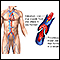
Renal vein thrombosis
Renal vein thrombosis is a blood clot that develops in the vein that drains blood from the kidney.
Blood clot
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
Causes
Renal vein thrombosis is an uncommon disorder. It may be caused by:
- Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
The aorta is the main blood vessel that supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs. An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) occurs when an area of t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hypercoagulable state: clotting disorders
- Dehydration (mostly in infants)
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Estrogen use
- Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms and abnormal test results that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high ch...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy
- Scar formation with pressure on the renal vein
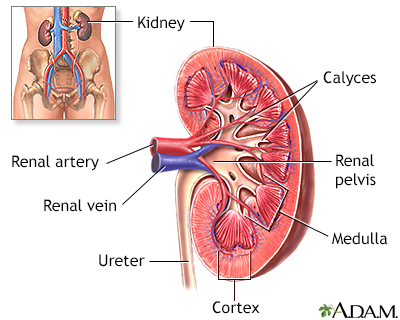
Renal
The term "renal" refers to the kidney. For example, renal failure means kidney failure. Related topics:Kidney diseaseKidney disease - dietKidney fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Trauma (to the back or abdomen)
- Tumor
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
In adults, the most common cause is nephrotic syndrome. In infants, the most common cause is dehydration.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Blood clot to the lung
- Bloody urine
- Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Flank pain or low back pain
Flank pain
Flank pain is pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
An exam may not reveal the specific problem. However, it may indicate nephrotic syndrome or other causes of renal vein thrombosis.
Tests include:
- Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal MRI
Abdominal MRI
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal ultrasound
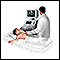
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Duplex Doppler exam of the renal veins
- Urinalysis may show protein in the urine or red blood cells in the urine
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
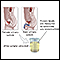
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleProtein in the urine
The urine protein dipstick test measures the presence of all proteins, including albumin, in a urine sample. Albumin and protein can also be measured...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRed blood cells in the urine
The RBC urine test measures the number of red blood cells in a urine sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - X-ray of the kidney veins (venography)
Treatment
The treatment helps to prevent the formation of new clots and reduces the risk of clot traveling to other locations in the body (embolization).
You may get medicines that prevent blood clotting (anticoagulants). You may be told to rest in bed or cut down on activity for a short time.
If sudden kidney failure develops, you may need dialysis for a short period.
Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney failure. It removes harmful substances from the blood when the kidneys cannot. This article focuses on peritoneal d...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
Renal vein thrombosis most often gets better over time without lasting damage to the kidneys.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Acute renal failure (especially if thrombosis occurs in a dehydrated child)
- End stage renal disease
- Blood clot moves to the lungs (pulmonary embolism)
Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Formation of new blood clots
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of renal vein thrombosis.
If you have experienced renal vein thrombosis, call your provider if you have:
- Decrease in urine output
- Blood in the urine
- Breathing problems (due to blood clot moving to your lung called pulmonary embolism)
Breathing problems
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Other new symptoms
Prevention
In most cases, there is no specific way to prevent renal vein thrombosis. Keeping enough fluids in the body may help reduce risk.
Aspirin is sometimes used to prevent renal vein thrombosis in people who have had a kidney transplant. Blood thinners such as warfarin may be recommended for some people with chronic kidney disease.
Reviewed By
Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Augustine J, Wee AC, Krishnamurthi V, Goldfarb DA. Renal insufficiency and ischemic nephropathy. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 87.
DuBose TD, Santos RM. Vascular disorders of the kidney. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 116.
Greco BA, Umanath K. Renovascular hypertension and ischemic nephropathy. In: Feehally J, Floege J, Tonelli M, Johnson RJ, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 41.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.