Jaundice
Conditions associated with jaundice; Yellow skin and eyes; Skin - yellow; Icterus; Eyes - yellow; Yellow jaundiceJaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jaundice can be a symptom of several health problems.
Causes
A small number of red blood cells in your body die each day, and are replaced by new ones. The liver removes the old blood cells. This creates bilirubin. The liver helps break down bilirubin so that it can be removed by the body through the stool.
Jaundice can occur when too much bilirubin builds up in the body.
Jaundice can occur if:
- Too many red blood cells are dying or breaking down and going to the liver.
- The liver is overloaded or damaged.
- The bilirubin from the liver is unable to move normally into the digestive tract.
Jaundice is often a sign of a problem with the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas. Things that can cause jaundice include:
Cause jaundice
Jaundice is a yellow color in the skin, mucous membranes, or eyes. The yellow color comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of your body processing old re...
- Infections, most commonly viral
- Use of certain drugs
- Cancer of the liver, bile ducts or pancreas
- Blood disorders, gallstones, birth defects and a number of other medical conditions
Symptoms
Jaundice may appear suddenly or develop slowly over time. Symptoms of jaundice commonly include:
- Yellow skin and the white part of the eyes (sclera) -- when jaundice is more severe, these areas may look brown
- Yellow color inside the mouth
- Dark or brown-colored urine
- Pale or clay-colored stools
- Itching (pruritis) usually occurs with jaundice
Note: If your skin is yellow and the whites of your eyes are not yellow, you may not have jaundice. Your skin can turn a yellow-to-orange color if you eat a lot of beta carotene, the orange pigment in carrots.
Other symptoms depend on the disorder causing the jaundice:
- Cancers may produce no symptoms, or there may be fatigue, weight loss, or other symptoms.
- Hepatitis may produce nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or other symptoms.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may show liver swelling.
A bilirubin blood test will be done. Other tests may include:
Bilirubin blood test
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...

- Hepatitis virus panel to look for infection of the liver
Hepatitis virus panel
The hepatitis virus panel is a series of blood tests used to detect current or past infection by hepatitis A, hepatitis B, or hepatitis C. It can sc...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver function tests to determine how well the liver is working
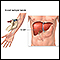
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count to check for low blood count or anemia
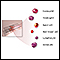
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal ultrasound
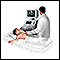
Abdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal CT scan
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
-
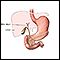
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
ERCP
ERCP is short for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. It is a procedure that looks at the bile and pancreatic ducts. It is done through...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
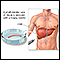
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTCA)
PTCA
A percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram (PTC) is an x-ray of the bile ducts. These are the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver biopsy
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cholesterol level
- Prothrombin time
Prothrombin time
Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot. It measures the functio...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the jaundice.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you develop jaundice.
References
Fargo MV, Grogan SP, Saquil A. Evaluation of jaundice in adults. Am Fam Physician. 2017;95(3):164-168. PMID: 28145671 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28145671/.
Korenblat KM, Berk PD. Approach to the patient with jaundice or abnormal liver tests. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 138.
Lidofsky SD. Jaundice. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
Zdradzinski MJ, Taylor TA. Jaundice. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.
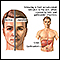
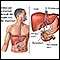
Jaundice - illustration
Jaundice is a condition produced when excess amounts of bilirubin circulating in the blood stream dissolve in the subcutaneous fat (the layer of fat just beneath the skin), causing a yellowish appearance of the skin and the whites of the eyes. With the exception of normal newborn jaundice in the first week of life, all other jaundice indicates overload or damage to the liver, or inability to move bilirubin from the liver through the biliary tract to the gut.
Jaundice
illustration
Jaundiced infant - illustration
Newborn jaundice (producing yellow skin) can have many causes, but the majority of these infants have a condition called physiological jaundice, a natural occurrence in the newborn due to the immature liver. This type of jaundice is short term, generally lasting only a few days. Jaundice should be evaluated by a physician until decreasing or normal levels of bilirubin are measured in the blood.
Jaundiced infant
illustration
Cirrhosis of the liver - illustration
A chronic liver disease which causes damage to liver tissue, scarring of the liver (fibrosis; nodular regeneration), progressive decrease in liver function, excessive fluid in the abdomen (ascites), bleeding disorders (coagulopathy), increased pressure in the blood vessels (portal hypertension), and brain function disorders (hepatic encephalopathy). Excessive alcohol use is the leading cause of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
illustration
Bili lights - illustration
Using bili lights is a therapeutic procedure performed on newborn or premature infants to reduce elevated levels of bilirubin. If blood levels of bilirubin become too high, the bilirubin begins to dissolve in the body tissues, producing the characteristic yellow eyes and skin of jaundice. Bilirubin also has an affinity for brain tissue, where it can accumulate and cause permanent brain damage.
Bili lights
illustration
Jaundice - illustration
Jaundice is a condition produced when excess amounts of bilirubin circulating in the blood stream dissolve in the subcutaneous fat (the layer of fat just beneath the skin), causing a yellowish appearance of the skin and the whites of the eyes. With the exception of normal newborn jaundice in the first week of life, all other jaundice indicates overload or damage to the liver, or inability to move bilirubin from the liver through the biliary tract to the gut.
Jaundice
illustration
Jaundiced infant - illustration
Newborn jaundice (producing yellow skin) can have many causes, but the majority of these infants have a condition called physiological jaundice, a natural occurrence in the newborn due to the immature liver. This type of jaundice is short term, generally lasting only a few days. Jaundice should be evaluated by a physician until decreasing or normal levels of bilirubin are measured in the blood.
Jaundiced infant
illustration
Cirrhosis of the liver - illustration
A chronic liver disease which causes damage to liver tissue, scarring of the liver (fibrosis; nodular regeneration), progressive decrease in liver function, excessive fluid in the abdomen (ascites), bleeding disorders (coagulopathy), increased pressure in the blood vessels (portal hypertension), and brain function disorders (hepatic encephalopathy). Excessive alcohol use is the leading cause of cirrhosis.
Cirrhosis of the liver
illustration
Bili lights - illustration
Using bili lights is a therapeutic procedure performed on newborn or premature infants to reduce elevated levels of bilirubin. If blood levels of bilirubin become too high, the bilirubin begins to dissolve in the body tissues, producing the characteristic yellow eyes and skin of jaundice. Bilirubin also has an affinity for brain tissue, where it can accumulate and cause permanent brain damage.
Bili lights
illustration
Review Date: 5/2/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.





