Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) and atrial flutter are common types of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) which affect the upper chambers (atria) of the heart.
Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

In atrial flutter, the heart beats too fast, but often continues to contract in a regular rhythm. AFib is a closely related condition in which the atria contract in a chaotic manner, or "quivers." This creates a very irregular heart rhythm that is also usually too fast. AFib and atrial flutter often occur in the same person at different times.
Atrial fibrillation - Animation
A lot of things can make your heart beat faster, like kissing the person you love or watching a scary movie. But sometimes, your heart beats not only faster but also out of rhythm. That can be a problem if this continues over a long period of time and isn't treated. Let's talk about a condition called atrial fibrillation. If you can listen to your heart through a stethoscope, your heart beat should sound something like this, or lub dub, lub dub, lub dub. If you have atrial fibrillation, the top two chambers of your heart contract too quickly, and in an irregular pattern. So what you'd hear if you listened through a stethoscope would be more like this. Atrial fibrillation doesn't just sound funny, this irregular beat can prevent your heart from pumping enough blood out to the rest of your body. Age may cause atrial fibrillation. As you get older, it's more common to have an irregular heartbeat. You're also more likely to have atrial fibrillation if you've had another heart problem, like valve disease, coronary artery disease, or heart failure. Some people get atrial fibrillation because they drink too much alcohol or take certain medicines. To find out you may have atrial fibrillation. You'll feel your heart race and flutter-and not just once in a while, but often. You may also have trouble breathing and feel tired and dizzy. Your doctor can listen for fluttering while listening to your heart with a stethoscope. You may also need a test that records your heart's rhythms, like an ECG, which you have in your doctor's office, or a Holter monitor that you wear around for a day. Your doctor may also prescribe imaging tests to look at your heart and check whether its electrical system is working properly. If you do have atrial fibrillation, your doctor can give you medicine to slow your racing heart. Often, the next step is to restore the normal heart rhythm with an electric shock, a process called Cardioversion. However, if the atria haven't been contracting well for 48 hours or more, blood clots may have formed there. These patients are usually given anti-coagulant medicines before Cardioversion to prevent the clots from moving to the brain and causing a stroke when normal rhythm is restored. If Cardioversion doesn't solve the problem, a procedure called Cardiac ablation can be done to destroy the bad areas of your heart that are causing your heart to beat abnormally. Usually doctors can treat atrial fibrillation so that it becomes a minor nuisance, instead of a big problem. But, the condition can come back, even after it's been treated. If it continues, atrial fibrillation can lead to heart failure. To avoid complications from atrial fibrillation, call your doctor if you're feeling flutters in your chest, and they don't go away.
Causes
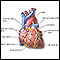
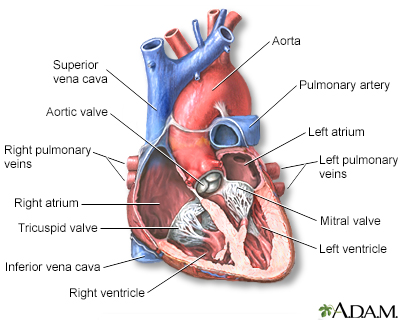
When working well, the 4 chambers of the heart contract (squeeze) in an organized way.
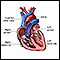
Electrical signals direct your heart to pump the right amount of blood for your body's needs. The signals begin in an area called the sinoatrial node (also called the sinus node or SA node).

Conduction system of the heart
The intrinsic conduction system sets the basic rhythm of the beating heart by generating impulses which stimulate the heart to contract.
In people with AFib, the electrical impulse of the heart is not regular. This is because the sinoatrial node no longer controls the sequence of heart muscle contractions (rhythm) in the upper chambers of the heart (atria).
In AFib:
- The atria do not contract in an organized pattern.
- The lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) contract in an irregular manner that is often too fast.
- As a result, the heart often cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
In people with atrial flutter, the atria beat very rapidly, but in a regular pattern.
These problems can affect both men and women. They become more common with increasing age.
Common causes of AFib include:
- Alcohol use (especially binge drinking)
- Coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack or heart bypass surgery
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeart bypass surgery
Heart bypass surgery creates a new route, called a bypass, for blood and oxygen to go around a blockage to reach your heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart failure or an enlarged heart
Heart failure
Heart failure is a condition in which the heart is no longer able to pump oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body efficiently. This causes symptom...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart valve disease (most often the mitral valve)
- Hypertension
Hypertension
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines
- Overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism)
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pericarditis
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is a condition in which the sac-like covering around the heart (pericardium) becomes inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sick sinus syndrome
Sick sinus syndrome
Normally, the heartbeat starts in an area in the top chambers of the heart (atria). This area is the heart's pacemaker. It is called the sinoatrial...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
You may not be aware that your heart is not beating in a normal pattern. When symptoms are present, they may include one or more of the following:
- Pulse that feels rapid, racing, pounding or thumping, fluttering, irregular, or too slow.
- Sensation of feeling the heart beat (palpitations).
Palpitations
Palpitations are feelings or sensations that your heart is pounding or racing. They can be felt in your chest, throat, or neck. You may:Have an unpl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Confusion.
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Dizziness, lightheadedness.
Dizziness
Dizziness is a term that is often used to describe 2 different symptoms: lightheadedness and vertigo. Lightheadedness is a feeling that you might fai...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fainting.
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Fatigue.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness.
- Loss of ability to exercise.
- Shortness of breath and anxiety.
- Sweating.
- Chest pain or pressure, which may be a sign of a heart attack. Call 911 or the local emergency number right away if you have chest pain or pressure.
Chest pain or pressure
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may hear a fast heartbeat while listening to your heart with a stethoscope. Your pulse may feel fast, uneven, or both.
The normal heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute. In Afib or flutter, the heart rate may be as high as 250 to 350 beats per minute and is very often over 100 beats per minute. Blood pressure may be normal or low.
An ECG (a test that records the electrical activity of the heart) may show AFib or atrial flutter.
ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.

If your abnormal heart rhythm comes and goes, you may need to wear a special monitor to diagnose the problem. The monitor records the heart's rhythms over a period of time.
- Event monitor (3 to 4 weeks)
- Holter monitor (24 to 48 hours)
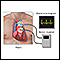
Holter monitor
A Holter monitor is a machine that continuously records the heart's rhythms. The monitor is worn for 24 to 48 hours during normal activity.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Patch monitor (1 to 2 weeks)
- Implanted loop recorder (extended monitoring)
Tests to find heart disease may include:
- Echocardiogram (ultrasound imaging of the heart)
Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create pictures of the heart. The picture and information it produces is more detailed than a s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tests to examine the blood supply of the heart muscle
- Tests to study the heart's electrical system
Tests to study the heart's electrical s...
Intracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS) is a test to look at how well the heart's electrical signals are working. It is used to evaluate abnormal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Cardioversion treatment may be used to get the heart back into a normal rhythm right away. There are two options for treatment:
Cardioversion
Cardioversion is a method to bring an abnormal heart rhythm back to normal.
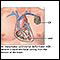
- Electric shocks to your heart
- Medicines given through a vein
These treatments may be done as emergency methods, or planned ahead of time.
Daily medicines taken by mouth are used to:
- Slow the irregular heartbeat and maintain normal heart rhythm -- These medicines may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, and anti-arrhythmics.
- Prevent blood clots -- Blood-thinning medicines are often given to reduce the risk of blood clots that can result from ongoing irregular heart rhythms.
- Prevent AFib from coming back -- These medicines work well in many people, but they can have serious side effects. AFib returns in many people, even while they are taking these medicines.
A procedure called radiofrequency ablation can be used to scar areas in your heart where the heart rhythm problems are triggered. This can prevent the abnormal electrical signals that cause AFib or flutter from moving through your heart. You may need a heart pacemaker after this procedure. All people with AFib will need to learn how to manage this condition at home.
Radiofrequency ablation
Cardiac ablation is a procedure that is used to scar small areas in your heart that may be involved in your heart rhythm problems. This can prevent ...
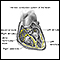
Pacemaker
A pacemaker is a small, battery-operated device. This device senses when your heart is beating too slowly. It sends a signal to your heart that mak...
Manage this condition at home
Atrial fibrillation (Afib) or flutter is a common type of abnormal heartbeat. The heart rhythm is fast and irregular. You were in the hospital to t...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticlePeople with AFib will most often need to take blood thinner medicines. These medicines are used to reduce the risk of developing a blood clot that travels in the body (and that can cause a stroke, for example). The irregular heart rhythm that occurs with AFib makes blood clots more likely to form.
Blood thinner medicines include heparin, warfarin (Coumadin), apixaban (Eliquis), rivaroxaban (Xarelto), edoxaban (Savaysa) and dabigatran (Pradaxa). Antiplatelet medicines such as aspirin or clopidogrel may also be prescribed. However, blood thinners increase the chance of bleeding, so not everyone can use them.
Heparin
Your health care provider prescribed a blood thinning medicine called heparin. It has to be given as a shot at home. A nurse or other health profess...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleWarfarin
Warfarin is a medicine that makes your blood less likely to form clots. It is important that you take warfarin exactly as you have been told. Chang...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleAspirin
Current guidelines recommend that people with coronary artery disease (CAD) receive antiplatelet therapy with either aspirin or clopidogrel. Aspirin ...

Clopidogrel
Platelets are small particles in your blood that your body uses to form clots and stop bleeding. If you have too many platelets or your platelets st...
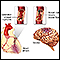
Another stroke prevention option for people who cannot safely take these medicines are left atrial appendage occlude (LAAO) devices. These are small implants that are placed inside the heart to block off the area of the heart where most of the clots form. This limits clots from forming.
Your provider will consider your age and other medical problems when deciding which stroke prevention methods are best for you.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Treatment can often control this disorder. Many people with AFib do very well with treatment.
AFib tends to return and get worse. It may come back in some people, even with treatment.
Clots that break off and travel to the brain can cause a stroke.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of AFib or flutter.
Prevention
Talk to your provider about steps to treat conditions that cause atrial fibrillation and flutter. Avoid binge drinking.
Reviewed By
Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Calkins H, Tomaselli GF, Morady F. Atrial fibrillation: clinical features, mechanisms, and management. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 66.
Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2024;149(1):e1–e156. PMID: 38033089 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38033089/.
Zimetbaum P, Goldman L. Supraventricular ectopy and tachyarrhythmias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 52.





 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.