High blood pressure in adults - hypertension
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the medical term used to describe high blood pressure.
Untreated high blood pressure can lead to many medical problems. These include heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, eye problems, and other health issues.
Blood pressure readings are given as two numbers. The top number is called systolic blood pressure. The bottom number is called diastolic blood pressure. For example, 120 over 80 (written as 120/80 mm Hg).
One or both of these numbers can be too high. (Note: The numbers below apply to people who are not taking medicines for blood pressure and who are not ill.)
- Normal blood pressure is when your blood pressure is lower than 120/80 mm Hg most of the time.
- High blood pressure (hypertension) is when one or both of your blood pressure readings are 130/80 mm Hg or higher most of the time.
- If the top blood pressure number is from 120 to 129 mm Hg, and the bottom blood pressure number is less than 80 mm Hg, it is called elevated blood pressure.
If you have heart or kidney problems, or you had a stroke, your health care provider may want your blood pressure to be even lower than that of people who do not have these conditions.
Hypertension - Animation
If your doctor told you that you have high blood pressure, you may have wondered, what's the big deal? Well high blood pressure IS a big deal, because it can lead to a heart attack, stroke, vision loss, and kidney disease, sometimes before you even realize you have it. When you have high blood pressure, you'll want to control it before it can lead to these dangerous complications. Let's talk about high blood pressure, otherwise known as hypertension. Blood pressure measures the force at which your blood rushes against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it through your body. The higher the force, meaning the higher your blood pressure, the harder your heart has to work. High blood pressure damages not only your heart but also your arteries. When your doctor or nurse measures your blood pressure, you'll see two numbers. The top number is called systolic blood pressure. That's the force of blood in your arteries whenever your heart beats. The bottom number measures diastolic blood pressure, or the force of blood in between heartbeats. You're more likely to have high blood pressure if you don't exercise regularly, you're obese, you eat too much salt, you have diabetes, you smoke, or you have a family history of high blood pressure. Most of the time, you won't know that you have high blood pressure. That's because high blood pressure usually doesn't cause symptoms. Unless you get your blood pressure checked, you may have no idea there's a problem until you develop heart disease or another complication. If your blood pressure is high, a few simple lifestyle changes can help bring it back down, and prevent its complications. Eat a heart-healthy diet that includes plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy, avoid fatty, salty, and sugary foods, exercise at least 30 minutes a day, limit salt to 1,500 milligrams or less a day, that's less than a teaspoon per day, and if you smoke, now is the perfect time to quit. Ask your doctor for tips on how to kick the habit. If these measures don't work, your doctor may prescribe one or more medicines to control your blood pressure. Because high blood pressure can sneak in without warning, stop it before it starts. Stay healthy, and your blood pressure checked at least once a year. If you already have high blood pressure, follow your doctor's advice to get it under control.
Causes
Many factors can affect blood pressure, including:
- The amount of water and salt you have in your body
- The condition of your kidneys, nervous system, or blood vessels
- Your hormone levels
You are more likely to be told your blood pressure is too high as you get older. This is because your blood vessels become stiffer as you age. When that happens, your blood pressure goes up. High blood pressure increases your chance of having a stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney disease, or early death.
You have a higher risk for high blood pressure if you:
- Are African American
- Are obese
- Are often stressed or anxious
- Drink alcohol (more than 1 drink per day for women and more than 2 drinks per day for men)
- Eat too much salt
Eat too much salt
Sodium is an element that the body needs to work properly. Salt contains sodium.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Have a family history of high blood pressure
- Have diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Smoke or use tobacco
Most of the time, no cause of high blood pressure is found. This is called essential hypertension.
High blood pressure that is caused by another medical condition or medicine you are taking is called secondary hypertension. Secondary hypertension may be due to:
- Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disorders of the adrenal gland (such as pheochromocytoma or Cushing syndrome)
Pheochromocytoma
Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of adrenal gland tissue that typically arises from the adrenal gland. It results in the release of too much epineph...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body has a high level of the hormone cortisol.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which 1 or more of the parathyroid glands in your neck produce too much parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy or preeclampsia
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines such as birth control pills, diet pills, some cold medicines, migraine medicines, corticosteroids, some antipsychotics, and certain medicines used to treat cancer
- Narrowed artery that supplies blood to the kidney (renal artery stenosis)
Renal artery stenosis
Renovascular hypertension is high blood pressure due to narrowing of the arteries that carry blood to the kidneys. This condition is also called ren...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)
Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a problem in which your breathing pauses during sleep. This occurs because of narrowed or blocked airways.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Most of the time, there are no symptoms. For most people, high blood pressure is found when they visit their provider or have it checked elsewhere.
Because there are no symptoms, people can develop heart disease and kidney problems without knowing they have high blood pressure.
Malignant hypertension is a dangerous form of very high blood pressure. Symptoms may include:
Malignant hypertension
Malignant hypertension is very high blood pressure that comes on suddenly and quickly.

- Severe headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion
- Vision changes
- Nosebleeds
Exams and Tests
Diagnosing and treating high blood pressure early can help prevent heart disease, stroke, eye problems, and chronic kidney disease.
Your provider will measure your blood pressure several times before diagnosing you with high blood pressure. It is normal for your blood pressure to be different based on the time of day.
Measure your blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force on the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. You can measure your blood pr...

All adults age 18 or older should have their blood pressure checked periodically. For people age 40 or older, checking blood pressure once per year is recommended. For some people age 18 to 39, checking less often may be fine. More frequent measurements may be needed for those with a history of high blood pressure readings or those with risk factors for high blood pressure. Check with your provider about what is best for you.
Blood pressure readings taken at home may be a better measure of your current blood pressure than those taken at your provider's office.
- Make sure you get a good quality, well-fitting home blood pressure monitor. It should have a properly sized cuff and a digital readout.
Home blood pressure monitor
Your health care provider may ask you to keep track of your blood pressure at home. To do this, you will need to get home blood pressure monitor. T...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Practice with your provider to make sure you are taking your blood pressure correctly.
- You should be relaxed and seated for five or more minutes prior to taking a reading.
- Bring your home monitor to your appointments so your provider can make sure it is working correctly.
Tracking your blood pressure at home - Animation
Following your blood pressure at home has gotten a lot easier in the last few years. I'm Dr. Alan Greene. I'd like to share with you a little bit about that. Not too long ago when you wanted to follow your blood pressure at home, you had to have the old fashioned sphygmomonometer, and the device was a complex as that word sounds. You had to pump something up, and put a stethoscope in your ears, and fumble all these different tubes and even so wouldn't get a very accurate reading. Now, there are simple, high quality, digital blood pressure cuffs. They're easy to use at home. They're built so they snap on the arm very easily, just press a single button, and the chip inside does the work for you. It blows it up, it gives you the reading, and some of the newer models even connect it to your PC and track the readings for you. Now, how accurate are they? They're really pretty good. I wouldn't trust a single reading that much if you get one that's high or low. I wouldn't be either reassured or panicked. But, I would trust the pattern of readings. So, if you have one that tracks it for you, that's great, if not, just write them down what date and time you took it and see what the pattern is over time. If there's anything of concern, be sure to report it to your physician.
Your provider will do a physical exam to look for signs of heart disease, damage to your eyes, and other changes in your body.
Tests may also be done to look for:
- High cholesterol level
High cholesterol level
Cholesterol is a soft, wax-like substance found in all parts of the body. Your body needs cholesterol to work properly. But too much cholesterol ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart disease, using tests such as an echocardiogram or electrocardiogram
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diabetes and kidney disease, using tests such as a basic metabolic panel blood test, urinalysis, or ultrasound of the kidneys
Basic metabolic panel
The basic metabolic panel is a group of blood tests that provides information about your body's metabolism.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUrinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce your blood pressure so that you have a lower risk of health problems caused by high blood pressure. You and your provider should set a blood pressure goal for you.
Whenever thinking about the best treatment for high blood pressure, you and your provider must consider other factors such as:
- Your age
- The medicines you take
- Your risk of side effects from possible medicines
- Other medical conditions you may have, such as a history of heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, or diabetes
If the top blood pressure number is from 120 to 129 mm Hg, and the bottom blood pressure number is less than 80 mm Hg, you have what is called elevated blood pressure.
- Your provider will recommend lifestyle changes to bring your blood pressure down to a normal range.
- Medicines are rarely used at this stage.
If your blood pressure is 130/80 or higher, but lower than 140/90 mm Hg, you have Stage 1 high blood pressure. When thinking about the best treatment, you and your provider must consider:
- If you have no other diseases or risk factors for heart or kidney disease, your provider may recommend lifestyle changes and repeat the measurements after a few months.
- If your blood pressure remains 130/80 or above, but lower than 140/90 mm Hg, your provider may recommend medicines to treat high blood pressure.
- If you have other diseases or risk factors for heart or kidney disease, your provider may be more likely to recommend medicines at the same time as lifestyle changes.
If your blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg or higher, you have Stage 2 high blood pressure. Your provider will most likely recommend medicines and lifestyle changes together.
Before making a final diagnosis of either elevated blood pressure or high blood pressure, your provider should ask you to have your blood pressure measured at home, at your pharmacy, or somewhere else besides their office or a hospital.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES
You can do many things to help control your blood pressure, including:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet, including potassium and fiber.
Heart-healthy diet
Making changes to your diet is a proven way to help control high blood pressure. These changes can also help you lose weight and lower your chance o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drink plenty of water.
- Get at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic exercise per week.
- If you smoke or use tobacco, quit.
- Limit how much alcohol you drink to 1 drink a day for women, and 2 drinks a day for men or less and consider quitting entirely.
- Limit the amount of sodium (salt) you eat. Aim for less than 1,500 mg per day of sodium.
- Reduce stress. Try to avoid things that cause you stress, and try meditation or yoga to de-stress.
- Stay at a healthy body weight.

Lifestyle changes
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by chronically high blood pressure. It must be monitored, treated and controlled by medicines, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both.
Your provider can help you find programs for losing weight, stopping smoking, and exercising.
You can also get a referral to a dietitian, who can help you plan a diet that is healthy for you.
How low your blood pressure should be and at what level you need to start treatment is individualized, based on your age and any medical problems you have. Ask your provider what your blood pressure goal is.
Heart disease modifiable risk factors - hypertension - Animation
Hypertension increases the workload of the heart causing the heart to thicken and become stiffer. Hypertension also increases the risk of stroke, MI, kidney failure, and chronic heart failure. When high blood pressure coexists with obesity, smoking, high blood cholesterol levels or diabetes, the risk of MI and stroke is increased. Worldwide, about half of all strokes and ischemic heart disease are attributable to high blood pressure. Treatment of high blood pressure begins with lifestyle changes, eating a healthy diet that is low in salt, and if needed, losing weight and increasing physical activity. Drug therapy may also be necessary.
MEDICINES FOR HYPERTENSION
Most of the time, your provider will suggest you try lifestyle changes first and check your blood pressure two or more times. Medicines will likely be recommended if your blood pressure readings remain at or above these levels:
- Top number (systolic pressure) of 130 or more
- Bottom number (diastolic pressure) of 80 or more
If you have diabetes, heart problems, or a history of a stroke, medicines may be started at lower blood pressure reading. The most commonly used blood pressure targets for people with these medical problems are below 120 to 130/80 mm Hg.
There are many different medicines to treat high blood pressure.
Medicines to treat high blood pressure
Treating high blood pressure will help prevent problems such as heart disease, stroke, loss of eyesight, chronic kidney disease, and other blood vess...

- Often, a single blood pressure medicine may not be enough to control your blood pressure, and you may need to take two or more medicines.
- It is very important that you take the medicines prescribed to you.
- If you have side effects, tell your provider promptly so they can substitute a different medicine.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, high blood pressure can be controlled with medicine and lifestyle changes.
When blood pressure is not well-controlled, you are at risk for:
- Bleeding from the aorta, the large blood vessel that supplies blood to the abdomen, pelvis, and legs
- Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack and heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Poor blood supply to the legs
- Problems with your vision
Problems with your vision
High blood pressure can damage blood vessels in the retina. The retina is the layer of tissue at the back part of the eye. It changes light and ima...
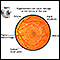 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain suddenly stops. A stroke is sometimes called a brain attack or cerebrovascular accident (CVA)...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If you have high blood pressure, you should have regular follow-up visits with your provider.
Even if you have not been diagnosed with high blood pressure, it is important to have your blood pressure checked during your regular check-up, especially if someone in your family has or had high blood pressure.
Contact your provider right away if home monitoring shows that your blood pressure is still high.
Prevention
Many people can prevent or delay high blood pressure from occurring by following lifestyle changes designed to bring blood pressure down.
Reviewed By
Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 10. Cardiovascular disease and risk management: standards of care in diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025;48(Supplement_1):S207-S238. PMID: 39651970 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39651970/.
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11);e596-e646. PMID: 30879355 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30879355/.
Bakris GL, Sorrentino MJ. Systemic hypertension: mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 26.
Flack JM. Arterial hypertension. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 64.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71(6):1269-1324. PMID: 29133354 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29133354/.






 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.