Irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder that leads to pain in abdomen and changes in bowel movements.
IBS is not the same as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
Irritable bowel syndrome - Animation
Are your off again, on again, bathroom habits affecting your daily life? If so, you may have Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS. IBS is a problem that causes abdominal pain, cramping, and changes in your bowel movements. IBS is known as a functional bowel disorder, and is not considered a disease. What I mean by that, is when a doctor passes a colonoscope into the colon to look around, everything may look perfectly normal - but yet, Your colon may not be not be acting normal at all! Symptoms of IBS can range from mild to severe. The main symptoms are diarrhea, constipation, or both. And you will probably experience abdominal pain, bloating, and gas. These symptoms often will temporarily improve after having a bowel movement, and that instant relief of course feels good. But, the important thing to understand is that the root of the problem often isn't here (abdomen), its here (head). IBS is a classic example of your mind affecting your bowels. It's rarely seen in folks who are not stressed, anxious, or depressed. It's often hard to determine why people get IBS. It has been found that IBS is twice as common in women as it is in men, and can develop at any age, but most get it as teenagers or in early adulthood. Diet can also cause IBS. Foods that often cause IBS symptoms are Fatty foods, such as French fries, or any drink containing caffeine like coffee and tea. One great idea is to keep a Food Diary. Write down what you're eating and when, and include the symptoms you experience after you eat. This information can be helpful to your doctor in identifying if you have IBS. The way most doctors diagnose IBS is by gathering your history and ruling out other things like lactose intolerance, gluten intolerance or some sort of bowel infection. Your doctor might recommend a colonoscopy just to make sure the colon looks okay. But remember, there is no specific test to diagnose IBS. So, how do you manage IBS? For some people, symptoms can reduce their ability to work, travel, and attend social events, and some may have to deal with IBS the rest of their life. There are several ways to manage your IBS. Large meals can make your symptoms worse. Try eating 4 to 5 smaller meals per day. Extra Fiber can bulk up your stools to help with diarrhea or help draw in extra water to help with constipation. Laxatives can help with difficult constipation. Drugs like Hyoscyamine help to calm down an overactive digestive tract. Lastly, since stress, depression and anxiety can fuel IBS, work on ways to relax. Perhaps, try exercise, meditation or yoga - and if that doesn't work, consider trying an antidepressant drug to help improve your mood. Oh, and keep in mind that blood in your stool or significant weight loss are not part of IBS, so be sure to let your doctor know if that ever shows up. Remember that the mind and the body are interconnected. You can't expect to feel good here (head), without feeling good down here (abdomen), and vice versa.
Causes
The reasons why IBS develops are not clear. It can occur after a bacterial infection or a parasitic infection (giardiasis) of the intestines. This is called postinfectious IBS. There may also be other triggers, including stress.
The intestine is connected to the brain by hormone and nerve signals that go back and forth between the bowel and the brain. These signals affect bowel function and symptoms. The nerves can become more active during stress. This can cause the intestines to be more sensitive and contract more.
IBS can occur at any age. Often, it begins in the teen years or early adulthood. It is twice as common in women as in men.
It is less likely to begin in people above 50 years of age.
About 10% to 15% of people in the United States have symptoms of IBS. It is the most common intestinal problem that causes people to be referred to a bowel specialist (gastroenterologist).
Symptoms
IBS symptoms vary from person to person, and range from mild to severe. Most people have mild symptoms. You are said to have IBS when symptoms are present for at least 3 days a month for a period of 3 months or more.
The main symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Gas
- Fullness
- Bloating
- Change in bowel habits. You can have either diarrhea (IBS-D), or constipation (IBS-C).
Pain and other symptoms will often be reduced or go away after a bowel movement. Symptoms may flare up when there is a change in the frequency of your bowel movements.
People with IBS may go back and forth between having constipation and diarrhea or have or mostly have one or the other.
- If you have IBS with diarrhea, you will have frequent, loose, watery stools. You may have an urgent need to have a bowel movement, which may be hard to control.
- If you have IBS with constipation, you will have a hard time passing stool, as well as fewer bowel movements. You may need to strain with a bowel movement and have cramps. Often, only a small amount or no stool at all will pass.
The symptoms may get worse for a few weeks or a month, and then decrease for a while. In other cases, symptoms are present most of the time.
You may also lose your appetite if you have IBS. However, blood in stools and unintentional weight loss are not a part of IBS.
Exams and Tests
There is no test to diagnose IBS. Most of the time, your health care provider can diagnose IBS based on your symptoms. Eating a lactose-free diet for 2 weeks may help the provider identify lactase deficiency (or lactose intolerance).
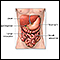
Lactase deficiency
Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and other dairy products. An enzyme called lactase is needed by the body to digest lactose. Lactose intoler...
The following tests may be done to rule out other problems:
- Blood tests to see if you have celiac disease or a low blood count (anemia)
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stool exam for occult blood (blood that is not visible)
- Stool cultures to check for an infection
- Microscopic exam of a stool sample for parasites
- Stool exam for a substance called fecal calprotectin
Your provider may recommend a colonoscopy. During this test, a flexible tube is inserted through the anus to examine the colon. You may need this test if:
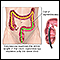
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
- Symptoms began later in life (age 50 or over)
- You have symptoms such as weight loss or bloody stools
- You have abnormal blood tests (such as a low blood count)
Other disorders that can cause similar symptoms include:
- Celiac disease
- Colon cancer (cancer rarely causes typical IBS symptoms, unless symptoms such as weight loss, blood in the stools, or abnormal blood tests are also present)
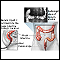
Colon cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). It is also sometimes simply called colon ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUlcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms.
In some cases of IBS, lifestyle changes can help. For example, regular exercise and improved sleep habits may reduce anxiety and help relieve bowel symptoms.
Lifestyle changes
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder that leads to abdominal pain and bowel changes. Your health care provider will talk about things you ca...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleDietary changes can be helpful. However, no specific diet can be recommended for IBS because the condition differs from one person to another.
The following changes may help:
- Avoiding foods and drinks that stimulate the intestines (such as caffeine-containing drinks, tea, or colas)
- Eating smaller meals
- Increasing fiber in the diet (this may improve constipation or diarrhea, but make bloating worse)
Talk with your provider before taking over-the-counter medicines.
No one medicine works for everyone. Some that your provider may suggest include:
- Anticholinergic medicines (dicyclomine, propantheline, belladonna, and hyoscyamine) taken about a half-hour before eating to control intestinal muscle spasms
- Loperamide to treat IBS-D
- Alosetron (Lotronex) for IBS-D
- Eluxadoline (Viberzi) for IBS-D
- Probiotics
- Low doses of tricyclic antidepressants to help relieve intestinal pain
- Lubiprostone (Amitiza) for IBS-C
- Bisacodyl to treat IBS-C
- Rifaximin, an antibiotic
- Linaclotide (Linzess) for IBS-C
Psychological therapy or medicines for anxiety or depression may help with the problem.
Outlook (Prognosis)
IBS may be a life-long condition. For some people, symptoms are disabling and interfere with work, travel, and social activities.
Symptoms often get better with treatment.
IBS does not cause permanent harm to the intestines. Also, it does not lead to a serious disease, such as cancer.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of IBS or if you notice changes in your bowel habits that do not go away.
Reviewed By
Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Aronson JK. Laxatives. In: Aronson JK, ed. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs. 16th ed. Waltham, MA: Elsevier; 2016:488-494.
Canavan C, West J, Card T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:71-80. PMID: 24523597 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24523597/.
Charles MB. Common clinical manifestations of gastrointestinal disease: abdominal pain. In: Wing EJ, Schiffman FJ, eds. Cecil Essentials of Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 31.
Ferri FF. Irritable bowel syndrome. In: Ferri FF, ed. Ferri's Clinical Advisor 2023. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:875-877.
Ford AC, Talley NJ. Irritable bowel syndrome. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 122.
Mayer EA. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: irritable bowel syndrome, dyspepsia, chest pain of presumed esophageal origin, and heartburn. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 128.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.