Hypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is a disorder in which the parathyroid glands in the neck do not produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH).
Causes
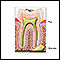
There are 4 tiny parathyroid glands in the neck, located near or attached to the back side of the thyroid gland.
The parathyroid glands help regulate calcium absorption, use, and removal by the body. They do this by producing PTH. PTH helps control calcium, phosphorus, and vitamin D levels in the blood and bone. It is important for healthy bones.
Hypoparathyroidism occurs when the glands produce too little PTH. The blood calcium level falls, and the phosphorus level rises.
The most common cause of hypoparathyroidism is injury to the parathyroid glands during thyroid or neck surgery. It may also be caused by any of the following:
- Autoimmune attack on the parathyroid glands (common)
Autoimmune
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Very low magnesium level in the blood (reversible)
- Radioactive iodine treatment for hyperthyroidism (very rare)
DiGeorge syndrome is a disease in which hypoparathyroidism occurs because all the parathyroid glands are missing at birth. This disease includes other health problems besides hypoparathyroidism. It is usually diagnosed in childhood.
Familial hypoparathyroidism occurs with other endocrine diseases such as adrenal insufficiency in a syndrome called type I polyglandular autoimmune syndrome (PGA I).
Symptoms
Onset of the disease is very gradual and symptoms can be mild. Many people diagnosed with hypoparathyroidism have had symptoms for years before they are diagnosed. Symptoms may be so mild that the diagnosis is made after a screening blood test that shows low calcium.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Tingling lips, fingers, and toes (most common)
Tingling
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle cramps (most common)
- Muscle spasms called tetany (can affect the larynx, causing breathing difficulties)
- Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abnormal heart rhythm
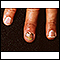
- Brittle nails
Brittle nails
Nail abnormalities are problems with the color, shape, texture, or thickness of the fingernails or toenails.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cataracts
- Calcium deposits in some tissues
- Decreased consciousness
- Dry hair
- Dry, scaly skin
- Pain in the face, legs, and feet
Pain in the face
Face pain may be dull and throbbing or an intense, stabbing discomfort in the face or forehead. It can occur in one or both sides.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Painful menstruation
- Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Teeth that do not grow in on time, or at all
- Weakened tooth enamel (in children)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will do a physical exam and ask about symptoms.
Tests that will be done include:
- PTH blood test
PTH blood test
The PTH test measures the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood. PTH stands for parathyroid hormone. It is a protein hormone released by the par...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Calcium blood test
Calcium blood test
The calcium blood test measures the level of calcium in the blood. This article discusses the test to measure the total amount of calcium in your blo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Magnesium
Magnesium
A serum magnesium test measures the level of magnesium in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - 24-hour urine calcium test
24-hour urine calcium test
The urine 24-hour volume test measures the amount of urine produced in a day. The amounts of creatinine, protein, and other chemicals released into ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests that may be ordered include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check for an abnormal heart rhythm
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
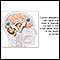
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Computed tomography (CT) scan to check for calcium deposits in the brain
Computed tomography (CT) scan
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and restore the calcium and mineral balance in the body.
Treatment involves calcium carbonate and vitamin D supplements. These usually must be taken for life. Blood levels are measured regularly to make sure that the dose is correct. A high-calcium, low-phosphorous diet is recommended.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins are stored in the body's fatty tissue and liver.
Injections of PTH may be recommended for some people. Your provider can tell you if this medicine is right for you.
People who have life-threatening attacks of low calcium levels or prolonged muscle contractions are given calcium through a vein (IV). Precautions are taken to prevent seizures or larynx spasms. Your heart is monitored for abnormal rhythms until you are stable. When the life-threatening attack has been controlled, treatment continues with medicine taken by mouth.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is likely to be good if the diagnosis is made early. But changes in the teeth, cataracts, and brain calcifications cannot be reversed in children who have undiagnosed hypoparathyroidism during development.
Calcifications
Calcification is a process in which calcium builds up in body tissue, causing the tissue to harden. This can be a normal or abnormal process....
Possible Complications
Hypoparathyroidism in children may lead to poor growth, abnormal teeth, and slow mental development.
Too much treatment with vitamin D and calcium can cause high blood calcium (hypercalcemia) or high urine calcium (hypercalciuria). Excess treatment may sometimes interfere with kidney function, or even cause kidney failure.
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia means you have too much calcium in your blood.

Hypoparathyroidism increases the risk for:
- Addison disease (only if the cause is autoimmune)
Addison disease
Addison disease is a disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cataracts
- Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease results from certain brain cells dying. These cells help control movement and coordination. The disease leads to shaking (tremors...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pernicious anemia (only if the cause is autoimmune)
Pernicious anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop any symptoms of hypoparathyroidism.
Seizures or breathing problems are an emergency. Call 911 or the local emergency number right away.
Reviewed By
Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Husebye E, Weetman AP. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 132.
Reid LM, Kamani D, Randolph GW. Management of parathyroid disorders. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 123.
Thakker RV. The parathyroid glands, hypercalcemia, and hypocalcemia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 227.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.