Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis
Thyrotoxic periodic paralysis (TPP) is a condition with episodes of severe muscle weakness. It occurs in people who have high levels of thyroid hormone in their blood. Examples of this include hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis.
Muscle weakness
Weakness is reduced strength in one or more muscles.
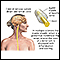
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.

Causes
This rare condition occurs only in people with high (usually very high) thyroid hormone levels (thyrotoxicosis). Men of Asian or Hispanic descent are affected more often. Most people who develop high thyroid hormone levels are not at risk of periodic paralysis.
Hypokalemic, or familial, periodic paralysis is a similar disorder. It is an inherited condition and not related to high thyroid levels, but has the same symptoms.
Hypokalemic
Hypokalemic periodic paralysis (hypoPP) is a disorder that causes occasional episodes of muscle weakness and sometimes a lower than normal level of p...
Risk factors include a family history of periodic paralysis and hyperthyroidism.
Symptoms
Symptoms involve attacks of muscle weakness or paralysis. Between attacks, normal muscle function returns. Attacks often begin after symptoms of hyperthyroidism have developed. Hyperthyroid symptoms may be subtle.
Paralysis
Muscle function loss is when a muscle does not work or move normally. The medical term for complete loss of muscle function is paralysis.
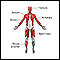
The attacks may occur daily to yearly. Episodes of muscle weakness or paralysis may:
- Come and go
- Last from a few hours up to several days (rare)
- Occur more often in the legs than the arms
- Be most common in the shoulders and hips
- Be triggered by heavy, high-carbohydrate, high-salt meals
- Be triggered during rest after exercise
Other rare symptoms may include any of the following:
- Trouble breathing
Trouble breathing
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Speech problems
- Trouble swallowing
- Vision changes
During attacks, you will be alert and can answer questions. Normal strength returns between attacks. With repeated attacks, you may develop muscle weakness.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include:
- Excessive sweating
- Fast heart rate
- Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heat intolerance
Heat intolerance
Heat intolerance is a feeling of being overheated when the temperature around you rises. It can often cause heavy sweating. Heat intolerance usually...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased appetite
- Insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is trouble falling asleep, staying asleep (usually through the night), or waking up too early in the morning. Episodes of insomnia may come ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Having bowel movements more often
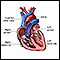
- Feeling strong heartbeat (palpitations)
Palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
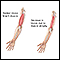
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tremors of the hand
Tremors
A tremor is a type of shaking movement. A tremor is most often noticed in the hands and arms. It may affect any body part, including the head, tong...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Warm, moist skin
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may suspect TPP based on:
-
Abnormal thyroid hormone levels
Thyroid hormone
Thyroid function tests are used to check whether your thyroid is working normally. The most common thyroid function tests are:Free T4 (free thyroxine...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A family history of the disorder
- Low blood potassium level during attacks
- Symptoms that come and go
Diagnosis involves ruling out disorders caused by low blood potassium.
Your provider may try to trigger an attack by giving you insulin and sugar. The sugar is glucose, which reduces your potassium level. Or you may be given thyroid hormone.
The following signs may be seen during the attack:
- Decreased or no reflexes
- Abnormal heartbeat (arrhythmia)
Abnormal heartbeat
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low potassium in the blood (potassium levels are normal between attacks)
Low potassium
This test measures the amount of potassium in the fluid portion (serum) of the blood. Potassium (K+) helps nerves and muscles communicate. It also ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Between attacks, the examination is normal. Or, there may be signs of hyperthyroidism. These include an enlarged thyroid, changes in the eyes, tremors, or hair and nail changes.
The following tests are used to diagnose hyperthyroidism:
- High thyroid hormone levels (T3 or T4)
T3
Triiodothyronine (T3) is a thyroid hormone. It plays an important role in the body's control of metabolism (the many processes that control the rate...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleT4
T4 (thyroxine) is the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A laboratory test can be done to measure the amount of free T4 in your blood. Fre...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low serum TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) levels
TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) level
A TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland. It prompts the thyroid g...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
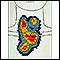
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid uptake and scan
Thyroid uptake and scan
A thyroid scan uses a radioactive iodine tracer to examine the structure and function of the thyroid gland. This test is often done together with a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other test results:
- Abnormal electrocardiogram (ECG) during attacks
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abnormal electromyogram (EMG) during attacks
Electromyogram
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
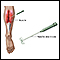 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low serum potassium during attacks, but normal between attacks
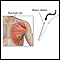
A muscle biopsy may sometimes be taken.
Muscle biopsy
A muscle biopsy is the removal of a small piece of muscle tissue for examination.
Treatment
Potassium should be given during the attack, most often by mouth. If weakness is severe, you may need to get potassium through a vein (IV).
IV
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleNote: You should only get IV potassium if your kidney function is normal and you are monitored in the hospital.
Weakness that involves the muscles used for breathing or swallowing is an emergency. People must be taken to a hospital. Serious irregularity of the heartbeat also occurs during attacks.
Irregularity of the heartbeat
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

Your provider may recommend a diet low in carbohydrates and salt to prevent attacks. You may be given beta-blocker medicines to reduce the number and severity of attacks while your hyperthyroidism is brought under control.
Acetazolamide is effective at preventing attacks in people with familial periodic paralysis. It is usually not effective for TPP.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If an attack isn't treated and the breathing muscles are affected, death can occur.
Chronic attacks over time can lead to muscle weakness. This weakness can continue even between attacks if the thyrotoxicosis is not treated.
TPP responds well to treatment. Treating hyperthyroidism will prevent attacks. It may even reverse muscle weakness.
Possible Complications
Untreated TPP can lead to:
- Difficulty breathing, speaking, or swallowing during attacks (rare)
- Heart arrhythmias during attacks
- Muscle weakness that gets worse over time
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call 911 or the local emergency number or go to the emergency room if you have periods of muscle weakness. This is especially important if you have a family history of periodic paralysis or thyroid disorders.
Emergency symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing, speaking, or swallowing
- Falls due to muscle weakness
Prevention
Genetic counseling may be advised. Treating the thyroid disorder prevents attacks of weakness.
Reviewed By
Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Hollenberg A, Wiersinga WM. Hyperthyroid disorders. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 12.
Kang MK, Kerchner GA, Ptacek LJ. Channelopathies: Episodic and electrical disorders of the nervous system. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 98.
Selcen D. Muscle diseases. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 389.
Weetman AP, Kahaly GJ. Graves disease. In: Robertson RP, ed. DeGroot's Endocrinology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 71.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.