Proximal renal tubular acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys don't properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, too much acid remains in the blood (called acidosis).
Acidosis
Acidosis is a condition in which there is too much acid in the body fluids. It is the opposite of alkalosis (a condition in which there is too much ...
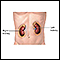
Causes
When the body performs its normal functions, it produces acid. If this acid is not removed or neutralized, the blood will become too acidic. This can lead to electrolyte imbalances in the blood. It can also cause problems with normal function of some cells.
Electrolyte
Electrolytes are minerals in your blood and other body fluids that carry an electric charge. Electrolytes affect how your body functions in many ways...
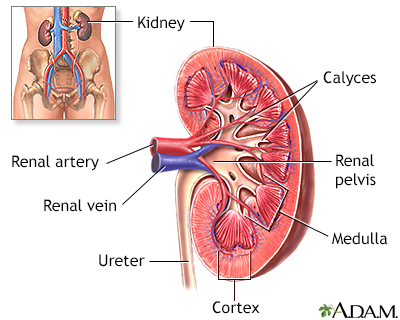
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleThe kidneys help control the body's acid level by removing acid from the blood and excreting it into the urine. Acidic substances in the body are neutralized by alkaline substances, mainly bicarbonate.
Proximal renal tubular acidosis (type II RTA) occurs when bicarbonate is not properly reabsorbed by the kidney's filtering system.
Type II RTA is less common than type I RTA. Type I is also called distal renal tubular acidosis. Type II most often occurs during infancy and may go away by itself.
Distal renal tubular acidosis
Distal renal tubular acidosis is a disease that occurs when the kidneys do not properly remove acids from the blood into the urine. As a result, too...

Causes of type II RTA include:
- Cystinosis (body is unable to break down the substance cysteine)
- Drugs such as ifosfamide (a chemotherapy drug), certain antibiotics that are no longer used much (tetracycline), or acetazolamide
- Fanconi syndrome, a disorder of the kidney tubes in which certain substances normally absorbed into the bloodstream by the kidneys are released into the urine instead
Fanconi syndrome
Fanconi syndrome is a disorder of the kidney tubes in which certain substances normally absorbed into the bloodstream by the kidneys are released int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inherited fructose intolerance, a disorder in which there is a lack of the protein needed to break down the fruit sugar fructose
Inherited fructose intolerance
Hereditary fructose intolerance is a disorder in which a person lacks the protein needed to break down fructose. Fructose is a fruit sugar that natu...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple myeloma, a type of blood cancer
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary hyperparathyroidism, a disorder in which the parathyroid glands in the neck produce too much parathyroid hormone
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which 1 or more of the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sjögren syndrome, an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed
Sjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. This causes dry mouth and dry eyes. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wilson disease, an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues
Wilson disease
Wilson disease is an inherited disorder in which there is too much copper in the body's tissues. The excess copper damages the liver and nervous sys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency
Rickets is a disorder that occurs in children before bone growth is complete. It is caused by a lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. It leads ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of proximal renal tubular acidosis include any of the following:
- Confusion or decreased alertness
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDecreased alertness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness from whi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Dehydration
Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when your body does not have as much water and fluids as it needs. Dehydration can be mild, moderate, or severe, based on how much...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased breathing rate
Increased breathing rate
Hyperventilation is rapid and deep breathing. It is also called overbreathing, and it may leave you feeling breathless.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Osteomalacia (softening of the bones)
Osteomalacia
Osteomalacia is softening of the bones. It most often occurs because of a problem that leads to vitamin D deficiency, which helps your body absorb c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle pain
Muscle pain
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than one muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascias are th...
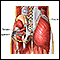 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness
Other symptoms can include:
- Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output
Decreased urine output means that you produce less urine than normal. Most adults make at least 500 milliliters of urine in 24 hours (a little over ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased heart rate or irregular heartbeat
Irregular heartbeat
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
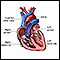 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps
Muscle cramps are when a muscle gets tight (contracts) without you trying to tighten it, and it does not relax. Cramps may involve all or part of on...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pain in the bones, back, flank, or abdomen
- Skeletal deformities
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about the symptoms.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Arterial blood gas
Blood gas
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood chemistry
Blood chemistry
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood pH level
- Urine pH and acid-loading test
Acid-loading test
The acid loading test (pH) measures the ability of the kidneys to send acid to the urine when there is too much acid in the blood. This test involve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal is to restore normal acid level and electrolyte balance in the body. This will help correct bone disorders and reduce the risk for osteomalacia and osteopenia in adults.
Osteopenia
Osteopenia is a decrease in the amount of calcium and phosphorus in the bone. This can cause bones to be weak and brittle. It increases the risk fo...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSome adults may need no treatment. All children need alkaline medicine such as potassium citrate and sodium bicarbonate. This is medicine that helps correct the acidic condition of the body. The medicine helps prevent bone disease caused by too much acid, such as rickets, and to allow normal growth.
Rickets
Rickets is a disorder that occurs in children before bone growth is complete. It is caused by a lack of vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate. It leads ...

Thiazide diuretics are also frequently used to preserve bicarbonate in the body.
The underlying cause of proximal renal tubular necrosis should be corrected if it can be found.
Vitamin D and calcium supplements may be needed to help reduce skeletal deformities resulting from osteomalacia.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissue and liver.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Although the underlying cause of proximal renal tubular acidosis may go away by itself, the effects and complications can be permanent or life threatening. Treatment is usually successful.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of proximal renal tubular acidosis.
Get medical help right away if any of the following emergency symptoms develop:
- Decreased alertness or disorientation
Disorientation
Mental status testing is done to check a person's thinking ability and to determine if any problems are getting better or worse. It is also called n...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Decreased consciousness
Decreased consciousness
Decreased alertness is a state of reduced awareness and is often a serious condition. A coma is the most severe state of decreased alertness from whi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Prevention
Most of the disorders that cause proximal renal tubular acidosis are not preventable.
Reviewed By
Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Bushinsky DA. Kidney stones. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 32.
Dixon BP. Renal tubular acidosis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 569.
Seifter JL. Acid-base disorders. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 104.


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.