CMV pneumonia
Pneumonia - cytomegalovirus; Cytomegalovirus pneumonia; Viral pneumoniaCytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia is a viral infection of the lungs that can occur in people who have a suppressed immune system.
Causes
CMV is a member of a group of herpes-type viruses. Infection with CMV is very common. Most people are exposed to CMV in their lifetime, but typically only those with weakened immune systems become ill from CMV infection.
Serious CMV infections can occur in people with weakened immune systems as a result of:
- HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow transplantation
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chemotherapy or other treatments that suppress the immune system
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Organ transplant (especially lung transplant)
Lung transplant
Lung transplant is surgery to replace one or both diseased lungs with healthy lungs from a human donor.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
In people who have had organ and bone marrow transplants, the risk for infection is greatest 5 to 13 weeks after the transplant.
Symptoms
In otherwise healthy people, CMV usually produces no symptoms, or it produces a temporary mononucleosis-type illness. However, those with a weakened immune system can develop serious symptoms. Symptoms may include:
- Cough
- Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever
- General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise)
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle aches or joint pains
Muscle aches
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than one muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascias are th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath
- Sweating, excessive (night sweats)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. In addition, the following tests may be done:
-
Venous and/or arterial blood gas
Arterial blood gas
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Oximetry
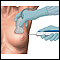
- Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests to detect and measure substances specific to CMV infection
- Bronchoscopy (may include biopsy)
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
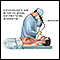 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBiopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of chest
CT scan of chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine culture (clean catch)
Urine culture (clean catch)
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sputum Gram stain and culture
Sputum Gram stain
A sputum Gram stain is a lab test used to detect bacteria in a sputum sample. Sputum is the material that comes up from your air passages when you c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCulture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to use antiviral medicines to stop the virus from copying itself in the body. Some people with CMV pneumonia need IV (intravenous) medicines. Some people may need oxygen therapy and breathing support with a ventilator to maintain oxygen until the infection is brought under control.
Intravenous
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
Antiviral medicines stop the virus from copying itself, but do not destroy it. The CMV suppresses the immune system, and may increase your risk for other infections.
Low oxygen level in the blood of people with CMV pneumonia often predicts death, especially in those who need to be placed on a breathing machine.
Possible Complications
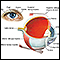
Complications of CMV infection in people with HIV/AIDS include spread of disease to other parts of the body, such as the esophagus, intestine, or eye.
Eye
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis is a viral infection of the retina of the eye resulting in inflammation.
Complications of CMV pneumonia include:
- Kidney function impairment (from medicines used to treat the condition)
- Low white blood cell count (from medicines used to treat the condition)
White blood cell count
A WBC count is a blood test to measure the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood. It is a part of a complete blood count (CBC). WBCs are a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Overwhelming infection that doesn't respond to treatment
- Resistance of CMV to standard treatment
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of CMV pneumonia.
Prevention
The following have been shown to help prevent CMV pneumonia in certain people:
- Using organ transplant donors who don't have CMV
- Using CMV-negative blood products for transfusion
- Using CMV-immune globulin in certain people
Preventing HIV/AIDS avoids certain other diseases, including CMV, that can occur in people who have a weakened immune system.
References
Britt WJ. Cytomegalovirus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 137.
Crothers K, Worodria W, Huang L. Pulmonary complications of HIV infection. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 123.
Singh N, Haidar G, Limay AP. Infections in solid-organ transplant recipients. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennetts Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 308.
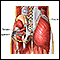
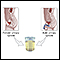
CMV pneumonia - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. CMV pneumonia is treated with antiviral medications, which may stop the replication of the virus but will not destroy it.
CMV pneumonia
illustration
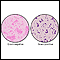
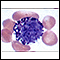
CMV (cytomegalovirus) - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. The infection may result in pneumonia, gastroenteritis, retinitis or encephalitis. Antiviral medicines may stop the replication of the virus, but will not destroy it.
CMV (cytomegalovirus)
illustration
CMV pneumonia - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. CMV pneumonia is treated with antiviral medications, which may stop the replication of the virus but will not destroy it.
CMV pneumonia
illustration
CMV (cytomegalovirus) - illustration
Cytomegalovirus is a large herpes-type virus commonly found in humans that can cause serious infections in people with impaired immunity. The infection may result in pneumonia, gastroenteritis, retinitis or encephalitis. Antiviral medicines may stop the replication of the virus, but will not destroy it.
CMV (cytomegalovirus)
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.