Nephrotic syndrome
NephrosisNephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms and abnormal test results that include protein in the urine, low blood protein levels in the blood, high cholesterol levels, high triglyceride levels, increased blood clot risk, and swelling.
Protein in the urine
The urine protein dipstick test measures the presence of all proteins, including albumin, in a urine sample. Albumin and protein can also be measured...
High cholesterol levels
Cholesterol is a fat (also called a lipid) that your body needs to work properly. Too much bad cholesterol in your blood can increase your chance of...

Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

Causes
Nephrotic syndrome is caused by different disorders that damage the kidneys. This damage leads to the release of too much protein in the urine.
The most common cause in children is minimal change disease. Membranous glomerulonephritis is the most common cause in adults. In both diseases, the glomeruli in the kidneys are damaged. Glomeruli are the structures that help filter wastes and fluids.
Minimal change disease
Minimal change disease is a kidney disorder that can lead to nephrotic syndrome. Nephrotic syndrome is a group of symptoms that include protein in t...
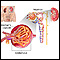
Membranous glomerulonephritis
Membranous nephropathy is a kidney disorder that leads to changes and inflammation of the structures inside the kidney that help filter wastes and fl...

This condition can also occur due to:
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Diseases such as diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple myeloma, and amyloidosis
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSystemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMultiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts from a type of white blood cell in the bone marrow called plasma cells. Bone marrow is the soft, spon...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAmyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genetic disorders
- Immune disorders
- Infections (such as strep throat, hepatitis, or mononucleosis)
Strep throat
Strep throat is a disease that causes a sore throat (pharyngitis). It is an infection with a bacteria called group A streptococcus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of certain drugs
It can occur with kidney disorders such as:
- Focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis
Segmental glomerulosclerosis
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is scar tissue in the filtering unit of the kidney. This structure is called the glomerulus. The glomeruli serve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis
Nephrotic syndrome can affect all age groups. In children, it is most common between ages 2 and 6. This disorder occurs slightly more often in males than females.
Symptoms
Swelling (edema) is the most common symptom. It may occur:
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

- In the face and around the eyes (facial swelling)
Facial swelling
Facial swelling is the buildup of fluid in the tissues of the face. Swelling may also affect the neck and upper arms.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - In the arms and legs, especially in the feet and ankles
- In the belly area (swollen abdomen)
Swollen abdomen
A swollen abdomen is when your belly area is bigger than usual.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms include:
- Skin rash or sores
Rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Foamy appearance of the urine
-
Poor appetite
Poor appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Weight gain (unintentional) from fluid retention
Weight gain (unintentional)
Unintentional weight gain is when you gain weight without trying to do so and you are not eating or drinking more.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Laboratory tests will be done to see how well the kidneys are working. They include:
-
Albumin blood test
Albumin
Albumin is a protein made by the liver. A serum albumin test measures the amount of this protein in the clear liquid portion of the blood. Albumin c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood chemistry tests, such as basic metabolic panel or comprehensive metabolic panel
Basic metabolic panel
The basic metabolic panel is a group of blood tests that provides information about your body's metabolism.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleComprehensive metabolic panel
A comprehensive metabolic panel is a group of blood tests. They provide an overall picture of your body's chemical balance and metabolism. Metaboli...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
Blood urea nitrogen
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Creatinine - blood test
Creatinine - blood test
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Creatinine clearance - urine test
Creatinine clearance - urine test
The creatinine urine test measures the amount of creatinine in urine. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Fats are often also present in the urine. Blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels may be high.
A kidney biopsy may be needed to find the cause of the disorder.
Kidney biopsy
A kidney biopsy is the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue for examination.

Tests to rule out various causes may include the following:
-
Antinuclear antibody
Antinuclear antibody
The antinuclear antibody panel is a blood test that looks at antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANA are antibodies produced by the immune system that bind...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cryoglobulins
Cryoglobulins
Cryoglobulins are antibodies that become solid or gel-like at low temperatures in the laboratory. This article describes the blood test used to chec...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complement levels
Complement levels
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of ne...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Glucose tolerance test
Glucose tolerance test
The glucose tolerance test is a lab test to check how your body moves sugar from the blood into tissues like muscle and fat. The test is often used ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hepatitis B antigen
- Hepatitis C antibodies
-
HIV test
HIV test
In general, testing for the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a 2-step process that involves a screening test and follow-up tests often called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a blood test that measures the amount of the RF antibody in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP)
Serum protein electrophoresis
This lab test measures the types of protein in the fluid (serum) part of a blood sample. This fluid is called serum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Syphilis serology
-
Urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP)
Urine protein electrophoresis
The urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP) test is used to measure how much of certain proteins are in the urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
This disease may also change the results of the following tests:
- Vitamin D level
-
Serum iron
Serum iron
A serum iron test measures how much iron is in your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinary casts
Urinary casts
Urinary casts are tiny tube-shaped particles that can be found when urine is examined under the microscope during a test called urinalysis. Urinary c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goals of treatment are to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, and delay kidney damage. To control nephrotic syndrome, the disorder that is causing it must be treated. You may need treatment for life.
Kidney damage
Injury to the kidney and ureter is damage to the organs of the upper urinary tract.

Treatments may include any of the following:
- Keeping blood pressure at or below 130/80 mm Hg to delay kidney damage. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are the medicines most often used. ACE inhibitors and ARBs may also help decrease the amount of protein lost in the urine.
- Corticosteroids and other drugs that suppress or quiet the immune system.
- Treating high cholesterol to reduce the risk for heart and blood vessel problems -- A low-fat, low-cholesterol diet is usually not enough for people with nephrotic syndrome. Medicines to reduce cholesterol and triglycerides (usually statins) may be needed.
- A low-sodium diet may help with swelling in the hands and legs. Water pills (diuretics) may also help with this problem.
Low-sodium diet
Too much sodium in your diet can be bad for you. If you have high blood pressure or heart failure, you may be asked to limit the amount of salt (whi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low-protein diets may be helpful. Your provider may suggest a moderate-protein diet (1 gram of protein per kilogram of body weight per day).
- Taking vitamin D supplements if nephrotic syndrome is long-term and is not responding to treatment.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissue and liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Taking blood thinner drugs to treat or prevent blood clots.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome varies. Some people recover from the condition. Others develop long-term kidney disease and need dialysis and eventually a kidney transplant.
Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney disease also called kidney failure. It removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleKidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

Possible Complications
Health problems that may result from nephrotic syndrome include:
-
Acute kidney failure
Acute kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hardening of the arteries and related heart diseases
Hardening of the arteries
Atherosclerosis, sometimes called "hardening of the arteries," occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid overload, heart failure, fluid buildup in lungs
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFluid buildup in lungs
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections, including pneumococcal pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that occurs when your body does not get enough nutrients.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Renal vein thrombosis
Renal vein thrombosis
Renal vein thrombosis is a blood clot that develops in the vein that drains blood from the kidney.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You or your child develops symptoms of nephrotic syndrome, including swelling in face, belly, or arms and legs, or skin sores
- You or your child are being treated for nephrotic syndrome, but symptoms don't improve
- New symptoms develop, including cough, decreased urine output, discomfort with urination, fever, severe headache
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleFever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeadache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Go to the emergency room or call the local emergency number (such as 911) if you have seizures.
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...

Prevention
Treating conditions that can cause nephrotic syndrome may help prevent the syndrome.
References
Erkan E. Nephrotic syndrome. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 545.
Radhakrishnan J, Stokes MB. Glomerular disorders and nephrotic syndromes. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 107.
Saha MK, Pendergraft WF, Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Primary glomerular disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
-
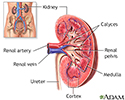
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
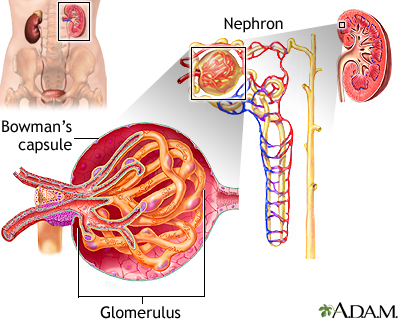
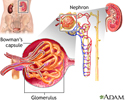
Glomerulus and nephron - illustration
The kidneys remove excess fluid and waste from your body. Blood is filtered in the kidneys through nephrons. Each nephron contains a network of small blood vessels, called glomerulus, which are enclosed in a sac called Bowman's capsule. The filtered waste product (urine) flows through tiny tubes and is then passed from the kidneys to the bladder through bigger tubes called ureters.
Glomerulus and nephron
illustration
-
Kidney anatomy - illustration
The kidneys are responsible for removing wastes from the body, regulating electrolyte balance and blood pressure, and the stimulation of red blood cell production.
Kidney anatomy
illustration
-
Glomerulus and nephron - illustration
The kidneys remove excess fluid and waste from your body. Blood is filtered in the kidneys through nephrons. Each nephron contains a network of small blood vessels, called glomerulus, which are enclosed in a sac called Bowman's capsule. The filtered waste product (urine) flows through tiny tubes and is then passed from the kidneys to the bladder through bigger tubes called ureters.
Glomerulus and nephron
illustration
Review Date: 8/28/2023
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.