Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a type of kidney disease in which the part of your kidneys that helps filter waste and fluids from the blood is damaged.
Causes
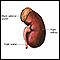
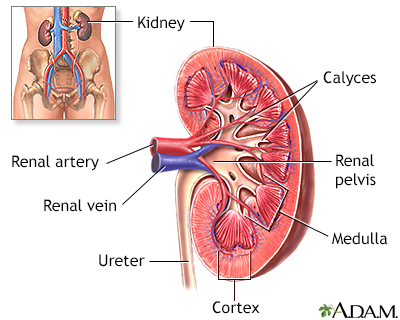
The filtering unit of the kidney is called the glomerulus. Each kidney has many thousands of glomeruli. The glomeruli help the body get rid of harmful substances.
Glomerulonephritis may be caused by problems with the body's immune system. Often, the exact cause of this condition is unknown.
Damage to the glomeruli causes blood and protein to be lost in the urine.
The condition may develop quickly, and kidney function is lost within weeks or months. This is called rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
Some people with chronic glomerulonephritis have no history of kidney disease.
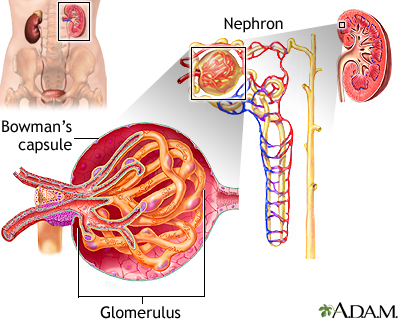
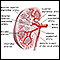
Glomerulus and nephron
The kidneys remove excess fluid and waste from your body. Blood is filtered in the kidneys through nephrons. Each nephron contains a network of small blood vessels, called glomerulus, which are enclosed in a sac called Bowman's capsule. The filtered waste product (urine) flows through tiny tubes and is then passed from the kidneys to the bladder through bigger tubes called ureters.
The following may increase your risk for this condition:
- Blood or lymphatic system disorders
- Exposure to hydrocarbon solvents
- History of cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections such as strep infections, viruses, heart infections, or abscesses
Strep infections
Poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis (GN) is a kidney disorder that occurs after infection with certain strains of streptococcus bacteria.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbscesses
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Many conditions cause or increase the risk for glomerulonephritis, including:
- Amyloidosis (disorder in which a protein called amyloid builds up in the organs and tissues)
- Disorder that affects the glomerular basement membrane, the part of the kidney that helps filter waste and extra fluid from the blood
- Blood vessel diseases, such as vasculitis or polyarteritis
Polyarteritis
Polyarteritis nodosa is a serious inflammatory blood vessel disease. The small and medium-sized arteries become swollen and damaged.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (scarring of the glomeruli)
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis is scar tissue in the filtering unit of the kidney. This structure is called the glomerulus. The glomeruli serve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease (disorder in which the immune system attacks the glomeruli)
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disea...
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease (anti-GBM disease) is a rare disorder that can involve quickly worsening kidney failure and lung disease. S...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Analgesic nephropathy syndrome (kidney disease due to heavy use of pain relievers, especially NSAIDs)
Analgesic nephropathy syndrome
Analgesic nephropathy involves damage to one or both kidneys caused by overexposure to mixtures of medicines, especially over-the-counter pain medici...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Henoch-Schönlein purpura (disease that involves purple spots on the skin, joint pain, gastrointestinal problems and glomerulonephritis)
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
IgA vasculitis is a disease that involves purple spots on the skin, joint pain, gastrointestinal problems, and glomerulonephritis (a type of kidney d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - IgA nephropathy (disorder in which antibodies called IgA build up in kidney tissue)
IgA nephropathy
IgA nephropathy is a kidney disorder in which antibodies (called IgA) build up in kidney tissue. Nephropathy is damage, disease, or other problems w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lupus nephritis (kidney complication of systemic lupus erythematosus)
Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis, which is a kidney disorder, is a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Membranoproliferative GN (form of glomerulonephritis due to abnormal buildup of antibodies in the kidneys)
Membranoproliferative GN
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis is a kidney disorder that involves inflammation and changes to kidney cells. It may lead to kidney failure....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Common symptoms of glomerulonephritis are:
- Blood in the urine (dark, rust-colored, or brown urine)
- Foamy urine (due to excess protein in the urine)
- Swelling (edema) of the face, eyes, ankles, feet, legs, or abdomen
Symptoms may also include the following:
- Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood in the vomit or stools
- Cough and shortness of breath
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea
- Excessive urination
- Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
General ill feeling, fatigue, and loss of appetite
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint or muscle aches
Muscle aches
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than one muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascias are th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nosebleed
Nosebleed
A nosebleed is loss of blood from the tissue lining the nose. Bleeding most often occurs from one nostril only.
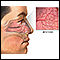 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The symptoms of chronic kidney disease may develop over time.
Chronic kidney failure symptoms may gradually develop.
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...

Exams and Tests
Because symptoms may develop slowly, the disorder may be discovered when you have an abnormal urinalysis during a routine physical or examination for another condition.
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...

Signs of glomerulonephritis can include:
- Anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Signs of reduced kidney function
A kidney biopsy confirms the diagnosis.
Kidney biopsy
A kidney biopsy is the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue for examination.

Later, signs of chronic kidney disease may be seen, including:
- Nerve inflammation (polyneuropathy)
- Signs of fluid overload, including abnormal heart and lung sounds
- Swelling (edema)
Edema
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Imaging tests that may be done include:
- Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney ultrasound
- Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
IVP
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a special x-ray exam of the kidneys, bladder, and ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladd...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Urinalysis and other urine tests include:
- Creatinine clearance
Creatinine clearance
The creatinine clearance test helps provide information about how well the kidneys are working. The test compares the creatinine level in urine with...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Examination of the urine under a microscope
- Uric acid in the urine
Uric acid in the urine
The uric acid urine test measures the level of uric acid in the urine. The uric acid blood level can be checked using a blood test.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine concentration test
Urine concentration test
A urine concentration test measures the ability of the kidneys to conserve or excrete water.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine creatinine
Urine creatinine
The creatinine urine test measures the amount of creatinine in urine. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine protein
Urine protein
The urine protein dipstick test measures the presence of all proteins, including albumin, in a urine sample. Albumin and protein can also be measured...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine RBC
Urine RBC
The RBC urine test measures the number of red blood cells in a urine sample.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine specific gravity
Urine specific gravity
Urine specific gravity is a laboratory test that shows the total concentration of all chemical particles in the urine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine osmolality
Urine osmolality
The osmolality urine test measures the concentration of chemicals in urine. Osmolality in the blood can be measured using a blood test.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
This disease may also cause abnormal results on the following blood tests:
- Albumin
Albumin
Albumin is a protein made by the liver. A serum albumin test measures the amount of this protein in the clear liquid portion of the blood. Albumin c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antiglomerular basement membrane antibody test
Antiglomerular basement membrane
The glomerular basement membrane is the part of the kidney that helps filter waste and extra fluid from the blood. Anti-glomerular basement membrane ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs)
- Antinuclear antibodies
- BUN and creatinine
BUN
BUN stands for blood urea nitrogen. Urea nitrogen is what forms when protein breaks down. A test can be done to measure the amount of urea nitrogen ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCreatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complement levels
Complement
Complement is a blood test that measures the activity of certain proteins in the liquid portion of your blood. The complement system is a group of ne...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Uric acid
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the disorder, and the type and severity of symptoms. Controlling high blood pressure is usually an important part of treatment.
Medicines that may be prescribed include:
- Blood pressure drugs, most often angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Corticosteroids
- Drugs that suppress the immune system
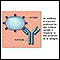
A procedure called plasmapheresis may sometimes be used for glomerulonephritis caused by immune system problems. The fluid part of the blood that contains antibodies is removed and replaced with intravenous fluids or donated plasma (that does not contain antibodies). Removing antibodies may reduce inflammation in the kidney tissues.
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
You may need to limit your intake of sodium, fluids, protein, and other substances.
People with this condition should be closely watched for signs of kidney failure. Dialysis or a kidney transplant may eventually be needed.
Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney disease also called kidney failure. It removes waste from your blood when your kidneys can no longer do their job. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleKidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

Support Groups
More information and support for people with glomerulonephritis and their families can be found at kidney disease support group.
Support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on kidney disease:American Geriatrics Society -- www. healthinaging. org/a-z-topic/kid...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Glomerulonephritis may be temporary and reversible, or it may get worse. Progressive glomerulonephritis may lead to:
- Chronic kidney failure
- Reduced kidney function
- End-stage kidney disease
End-stage kidney disease
End-stage kidney disease (ESKD) is the last stage of long-term (chronic) kidney disease. This is when your kidneys can no longer support your body's...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If you have nephrotic syndrome and it can be controlled, you may also be able to control other symptoms. If it cannot be controlled, you may develop end-stage kidney disease.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You have a condition that increases your risk for glomerulonephritis
- You develop symptoms of glomerulonephritis
Prevention
Most cases of glomerulonephritis can't be prevented. Some cases may be prevented by avoiding or limiting exposure to organic solvents, mercury, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Reviewed By
Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Radhakrishnan J, Stokes MB. Glomerular disorders and nephrotic syndromes. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 107.
Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB, D'Agati VD. Secondary glomerular disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 32.
Reich HN, Cattran DC. Treatment of glomerulonephritis. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 33.
Saha MK, Pendergraft WF, Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Primary glomerular disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.