Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS) is a rare disorder in which faulty communication between nerves and muscles leads to muscle weakness.
Muscle weakness
Weakness is reduced strength in one or more muscles.
Causes
LEMS is an autoimmune disorder. This means your immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells and tissues in the body. With LEMS, antibodies produced by the immune system attack nerve cells. This makes nerves cells unable to release enough of a chemical called acetylcholine. This chemical transmits impulses between nerves and muscles. The result is muscle weakness.
Autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
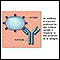
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
LEMS may occur with cancers such as small cell lung cancer or autoimmune disorders such as vitiligo, which leads to a loss of skin pigment.
Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It spreads much more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two typ...
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a skin condition in which there is a loss of color (pigment) from areas of skin. This results in uneven white patches that have no pigme...

LEMS affects men more often than women. The most common age of occurrence is around age 60 years. LEMS is rare in children.
Symptoms
Weakness or loss of movement that can be more or less severe, including:
- Difficulty climbing stairs, walking, or lifting things
- Muscle pain
- Drooping of the head
- The need to use the hands to get up from a sitting or lying position
- Problems talking
- Problems chewing or swallowing, which may include gagging or choking
Choking
Choking is when someone is having a very hard time breathing because food, a toy, or other object is blocking the throat or windpipe (airway). A cho...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vision changes, such as blurry vision, double vision, and problem keeping a steady gaze
Blurry vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Weakness is generally mild in LEMS. Leg muscles are mostly affected. Weakness may improve after exercise, but continuous exertion causes fatigue in some cases.
Symptoms related to the other parts of the nervous system often occur, and may include:
- Blood pressure changes
- Dizziness upon standing
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dry mouth
Dry mouth
Dry mouth occurs when you don't make enough saliva. This causes your mouth to feel dry and uncomfortable. Dry mouth that is ongoing may be a sign o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction
An erection problem occurs when a man cannot get or keep an erection that is firm enough for intercourse. You may not be able to get an erection at ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dry eyes
- Constipation
- Decreased sweating
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms. The exam may show:
- Decreased reflexes
- Possible loss of muscle tissue
- Weakness or paralysis that gets slightly better with activity
Tests to help diagnose and confirm LEMS may include:
- Blood tests to look for the antibodies that attack the nerves
- Electromyography (EMG) to test the health of the muscle fibers
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
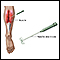 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) to test the speed of electrical activity along nerves
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
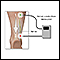 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
A CT scan and an MRI of the chest and the abdomen, followed by bronchoscopy for smokers may be done to evaluate for cancer. PET scan may also be done if a lung tumor is suspected. You may be referred to an oncologist (cancer specialist) to determine if other cancer testing is needed.
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleTreatment
The main goals of treatment are to:
- Identify and treat any underlying disorders, such as lung cancer
- Give treatment to help with the weakness
Plasma exchange, or plasmapheresis, is a treatment that helps remove from the body any harmful proteins (antibodies) that are interfering with nerve function. This involves removing blood plasma that contains the antibodies. Other proteins (such as albumin) or donated plasma are then infused into the body.
Another procedure involves using intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) to infuse a large amount of helpful antibodies directly into the bloodstream.
Medicines that may also be tried include:
- Medicines that suppress the immune system's response
Immune system's response
The immune response is how your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and substances that appear foreign and harmful....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Anticholinesterase medicines to improve muscle tone (although these are not very effective when given alone)
- Medicines that increase the release of acetylcholine from nerve cells
Outlook (Prognosis)
Symptoms of LEMS may improve by treating the underlying disease, suppressing the immune system, or removing the antibodies. However, paraneoplastic LEMS may not respond as well to treatment. (Paraneoplastic LEMS symptoms are due to an altered immune system response to a tumor). Death is due to underlying malignancy.
Possible Complications
Complications of LEMS may include:
- Difficulty breathing, including respiratory failure (less common)
Respiratory failure
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when your lungs can't remove all of the carbon dioxide produced by your body. This causes the blood ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty swallowing
- Infections, such as pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Injuries from falls and problems with coordination
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if symptoms of LEMS develop.
Reviewed By
Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Guptill JT, Sanders DB. Disorders of neuromuscular transmission. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 108.
Kaminski HJ. Disorders of neuromuscular transmission. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 390.
Moss HE. Eyelid and facial nerve disorders. In: Liu GT, Volpe NJ, Galetta SL, eds. Liu, Volpe, and Galetta's Neuro-Ophthalmology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 14.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.