Solitary fibrous tumor
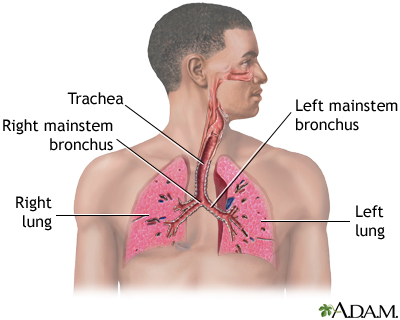
Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT) is a noncancerous tumor of the lining of the lung and chest cavity, an area called the pleura. SFT used to be called localized fibrous mesothelioma.
Tumor
A tumor is an abnormal growth of body tissue. Tumors can be cancerous (malignant) or noncancerous (benign).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCauses
The exact cause of SFT remains unknown. This type of tumor affects men and women equally.
Symptoms
About one half of the people with this type of tumor do not show any symptoms.
If the tumor grows to a large size and pushes on the lung, it can lead to symptoms, such as:
- Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic cough
- Shortness of breath
- Clubbed appearance of the fingers
Clubbed appearance of the fingers
Clubbing is changes in the areas under and around the toenails and fingernails that occur with some disorders. The nails may also show changes....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
SFT is usually found by accident when a chest x-ray is done for other reasons. If the health care provider suspects SFT, tests will be ordered. These may include:
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.

- CT scan of the chest
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Open lung biopsy
Open lung biopsy
An open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The diagnosis of SFT is difficult compared with the cancerous type of this disease, called malignant mesothelioma, which is caused by exposure to asbestos (as cancer needs to be ruled out). SFT is not caused by asbestos exposure.
Malignant mesothelioma
Malignant mesothelioma is an uncommon cancerous tumor. It mainly affects the lining of the lung and chest cavity (pleura) or lining of the abdomen (...
Treatment
SFT is usually treated by removing the tumor.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is expected to be good with prompt treatment. In rare cases, the tumor may return.
Possible Complications
Fluid escaping into the membranes around the lungs (pleural effusion) is a complication.
Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if you notice symptoms of SFT.
Reviewed By
Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron, Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Kaidar-Person O, Zagar T, Haithcock BE, Weiss, J. Diseases of the pleura and mediastinum. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 70.
Konopka K, Arenberg DA. Benign lung tumors. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King Jr TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 80.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.