Multifocal atrial tachycardia
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is a rapid heart rate. It occurs when too many signals (electrical impulses) are sent from the upper heart (atria) to the lower heart (ventricles).
Rapid heart rate
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.

Causes
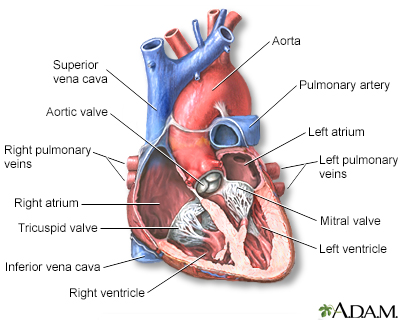
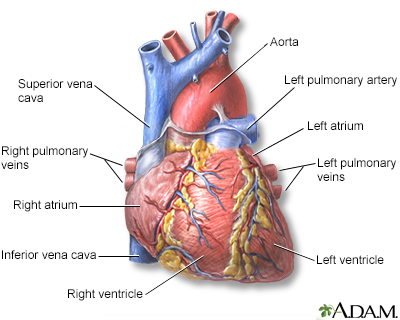
The human heart gives off electrical impulses, or signals, which tell it to beat. Normally, these signals begin in an area of the upper right chamber called the sinoatrial node (sinus node or SA node). This node is considered the heart's "natural pacemaker." It helps control the heartbeat. When the heart detects a signal, it contracts (or beats).
What makes your heart beat? - Animation
Let’s take a closer look inside the heart. The yellow objects are not nerves. They’re actually specialized cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the heart. Their job is to send signals to the rest of the heart muscle and cause a contraction. Together, this group of cells is called the Cardiac conduction system. The main components of the Cardiac conduction system are the SA node, AV node, Bundle of His, Bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers. Let’s follow a signal through the contraction process. The SA node starts the sequence by causing the atrial muscles to contract. That’s why doctors sometimes call it the anatomical pacemaker. From there, the signal travels to the AV node, through the Bundle of His, down the Bundle branches, and through the Purkinje fibers, causing the ventricles to contract. This signal creates an electrical current that can be seen on a graph called an Electrocardiogram, or EKG. Doctors us an EKG as a way of seeing how well the Cardiac conduction system works. Any changes to the EKG can mean serious problems.
The normal heart rate in adults is 60 to 100 beats per minute. The normal heart rate is faster in children.

Conduction system of the heart
The intrinsic conduction system sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart by generating impulses which stimulate the heart to contract.
In MAT, many locations in the atria fire signals at the same time. Too many signals lead to a rapid heart rate. It most often ranges from 100 to 130 beats per minute or more in adults. The rapid heart rate may cause the heart to work too hard and not move blood efficiently. If the heartbeat is very fast, there is less time for the heart chamber to fill with blood between beats. Therefore, not enough blood is pumped to the brain and the rest of the body with each contraction.
MAT is most common in people age 50 and over. It is often seen in people with conditions that lower the amount of oxygen in the blood. These conditions include:
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart failure (also called congestive heart failure)
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung cancer
Lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It spreads much more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two typ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung failure
- Pneumonia
- Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may be at higher risk for MAT if you have:
- Coronary heart disease
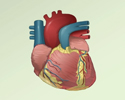
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Had surgery within the last 6 weeks
- Overdosed on the drug theophylline
- Sepsis
When the heart rate is less than 100 beats per minute, the arrhythmia is called "wandering atrial pacemaker."
Symptoms
Some people may have no symptoms. When symptoms occur, they can include:
- Chest tightness
- Fainting
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Lightheadedness
Lightheadedness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sensation of feeling the heart is beating irregularly or too fast (palpitations)
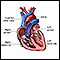
Palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight loss and failure to thrive in infants
Failure to thrive
Failure to thrive refers to children whose current weight or rate of weight gain is much lower than that of other children of similar age and sex....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms that can occur with this disease:
- Breathing difficulty when lying down
Breathing difficulty when lying down
Breathing difficulty while lying down is an abnormal condition in which a person has a problem breathing normally when lying flat. The head must be ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dizziness
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A physical exam shows a fast irregular heartbeat of over 100 beats per minute. Blood pressure is normal or low. There may be signs of poor circulation.
Tests to diagnose MAT include:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electrophysiologic study (EPS)
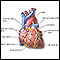
Electrophysiologic study
Intracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS) is a test to look at how well the heart's electrical signals are working. It is used to evaluate abnormal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Heart monitors may be used to record the rapid heartbeat. These include:
- 24-hour Holter monitor
Holter monitor
A Holter monitor is a machine that continuously records the heart's rhythms. The monitor is worn for 24 to 48 hours during normal activity.
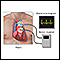 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Portable, long-term loop recorders that allow you to start recording if symptoms occur
If you are in the hospital, your heart rhythm will be monitored 24 hours a day, at least at first.
Treatment
If you have a condition that can lead to MAT, that condition should be treated first.
Treatment for MAT includes:
- Improving blood oxygen levels
- Giving magnesium or potassium through a vein
- Stopping medicines, such as theophylline, which can increase heart rate
- Taking medicines to slow the heart rate (if the heart rate is too fast), such as calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) or beta-blockers
Outlook (Prognosis)
MAT can be controlled if the condition that causes the rapid heartbeat is treated and controlled.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is disease in which the heart muscle becomes weakened, stretched, or has another structural problem. It often contributes to the hear...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart failure
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Reduced pumping action of the heart
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if:
- You have a rapid or irregular heartbeat with other MAT symptoms
Irregular heartbeat
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You have MAT and your symptoms get worse, do not improve with treatment, or you develop new symptoms
Prevention
To reduce the risk for developing MAT, treat the disorders that cause it right away.
Reviewed By
Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Kalman JM, Sanders P. Supraventricular tachycardias. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 65.
Zimetbaum P, Goldman L. Supraventricular ectopy and tachyarrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 52.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.