pain is usually only on one side of the face, often around the eye, cheek, and lower part of the face.
- There is usually no loss of sensation or movement of the affected part of the face.
- Pain may be triggered by touch or sounds.
Painful attacks of TN can be triggered by common, everyday activities, such as:
- Talking
- Smiling
- Brushing teeth
- Chewing
- Drinking
- Eating
- Exposure to hot or cold temperature
- Touching the face
- Shaving
- Wind
- Applying make-up
The right side of the face is mostly affected. In some cases, TN goes away on its own.
Exams and Tests
A brain and nervous system (neurologic) exam is often normal. Tests that are done to look for the cause may include:
- Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is commonly called a "sed rate. "It is a test that indirectly measures the level of certain protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI of the head
MRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRA (angiography) of brain or CTA
MRA (angiography) of brain
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an MRI exam of the blood vessels. Unlike traditional angiography that involves placing a tube (catheter) int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCTA
CT angiography (CTA) combines a CT scan with the injection of dye. CT stands for computed tomography. This technique is able to create pictures of ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eye examination (to rule out intraocular disease)
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture)
Spinal tap
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of head (who cannot undergo MRI)
CT scan of head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Trigeminal reflex testing (in rare cases)
Treatment
Your primary care provider, a neurologist, or a pain specialist may be involved in your care.
Certain medicines sometimes help reduce pain and the rate of attacks. These medicines include:
- Anti-seizure medicines, such as carbamazepine
- Muscle relaxants, such as baclofen
- Tricyclic antidepressants
If you are found to have MS as a cause of TN, your health care provider will discuss medicines that can treat the underlying MS.
Short-term pain relief occurs through surgery, but is associated with risk of complications. One surgery is called microvascular decompression (MVD) or the Jannetta procedure. During surgery, a sponge-like material is placed between the nerve and the blood vessel that is pressing on the nerve.
Trigeminal nerve block (injection) with local anesthetic and steroid is an excellent treatment option to rapidly relieve pain while waiting for medicines to take effect.
Other techniques involve destroying or cutting parts of the trigeminal nerve root. Methods used include:
- Radiofrequency ablation (uses high-frequency heat)
- Injection of glycerol or alcohol
- Balloon microcompression
- Radiosurgery (uses high power energy)
Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a form of radiation therapy that focuses high-power energy on a small area of the body. Despite its name, radiosu...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
If a tumor is the cause of TN, surgery is done to remove it.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on the cause of the problem. If there is no disease causing the problem, treatment can provide some relief.
In some people, the pain becomes constant and severe.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Side effects of medicines used to treat TN
- Problems caused by procedures, such as loss of feeling in the treated area
- Weight loss from not eating to avoid triggering pain
- Avoiding other people if talking triggers pain
- Depression, suicide
Depression
Depression may be described as feeling sad, blue, unhappy, miserable, or down in the dumps. Most of us feel this way at one time or another for shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High levels of anxiety during acute attacks
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of TN, or your TN symptoms get worse.
References
Bendtsen L, Zakrzewska JM, Heinskou TB, et al. Advances in diagnosis, classification, pathophysiology, and management of trigeminal neuralgia. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19(9):784-796. PMID: 32822636 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32822636/.
Dinakar P. Pain management. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 52.
Smith AG, Shy ME. Peripheral neuropathies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 388.
Waldman SD. Trigeminal neuralgia. In: Waldman SD, ed. Atlas of Common Pain Syndromes. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 10.
Westmark NLW. Facial pain and neuromuscular diseases. In: Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC, eds. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 5th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2024:chap 18.
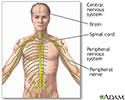
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Review Date: 6/13/2024
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.