Cerebral amyloid angiopathy
Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is a condition in which proteins called amyloid build up on the walls of the arteries in the brain. CAA causes bleeding into the brain (hemorrhagic stroke) and dementia.
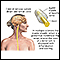
Hemorrhagic stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...

Dementia
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. It affects one or more brain functions such as memory, thinking, language, j...

Causes
People with CAA have deposits of amyloid protein in the walls of blood vessels in the brain. The protein is usually not deposited anywhere else in the body.
The major risk factor is increasing age. CAA is more often seen in people older than 55. Sometimes, it is passed down through families.
Symptoms
CAA can cause bleeding into the brain. Bleeding often occurs in the outer parts of the brain, called the cortex, and not the deep areas. Symptoms occur because bleeding in the brain harms brain tissue. Some people have gradual memory problems. When a CT scan is done, there are often signs that they have had bleeding in the brain that they may not have realized.
If there is a lot of bleeding, immediate symptoms occur and resemble a stroke. These symptoms include:
- Drowsiness
Drowsiness
Drowsiness refers to feeling more sleepy than normal during the day. People who are drowsy may fall asleep when they do not want to or at times whic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache (usually in a certain part of the head)
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nervous system changes that may start suddenly, including confusion, delirium, double vision, decreased vision, sensation changes, speech problems, weakness, or paralysis
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDelirium
Delirium is sudden severe confusion due to rapid changes in brain function that can occur with physical or mental illness.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDouble vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleParalysis
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stupor or coma (rarely)
Coma
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness from whi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Vomiting
If bleeding is not severe or widespread, symptoms can include:
- Episodes of confusion
- Headaches that come and go
- Loss of mental function (dementia)
- Weakness or unusual sensations that come and go, and involve smaller areas
- Seizures
Exams and Tests
CAA is hard to diagnose with certainty without a sample of brain tissue. This is usually done after death or when a biopsy of the blood vessels of the brain is done.
A physical exam can be normal if the bleed is small. There may be some brain function changes. It is important for your health care provider to ask detailed questions about the symptoms and medical history. The symptoms and results of the physical exam and any imaging tests may cause your provider to suspect CAA.
Imaging tests of the head that may be done include:
- CT scan or MRI scan to check for bleeding in the brain
CT scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI scan
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRA scan to check for large bleeds and rule out other causes of bleeding
MRA scan
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an MRI exam of the blood vessels. Unlike traditional angiography that involves placing a tube (catheter) int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - PET scan to check for amyloid deposits in the brain
PET scan
A brain positron emission tomography (PET) scan is an imaging test of the brain. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
There is no known effective treatment. The goal of treatment is to reduce risk by modifying risk factors, such as hypertension, and to relieve symptoms. In some cases, rehabilitation is needed for weakness or clumsiness. This can include physical, occupational, or speech therapy.
Sometimes, medicines that help improve memory, such as those for Alzheimer disease, are used.
Alzheimer disease
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. It affects memo...
Seizures, also called amyloid spells, may be treated with anti-seizure medicines.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The disorder slowly gets worse.
Possible Complications
Complications of CAA may include:
- Dementia
- Hydrocephalus (rarely)
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures
- Repeated episodes of bleeding in the brain
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have sudden loss of movement, sensation, vision, or speech.
Loss of movement
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.

Reviewed By
Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Polster SP, Carrión-Penagos J, Awad IA. Nonlesional spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 423.
Shoamanesh A, Kase CS. Intracerebral hemorrhage. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 66.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.