Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It can affect the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs.
Autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
Systemic lupus erythematosus - Animation
When your joints are sore and achy, you might assume you have arthritis. But if that joint pain strikes when you're still in your 30's, or even your 20's, it might be another condition entirely. You might have an autoimmune disease called systemic lupus erythematosus, or lupus, for short. An autoimmune disease means that your immune system, which normally serves as your body's first defense against infections, mistakenly attacks your own tissues. Imagine if you hit your hand over and over and over again. The skin would turn red and swell up, and it would probably hurt quite a bit. Well, the same kind thing happens inside your body when your immune system attacks your tissues. They swell up, and they hurt. Almost everyone with lupus has joint pain and swelling, but depending on what part of your body the lupus is attacking, you could have other symptoms too. If it's your skin, you might have a rash on your face and body. If lupus attacks your digestive tract, you might feel sick to your stomach. If it attacks your brain or nervous system, you may have numbness, tingling, vision problems, and headaches. So, how do you know that you have lupus? Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, listen to your heartbeat, and examine your nervous system. Doctors often use a test to check for antinuclear antibodies, the immune substances that attack your tissues. You'll likely also need other blood or urine tests, and perhaps an x-ray, CT, ultrasound or biopsy, depending on your symptoms. Taken together, your symptoms and the results of these tests can help your doctor determine whether you have lupus. If you do have lupus, lupus is a chronic condition, but, you can control its symptoms. For example, taking steroid medicines by mouth might help control the overactive immune response that's causing your lupus. Steroid creams can treat skin rashes. For achy joints, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines like ibuprofen, and anti-malaria drugs might help. You may need stronger drugs if these medicines alone don't control your lupus symptoms. When you have lupus, you need to be extra careful about your health. Wear sunscreen and protective clothing whenever you're out in the sun, so your skin doesn't get even more irritated. Stop smoking and make sure you're up-to-date on your vaccines. Have your heart checked regularly because lupus can cause heart complications. Lupus can be a lifelong journey, but life with lupus is a lot better today than it was just a few decades ago. Improved treatments can help control your joint pain and other symptoms so you can live a pretty normal life. To improve your outlook with lupus, stay on top of your health care, and do call your doctor right away if your symptoms get worse or you develop any new symptoms.
Causes
The cause of SLE is not clearly known. It may be linked to the following factors:
- Genetic
- Environmental
- Hormonal
- Certain medicines
SLE is more common in women than men by nearly 10 to 1. It may occur at any age. However, it appears most often in young women between the ages of 15 and 44. In the United States, the disease is more common in African Americans, Asian Americans, African Caribbeans, and Hispanic Americans than non-Hispanic white people.
Symptoms
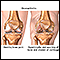
Symptoms vary from person to person, and may come and go. Everyone with SLE has joint pain and swelling at some time. Some develop arthritis. SLE often affects the joints of the fingers, hands, wrists, and knees.
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
Other common symptoms include:
- Chest pain when taking a deep breath.
- Fatigue.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fever with no other cause.
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise).
- Hair loss.
Hair loss
Partial or complete loss of hair is called alopecia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight loss.
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Mouth sores.
Mouth sores
There are different types of mouth sores. They can occur anywhere in the mouth including bottom of the mouth, inner cheeks, gums, lips, and tongue....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensitivity to sunlight.
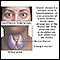
- Skin rash -- A "butterfly" rash develops in about half the people with SLE. The rash is mostly seen over the cheeks and bridge of the nose. It can be widespread. It gets worse in sunlight.
Skin rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen lymph nodes.
Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms and signs depend on which part of the body is affected:
- Brain and nervous system -- Headaches, weakness, numbness, tingling, seizures, vision problems, memory and personality changes
Headaches
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleNumbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSeizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Digestive tract -- Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
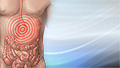 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart -- Valve problems, inflammation of heart muscle, or the sac around the heart (pericardium)
Inflammation of heart muscle
Cardiomyopathy is disease in which the heart muscle becomes weakened, stretched, or has another structural problem. It often contributes to the hear...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung -- Buildup of fluid in the pleural space, difficulty breathing, coughing up blood
- Skin -- Sores in the mouth
- Kidney -- Swelling in the legs
- Circulation -- Clots in veins or arteries, inflammation of blood vessels, constriction of arteries in response to cold (Raynaud phenomenon)
Raynaud phenomenon
Raynaud phenomenon is a condition in which cold temperatures or strong emotions cause blood vessel spasms. This blocks blood flow to the affected re...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood abnormalities including anemia, low white blood cell or platelet count
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Some people have only skin symptoms. This is called discoid lupus.

Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disorder which may affect many organ systems including the skin, joints and internal organs. The disease may be mild or severe and life-threatening. African-Americans and Asians are disproportionately affected.
Exams and Tests
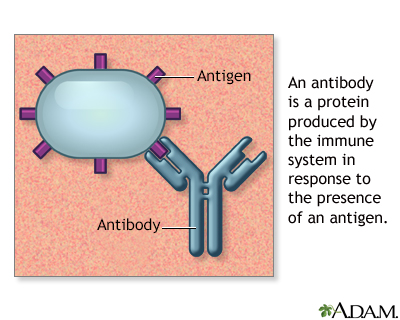
The American and European Rheumatology societies have published classification criteria to assist the diagnosis of SLE. These include specific symptoms, physical finding and laboratory tests. Nearly all people with SLE have a positive test for an antinuclear antibody (ANA). However, having a positive ANA alone does not mean you have SLE.
The health care provider will do a complete physical exam. You may have a rash, arthritis, or swelling in the ankles. There may be an abnormal sound called a pericardial friction rub or pleural friction rub. Your provider will also do a nervous system exam.
Tests used to diagnose SLE may include:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA)
- Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
Complete blood count (CBC)
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
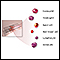 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum creatinine
- Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may also have other tests to learn more about your condition. Some of these are:
- Antinuclear antibody (ANA) panel
Antinuclear antibody
The antinuclear antibody panel is a blood test that looks at antinuclear antibodies (ANA). ANA are antibodies produced by the immune system that bind...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complement components (C3 and C4)
Complement components
Complement C3 is a blood test that measures the activity of a certain protein. This protein is part of the complement system. The complement system ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antibodies to double-stranded DNA
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is produced by the liver. The level of CRP rises when there is inflammation in the body. It is one of a group of proteins,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Coombs test -- direct
Coombs test -- direct
The Coombs test looks for antibodies that may stick to your red blood cells and cause red blood cells to die too early.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cryoglobulins
Cryoglobulins
Cryoglobulins are antibodies that become solid or gel-like at low temperatures in the laboratory. This article describes the blood test used to chec...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
ESR stands for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. It is commonly called a "sed rate. "It is a test that indirectly measures the level of certain protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney function blood tests
Kidney function blood tests
Kidney function tests are common lab tests used to evaluate how well the kidneys are working. Such tests include:BUN (Blood urea nitrogen) Creatinin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver function blood tests
Liver function blood tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
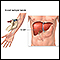 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor
Rheumatoid factor (RF) is a blood test that measures the amount of the RF antibody in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antiphospholipid antibodies and lupus anticoagulant test
- Kidney biopsy
Kidney biopsy
A kidney biopsy is the removal of a small piece of kidney tissue for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Imaging tests of the heart, brain, lungs, joints, muscles or intestines
Treatment
There is no cure for SLE. The goal of treatment is to control symptoms. Severe symptoms that involve the heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs often need treatment by specialists. Each person with SLE needs evaluation regarding:
- How active the disease is
- What part of the body is affected
- What form of treatment is needed
Mild forms of SLE may be treated with:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for joint symptoms and pleurisy. Talk to your provider before taking these medicines.
- Low doses of corticosteroids, such as prednisone, for skin and arthritis symptoms.
- Corticosteroid creams for skin rashes.
- Hydroxychloroquine, a medicine also used to treat malaria.
- Methotrexate may be used to reduce the dose of corticosteroids.
- Belimumab, rituximab, and anifrolumab are biologic medicines that may be helpful in some people.
Treatments for more severe SLE may include:
- High-dose corticosteroids.
- Immunosuppressive medicines (these medicines suppress the immune system). These medicines are used if you have severe SLE that is affecting your nervous system, kidney, or other organs. They may also be used if you do not get better with corticosteroids, or if your symptoms get worse when you stop taking corticosteroids.
- Medicines most commonly used include mycophenolate, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, and valcosporin. Because of its toxicity, cyclophosphamide is limited to a short course of 3 to 6 months. Rituximab is used in some cases as well.
- Blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin), for clotting disorders such as antiphospholipid syndrome.
If you have SLE, it is also important to:
- Wear protective clothing, sunglasses, and sunscreen when in the sun.
- Get preventive heart care.
- Stay up-to-date with immunizations.
- Have tests to screen for thinning of the bones (osteoporosis).
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Avoid tobacco and drink minimal amounts of alcohol.
Support Groups
Counseling and support groups may help with the emotional issues involved with the disease.
Counseling and support groups
The following organizations are good resources for information on systemic lupus erythematosus:US National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus -- medlin...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
The outcome for people with SLE has improved in recent years. Many people with SLE have mild symptoms. How well you do depends on how severe the disease is. Most people with SLE will require medicines for a long time. Nearly all will require hydroxychloroquine indefinitely. However, in the United States, SLE is one of the top 20 leading causes of death in females between the ages of 5 and 64. Many new medicines are being studied to improve the outcome of women with SLE.
The disease tends to be more active:
- During the first years after diagnosis
- In people younger than 40 years
Many women with SLE can get pregnant and deliver a healthy baby. A good outcome is more likely for women who receive proper treatment and do not have serious heart or kidney problems. However, the presence of certain SLE antibodies or antiphospholipid antibodies raises the risk of miscarriage.
Possible Complications
LUPUS NEPHRITIS
Some people with SLE have abnormal immune deposits in the kidney cells. This leads to a condition called lupus nephritis. People with this problem may develop kidney failure. They may need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Lupus nephritis
Lupus nephritis, which is a kidney disorder, is a complication of systemic lupus erythematosus.

Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...

Dialysis
Dialysis treats end-stage kidney failure. It removes harmful substances from the blood when the kidneys cannot. This article focuses on peritoneal d...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleKidney transplant
A kidney transplant is surgery to place a healthy kidney into a person with kidney failure.

A kidney biopsy is done to detect the extent of damage to the kidney and to help guide treatment. If active nephritis is present, treatment with immunosuppressive medicines including high doses of corticosteroids along with either cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate are needed.
OTHER PARTS OF THE BODY
SLE can cause damage in many different parts of the body, including:
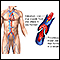
- Blood clots in arteries or veins of the legs, lungs, brain, or intestines
Blood clots
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis) or anemia of long-term (chronic) disease
Anemia of long-term (chronic) disease
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
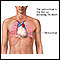
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid around the heart (pericarditis), or inflammation of the heart (myocarditis or endocarditis)
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
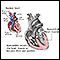
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMyocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle. The condition is called pediatric myocarditis when it occurs in children.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleEndocarditis
Endocarditis is inflammation of the inside lining of the heart chambers and heart valves (endocardium). It is most often caused by a bacterial or, r...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
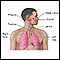
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid around the lungs (pleuritis) and damage to lung tissue
Pleuritis
Pleurisy is an inflammation of the lining of the lungs and chest (the pleura) that leads to chest pain when you take a breath or cough.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pregnancy problems, including miscarriage
- Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bowel damage with abdominal pain and obstruction
- Inflammation in the intestines
- Severely low blood platelet count called thrombocytopenia (platelets are needed to stop any bleeding)
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia means there is an abnormally low amount of platelets. Platelets are parts of the blood that help blood to clot. This condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammation of the blood vessels
SLE AND PREGNANCY
Both SLE and some of the medicines used for SLE can harm an unborn child. Talk to your provider before you become pregnant. If you become pregnant, find a provider who is experienced with SLE and pregnancy.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of SLE. Also contact your provider if you have this disease and your symptoms get worse or a new symptom occurs.
Reviewed By
Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Aringer M, Costenbader K, Daikh D, et al. 2019 European League against rheumatism/American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(9):1400-1412. PMID: 31385462 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31385462/.
Crow MK. Etiology and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Firestein GS, Mclnnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 80.
Crow MK. Systemic lupus erythematosus. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 245.
Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Alunno A, et al. 2019 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(6):736-745. PMID: 30926722 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30926722/.




 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.