Polymyositis - adult
Polymyositis and dermatomyositis are rare inflammatory diseases. These diseases lead to muscle weakness, swelling, tenderness, and tissue damage. They are part of a larger group of diseases called myopathies, more specifically inflammatory myopathies.
Causes
Polymyositis affects the skeletal muscles. It is also known as idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. The exact cause is unknown, but it may be related to an autoimmune reaction or infection.
Autoimmune
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
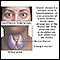
Polymyositis can affect people at any age. It is most common in adults between ages 50 and 60, and in older children. It affects women twice as often as men. It is more common in African Americans than white people.
Symptoms
Polymyositis is a systemic disease. This means it affects the whole body. Muscle weakness and tenderness can be signs of polymyositis. A rash is a sign of a related condition, dermatomyositis.
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis is a disease that involves muscle inflammation and a skin rash. Polymyositis is a similar inflammatory condition that also involves ...

Common symptoms include:
- Muscle weakness in the shoulders and hips. This can make it hard to raise the arms over the head, get up from a sitting position, or climb stairs.
-
Difficulty swallowing.
Difficulty swallowing
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Muscle pain.
Muscle pain
Muscle aches and pains are common and can involve more than one muscle. Muscle pain also can involve ligaments, tendons, and fascia. Fascias are th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Problems with the voice (caused by weak throat muscles).
-
Shortness of breath.
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may also have:
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
-
Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Morning stiffness
- Weight loss
-
Skin rash on the back of the fingers, on the eyelids, or on the face
Skin rash
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Tests may include:
- Autoimmune antibodies and inflammation tests
-
Serum CPK (creatine phosphokinase)
CPK (creatine phosphokinase)
Creatine phosphokinase (CPK) is an enzyme in the body. It is found mainly in the heart, brain, and skeletal muscle. This article discusses the test...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum aldolase
Serum aldolase
Aldolase is a protein (called an enzyme) that helps break down certain sugars to produce energy. It is found in high amount in muscle and liver tiss...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
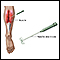
Electromyography
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI of affected muscles
-
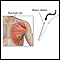
Muscle biopsy
Muscle biopsy
A muscle biopsy is the removal of a small piece of muscle tissue for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Myoglobin in the urine
Myoglobin in the urine
The myoglobin urine test is done to detect the presence of myoglobin in urine. Myoglobin can also be measured with a blood test.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray and CT scan of the chest
CT scan of the chest
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the heart is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create detailed pictures of the heart and its blood vessels. Th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary function tests
- Esophageal swallowing study
- Myositis specific and associated autoantibodies
People with this condition also must be watched carefully for signs of cancer.
Treatment
The initial treatment is the use of corticosteroid medicines. The dose of medicine is slowly tapered off as muscle strength improves. Medicines to suppress the immune system may be used to replace the corticosteroids. These medicines may include azathioprine, methotrexate, rituximab (Rituxan), or mycophenolate.
For disease that remains active in spite of corticosteroids, intravenous gamma globulin can be given. It is important to check for other conditions in people who do not respond to treatment. A repeat muscle biopsy may be needed to make this diagnosis.
If the condition is associated with a tumor, it may improve if the tumor is removed.
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
Response to treatment varies, based on the complications. As many as 1 in 5 people may die within 5 years of developing the condition.
Many people, especially children, recover from the illness and do not need ongoing treatment. For most adults, however, immunosuppressant medicines are needed to control the disease.
The outlook for people with lung disease with the anti-MDA-5 antibody is poor despite current treatment.
In adults, death may result from:
- Malnutrition
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Respiratory failure
- Severe, long-term muscle weakness
The major causes of death are cancer and lung disease.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Calcium deposits in the affected muscles, especially in children with the disease
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart disease, lung disease, or abdominal complications
Lung disease
Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease:Airway diseases -...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of this disorder. Seek emergency treatment if you have shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing.
References
Greenberg SA. Inflammatory myopathies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 248.
Nagaraju K, Aggarwal R, Lundberg IE. Inflammatory diseases of muscle and other myopathies In: Firestein GS, Mclnnes IB, Koretzky GA, Mikuls TR, Neogi T, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein & Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 86.
National Organization for Rare Disorders website. Polymyositis and necrotizing myopathy. rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/polymyositis/. Updated August 26, 2019. Accessed March 24, 2025.
-
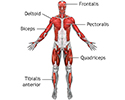
Superficial anterior muscles - illustration
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
Review Date: 1/28/2025
Reviewed By: Diane M. Horowitz, MD, Rheumatology and Internal Medicine, Northwell Health, Great Neck, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.