Essential thrombocythemia
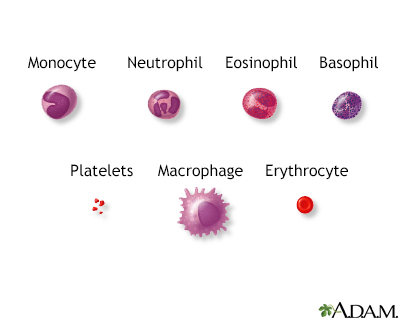
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a condition in which the bone marrow produces too many platelets. Platelets are particles in the blood that aid in blood clotting.
Blood clotting - Animation
Ouch! Here's how platelets form clots. This small artery has a cut. Blood flowing past the cut includes red blood cells that carry oxygen, platelets that come from white blood cell fragments, and clotting factors that help blood clot. When a blood vessel is damaged, blood cells and plasma ooze into surrounding tissue. Platelets immediately stick to the edges of the cut and release chemicals that attract more platelets. Eventually, a platelet plug is formed, and the outside bleeding stops. On the inside, clotting factors cause a cascade of activity that includes strands of blood-borne material called fibrin sticking together to seal the inside of the wound. Eventually, the blood vessel heals, and several days later, the blood clot dissolves.
Causes
ET results from an overproduction of platelets. As these platelets do not work normally, blood clots and bleeding are common problems. Untreated, ET worsens over time.
ET is part of a group of conditions known as myeloproliferative disorders. Others include:
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (an overproduction of white blood cells that starts in the bone marrow)
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is cancer that starts inside the bone marrow. This is the soft tissue in the center of bones that helps form all ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Polycythemia vera (bone marrow disease that leads to an abnormal increase in the number of red blood cells)
Polycythemia vera
Polycythemia vera (PV) is a bone marrow disease that leads to an abnormal increase in the number of blood cells. The red blood cells are the most af...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary myelofibrosis (disorder of the bone marrow in which the marrow is replaced by fibrous scar tissue)
Myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis is a disorder of the bone marrow in which the marrow is replaced by fibrous scar tissue.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Many people with ET have a mutation of a gene (JAK2, CALR, or MPL).
ET is most common in middle-aged people. It can also sometimes be seen in younger people, especially women under age 40.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Headache (most common)
- Tingling, coldness, or blueness in the hands and feet
- Feeling dizzy or lightheaded
- Vision problems
- Mini-strokes (transient ischemic attacks) or stroke
Transient ischemic attacks
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops for a brief time. A person will have stroke-like symptoms for ...
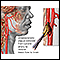 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleStroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If bleeding is a problem, symptoms may include any of the following:
- Easy bruising and nosebleeds
Bruising
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system, urinary tract, or skin
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding from the gums
- Prolonged bleeding from surgical procedures or tooth removal
Exams and Tests
Most of the time, ET is found through blood tests done for other health problems before symptoms appear.
Other tests may include:
- Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
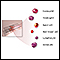 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genetic tests (to look for a change in the JAK2, CALR, or MPL gene)
Treatment
If you have life-threatening complications, you may have a treatment called platelet pheresis. It quickly reduces the number of platelets in the blood.
Long-term, medicines are used to decrease the platelet count to avoid complications. The most common medicines used include hydroxyurea, interferon-alpha, or anagrelide.
Aspirin at a low dose (81 to 100 mg per day) may decrease clotting episodes.
Many people do not need any treatment, but they must be followed closely by their provider.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcomes may vary. Most people can go for long periods without complications and have a normal lifespan. In a small number of people, complications from bleeding and blood clots can cause serious problems.
In rare cases, the disease can change into acute leukemia or myelofibrosis.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Acute leukemia or myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis
Myelofibrosis is a disorder of the bone marrow in which the marrow is replaced by fibrous scar tissue.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Stroke, heart attack, or blood clots
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
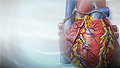 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have unexplained bleeding that continues longer than it should.
- You notice chest pain, leg pain, confusion, weakness, numbness, or other new symptoms.
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLeg pain
Leg pain is a common problem. It can be due to a cramp, injury, or other cause.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleConfusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNumbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Mark Levin, MD, Hematologist and Oncologist, Monsey, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Gotlib J. Polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and primary myelofibrosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 157.
Marcellino BK, Mascarenhas J, Iancu-Rubin C, Kremyanskaya M, Najfeld V, Hoffman R. Essential thrombocythemia. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 71.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.