Ectopic Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome - ectopic; Ectopic ACTH syndrome; Ectopic Cushing's syndromeEctopic Cushing syndrome is a form of Cushing syndrome in which a tumor outside the pituitary gland produces a hormone called adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
Cushing syndrome
Cushing syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body has a high level of the hormone cortisol.

Causes
Cushing syndrome is a disorder that occurs when your body has a higher than normal level of the hormone cortisol. This hormone is made in the adrenal glands. Too much cortisol can be due to various problems. One of the causes is if there is too much of the hormone ACTH in the blood. ACTH is usually made by the pituitary in small amounts and then signals the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. Sometimes other cells outside the pituitary can make large amounts of ACTH. This is called ectopic Cushing syndrome. Ectopic means that something is occurring in an abnormal place in the body.
Adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are two small triangle-shaped glands in the upper abdomen. One gland is located on top of each kidney.

Ectopic Cushing syndrome is caused by tumors that release ACTH. Tumors that can, in rare cases, release ACTH include:
Tumors
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article- Benign carcinoid tumors of the lung
-
Islet cell tumors of the pancreas
Islet cell tumors
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NET) are rare tumors of the pancreas that start from a type of cell called the islet cell.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is cancer of the thyroid gland that starts in cells that release a hormone called calcitonin. These cells are cal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Small cell tumors of the lung
Small cell tumors of the lung
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It spreads much more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two typ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors of the thymus gland
Symptoms
Ectopic Cushing syndrome can cause a lot of different symptoms. Some people have many symptoms while others have only a few. Most people with any type of Cushing syndrome have:
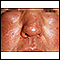
- Round, red, and full face (moon face)
Moon face
Facial swelling is the buildup of fluid in the tissues of the face. Swelling may also affect the neck and upper arms.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Slow growth rate in children
- Weight gain with fat accumulation on the trunk, but fat loss from the arms, legs, and buttocks (central obesity)
Skin changes that are often seen:
- Skin infections
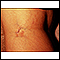
- Thick, purple stretch marks (1/2 inch or 1 centimeter or more wide) called striae on the skin of the abdomen, thighs, upper arms, and breasts
Striae
Stretch marks are irregular areas of skin that look like bands, stripes, or lines. Stretch marks are seen when a person grows or gains weight rapidl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thin skin with easy bruising
Muscle and bone changes include:
- Backache, which occurs with routine activities
- Bone pain or tenderness
- Collection of fat between the shoulders and above the collar bone
- Rib and spine fractures caused by thinning of the bones
Thinning of the bones
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weak muscles, especially of the hips and shoulders
Body-wide (systemic) problems may include:
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol and triglycerides
Women may have:
- Excess hair growth on the face, neck, chest, abdomen, and thighs
- Periods that become irregular or stop
Men may have:
- Decreased or no desire for sex
-
Impotence
Impotence
An erection problem occurs when a man cannot get or keep an erection that is firm enough for intercourse. You may not be able to get an erection at ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms that may occur include:
-
Mental changes, such as depression, anxiety, or changes in behavior
Depression
Depression may be described as feeling sad, blue, unhappy, miserable, or down in the dumps. Most of us feel this way at one time or another for shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
- Increased thirst and urination
Thirst
Excessive thirst is an abnormal feeling of always needing to drink fluids.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUrination
Excessive amount of urination means that your body makes larger than normal amounts of urine each day.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Tests that may be done include:
- 24-hour urine sample to measure cortisol and creatinine levels
Cortisol
The cortisol urine test measures the level of cortisol in the urine. Cortisol is a glucocorticoid (steroid) hormone produced by the adrenal gland. C...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCreatinine
The creatinine urine test measures the amount of creatinine in urine. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests to check ACTH, cortisol, and potassium levels (the potassium level is often very low in ectopic Cushing syndrome)
Cortisol
The cortisol blood test measures the level of cortisol in the blood. Cortisol is a steroid (glucocorticoid or corticosteroid) hormone produced by th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePotassium
This test measures the amount of potassium in the fluid portion (serum) of the blood. Potassium (K+) helps nerves and muscles communicate. It also ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dexamethasone suppression test (both high and low dose)
Dexamethasone suppression test
The dexamethasone suppression test measures whether cortisol secretion by the adrenal gland can be suppressed. It can also help assess the reason fo...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Inferior petrosal sinus sampling (a special test that measures ACTH from veins near the brain and in the chest)
-
Fasting glucose
Fasting glucose
A blood sugar test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in a sample of your blood. Glucose is a major source of energy for most cells of the body, ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI and high resolution CT scans to find the tumor (sometimes nuclear medicine scans may be needed)
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
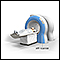 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scans
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The best treatment for ectopic Cushing syndrome is surgery to remove the tumor that is producing too much ACTH. Surgery is usually possible when the tumor is noncancerous (benign).
Benign
Benign refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. It does not in...
In some cases, the tumor is cancerous and spreads to other areas of the body before your provider can discover the problem with cortisol production. Surgery may not be possible in these cases. But your provider may prescribe medicines to block cortisol production.
Sometimes removal of both adrenal glands is needed if the tumor cannot be found and medicines do not fully block cortisol production.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Surgery to remove the tumor may lead to full recovery. But there is a chance that the tumor will come back.
Possible Complications
The tumor may spread or return after surgery. A high cortisol level may continue.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop symptoms of Cushing syndrome.
Prevention
Prompt treatment of tumors may reduce the risk in some cases. Many cases are not preventable.
References
Newell-Price JDC, Auchus RJ. The adrenal cortex. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, et al. Treatment of Cushing's syndrome: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(8):2807-2831. PMID 26222757 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26222757/.
-
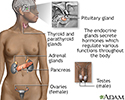
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
Review Date: 5/12/2023
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.