Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
Pseudotumor cerebri syndrome; Benign intracranial hypertensionIdiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a condition in which the pressure inside the skull is increased. The brain is affected in a way that the condition appears to be, but is not, a tumor.
Causes
The condition occurs more often in women than men, especially in young obese women 20 to 40 years old. It is rare in infants, but can occur in children. Before puberty, it occurs equally in boys and girls.
The cause is unknown.
Certain medicines can increase the risk of developing this condition. These medicines include:
- Amiodarone
- Birth control pills such as levonorgestrel (Norplant)
- Cyclosporine
- Cytarabine
- Growth hormone
- Isotretinoin
- Levothyroxine (children)
- Lithium carbonate
- Minocycline
- Nalidixic acid
- Nitrofurantoin
- Phenytoin
- Steroids (starting or stopping them)
- Sulfa antibiotics
- Tamoxifen
- Tetracycline
- Certain drugs that contain Vitamin A, such as cis-retinoic acid (Accutane)
The following factors are also related to this condition:
- Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which a person has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Behcet disease
- Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney failure
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endocrine (hormone) disorders such as Addison disease, Cushing disease, hypoparathyroidism, polycystic ovary syndrome
Addison disease
Addison disease is a disorder that causes the adrenal glands to not produce enough hormones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCushing disease
Cushing disease is a condition in which the pituitary gland releases too much adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). The pituitary gland is an organ of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHypoparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism is a disorder in which the parathyroid glands in the neck do not produce enough parathyroid hormone (PTH).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePolycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which a woman has increased levels of male hormones (androgens). Many problems occur as a result ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Following treatment (embolization) of an arteriovenous malformation
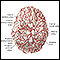
Arteriovenous malformation
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infectious diseases such as HIV/AIDS, Lyme disease, following chickenpox in children
- Iron deficiency anemia
- Obesity
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Pregnancy
- Sarcoidosis (a disease that causes inflammation of the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, or other tissues)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome
Turner syndrome is a rare genetic condition in which a female does not have the usual pair of X chromosomes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Headaches, throbbing, daily, irregular and worse in the morning
- Neck pain
- Blurred vision
- Buzzing sound in the ears (tinnitus)
- Dizziness
- Double vision (diplopia)
Double vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea, vomiting
- Vision problems such as flashing lights or even loss of vision
- Low back pain, radiating along both legs
Headaches may get worse during physical activity, especially when you tighten the stomach muscles during coughing or straining.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. Signs of this condition include:
- Bulging anterior fontanelle in infants
Bulging anterior fontanelle
A bulging fontanelle is an outward curving of an infant's soft spot (fontanelle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased head size in infants
- Swelling of the optic nerve in the back of the eye (papilledema)
- Vision problems including loss of peripheral vision
- Inward turning of the eye toward the nose (sixth cranial, or abducens, nerve palsy)
Even though there is increased pressure in the skull, there is no change in alertness.
Tests that may be done include:
- Funduscopic examination of the eyes
- CT scan of the head
CT scan of the head
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eye exam, including visual field testing
Visual field
The visual field refers to the total area in which objects can be seen in the side (peripheral) vision as you focus your eyes on a central point. Thi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI of the head with MR venography
MRI of the head
A head MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the brain and surrounding...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The diagnosis is made when other health conditions are ruled out. These include conditions that may cause increased pressure in the skull, such as:
- Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumor
- Venous sinus thrombosis
- Infection
Treatment
Treatment is aimed at the cause of IIH. The main goal of treatments is to preserve vision and reduce the severity of headaches.
A lumbar puncture (spinal tap) can help relieve pressure in the brain and prevent vision problems. Repeat lumbar punctures are helpful for pregnant women in order to delay surgery until after delivery.
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Other treatments may include:
- Fluid or salt restriction
- Medicines such as corticosteroids, acetazolamide, furosemide, and topiramate
- Shunting procedures to relieve pressure from spinal fluid buildup
- Surgery to relieve pressure on the optic nerve
- Weight loss
- Treatment of the underlying disease, such as vitamin A overdose
People will need to have their vision closely monitored. There can be vision loss, which is sometimes permanent. Follow-up MRI or CT scans may be done to rule out problems such as tumors or hydrocephalus (buildup of fluid inside the skull).
In some cases, the pressure inside the brain remains high for many years. Symptoms can return in some people. A small number of people have symptoms that slowly get worse and lead to blindness.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The condition sometimes disappears on its own within 6 months. Symptoms can return in some people. A small number of people have symptoms that slowly get worse and lead to blindness.
Possible Complications
Vision loss is a serious complication of this condition.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child has any of the symptoms listed above.
References
Alrobaian M, Miller NR. Pseudotumor cerebri. In: Winn HR, ed. Youmans and Winn Neurological Surgery. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 189.
Rosenberg GA. Brain edema and disorders of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 88.
Safier RA, Cleves-Bayon C, Gaesser J. Neurology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2023:chap 16.
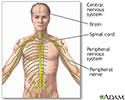
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.