Flu
Influenza A; Influenza B; Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) - flu; Zanamivir (Relenza) - flu; Vaccine - fluThe flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to person. The flu can cause moderate to severe symptoms. Most people recover fully. Children, older adults, and people with certain health conditions are at risk for severe illness and even death.
Causes
The flu is caused by an influenza virus.
Most people get the flu when they breathe in tiny airborne droplets from the coughs or sneezes of someone who has the flu. You can also catch the flu if you touch something with the virus on it, and then touch your mouth, nose, or eyes.
People often confuse colds, flu, and COVID-19. They are different, but they do have some of the same symptoms. Most people get a cold several times a year. In contrast, people generally get the flu only once every few years. Cold symptoms tend to be more mild compared to the flu and COVID-19. The flu and COVID-19 share many symptoms, so it can be hard to tell them apart. The best way to know is to get tested. COVID-19 self-tests are available over-the-counter at most pharmacies. If needed, your health care provider can test you for the flu, COVID-19, and other respiratory infections.
Colds
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....

COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur....

COVID-19 self-tests
Testing for the virus that causes COVID-19 involves taking a mucus sample from your upper respiratory tract. This test is used to diagnose COVID-19....
The flu spreads easily. It can affect a large group of people in a very short amount of time. For example, students and co-workers often get sick within 2 or 3 weeks of the flu's arrival in a school or workplace.
Sometimes, you can get a virus that makes you throw up or have diarrhea. Some people call this the "stomach flu." This is a misleading name because this virus is usually not the actual flu. The flu mostly affects your nose, throat, and lungs.
Stomach flu
Viral gastroenteritis is an infection of the stomach and intestine caused by a virus. The infection can lead to diarrhea and vomiting. It is someti...

While certain people are at a higher risk, anyone at any age can develop serious complications from the flu. Those at highest risk include:
- People age 65 and older
- Children younger than 5 years old
- Women who are more than 3 months pregnant
- Anyone living in a long-term care facility
- Anyone with chronic heart, lung, or kidney conditions, diabetes, or a weakened immune system
- People with severe obesity (BMI of 40 or higher)
Symptoms
Flu symptoms often start quickly. You can start to feel sick about 1 to 7 days after you come in contact with the virus. Most of the time, symptoms appear within 2 to 3 days.
The first symptom is often a fever between 100°F (37.8°C) and 104°F (40°C) that comes on suddenly. An adult often has a lower fever than a child. But not everyone with the flu has a fever.
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...

Other common symptoms include:
- Body aches
-
Chills
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lack of energy
- Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose
-
Sneezing
Sneezing
A sneeze is a sudden, forceful, uncontrolled burst of air through the nose and mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sore throat
Sore throat
Pharyngitis, or sore throat, is discomfort, pain, or scratchiness in the throat. It often makes it painful to swallow.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nausea, vomiting and diarrhea (more common in children)
Nausea, vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Fever usually goes away in 3 to 4 days but may last up to 8 days. Other symptoms get better in 7 to 14 days. The cough and tired feeling may last for weeks. Sometimes, the fever comes back.
Some people may not feel like eating.
The flu can make asthma, breathing problems, and other long-term (chronic) illnesses and conditions worse.
Exams and Tests
Most people do not need to see a provider when they have flu symptoms. This is because most people are not at risk for a severe case of the flu.
If you are very sick with the flu, or you are at high risk for severe illness, you should contact your provider.
There is a test to detect the flu. It is done by swabbing the nose or throat. Most of the time, test results are available very fast. The test can help your provider determine the best treatment.
Provider determine the best treatment
Many different germs, called viruses, cause colds. Symptoms of the common cold include:CoughHeadacheNasal congestionRunny noseSneezingSore throat Th...

Treatment
HOME CARE
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) help lower fever and relieve aches. Providers sometimes suggest that you use both types of medicine. Aspirin can also reduce fever and aches, but it may have potential serious side effects, such as stomach bleeding. So it's best to avoid using aspirin and it should never be given to treat flu in someone age 18 or less.
A fever does not need to come all the way down to a normal temperature to make a difference in how a person feels. Most people feel at least somewhat better when their temperature drops by 1 degree Fahrenheit.
Here are other ways to relieve symptoms:
- Over-the-counter cold medicines may make some of your symptoms better.
- Cough drops or throat sprays will help with your sore throat.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink plenty of liquids.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
Certain medicines should not be given to children, or only after a certain age.
- Do not give cold medicines to children younger than 4 years old.
- Only give cold medicines to children ages 4 to 6 years if your provider recommends it.
- Do not give ibuprofen to children younger than 6 months unless directed by your provider.
- Aspirin should not be used in children and teens due to the risk of Reye syndrome.
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ANTIVIRAL DRUGS
Most people with milder symptoms do not need to see a provider or take antiviral medicines. Your provider may recommend antiviral treatment if you are very sick with the flu. You also may be given antivirals if you are at risk for serious illness. Children at risk for a severe case of the flu may also need these medicines.
The health problems below may increase the risk of getting sicker with the flu:
- Being younger than age 5 years (those under age 2 are even more at risk) or age 65 or older
- Lung disease (including asthma)
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart conditions (except high blood pressure)
- Kidney, liver, nerve, and muscle conditions
- Blood disorders (including sickle cell disease)
-
Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A weakened immune system due to diseases (such as AIDS), radiation therapy, or certain medicines, including chemotherapy and corticosteroids
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neurological diseases such as cerebral palsy, epilepsy, intellectual disability, and muscular dystrophy
- Other long-term medical problems
These medicines may shorten the time you have symptoms by about 1 day. They work better if you start taking them within 2 days of your first symptoms.
Antibiotics are NOT used to treat the flu. Antibiotics kill bacteria. They won't work on the viruses that cause the flu.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Millions of people in the United States get the flu each year. Most people get better within a week or two, but thousands of people with the flu develop pneumonia or a brain infection. They may need to stay in the hospital. About 21,000 people in the United States die each year of problems from the flu.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Ear infection
- Sinus infection
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Myocarditis
-
Encephalitis (infection of the brain)
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Multi-organ failure
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child get the flu and are at risk for having complications.
Also contact your provider if flu symptoms are very bad and not getting better.
Contact your provider right away if you or your child have:
- Difficulty breathing
- High fever
- Shortness of breath
Any breathing problems are an emergency. Seek medical help right away.
Prevention
You can take steps to avoid catching or spreading the flu. The best step is for everyone age 6 months and older to get a flu vaccine. There are two types:
Influenza (flu) vaccine (live, intranasal): This vaccine is a nasal spray. People ages 2 through 49 years who are not pregnant may receive LAIV.
Influenza (flu) vaccine (live, intranas...
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Influenza Live, Intranasal Flu Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hc...
Influenza (flu) vaccine (inactivated or recombinant): This vaccine is delivered by injection. Everyone 6 months and older can get the vaccine.
Influenza (flu) vaccine (inactivated or...
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Inactivated Influenza Vaccine Information Statement (VIS) www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-...

To help prevent spreading the flu when you are sick, stay home and away from others both inside and outside your household
- As much as possible, stay in a specific room and away from others in your home. Use a separate bathroom if you can.
- Keep track of your symptoms. You may receive instructions from your provider on how to check and report your symptoms.
- Wear a well-fitted face mask or respirator that fits well over your nose and mouth without gaps when you see your provider and anytime other people are in the same room with you. If you can't wear a mask, for example, due to breathing problems, people in your home should wear a mask if they need to be in the same room with you.
Face mask or respirator
In places where respiratory viruses are spreading, wearing a face mask in public helps protect other people from possible infection with viruses such...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your sleeve (not your hands) when coughing or sneezing. Throw away the tissue after use.
- Wash your hands many times a day with soap and running water for at least 20 seconds. Do this before eating or preparing food, after using the toilet, and after coughing, sneezing, or blowing your nose. Use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer (at least 60% alcohol) if soap and water are not available.
- Do not share personal items such as cups, eating utensils, towels, or bedding. Wash anything you have used in soap and water.
- Clean all "high-touch" areas in the home, such as doorknobs, bathroom and kitchen fixtures, toilets, phones, tablets, counters, and other surfaces. Use a household cleaning spray and follow instructions for use.
- Take steps for cleaner air in your home. You can do this by opening windows, turning on exhaust fans in your bathrooms and kitchen, using portable high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) cleaners, and setting the fan on your furnace or air conditioning to "on" if you have central heating and cooling in your home.
You can go back to your normal activities if both of the following things are true:
- For at least 24 hours, you have been feeling better and your symptoms are improving AND
- You have not had a fever for at least 24 hours (and you are not using fever-reducing medicine)
Even though you feel better, you may still be able to spread the virus to others for several days. For this reason, once you go back to your normal activities, continue to protect others from illness by taking these steps for 5 days:
- Practice good hygiene
- Take steps for cleaner air
- Wear a mask around others
- Practice physical distancing by avoiding close contact and avoiding crowds
If your fever returns after resuming normal activities, you should go back to staying home and away from others. Once your fever and symptoms improve for more than 24 hours, you can resume activities while taking steps to protect others for 5 more days.
References
Aoki FY. Antiviral drugs for influenza and other respiratory virus infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 45.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. About influenza. www.cdc.gov/flu/about/. Updated August 13, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Respiratory illnesses: preventing spread of respiratory viruses when you're sick. www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/prevention/precautions-when-sick.html. Updated March 1, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Seasonal flu vaccine basics. www.cdc.gov/flu/vaccines/. Updated September 17, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Signs and symptoms of flu. www.cdc.gov/flu/signs-symptoms/. Updated August 26, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Treating flu with antiviral drugs. www.cdc.gov/flu/treatment/antiviral-drugs.html. Updated September 11, 2024. Accessed December 24, 2024.
Ison MG, Lee N. Influenza. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 332.
Munoz FM. Influenza viruses. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 305.
Treanor JJ. Influenza viruses, including avian influenza and swine influenza. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 165.
-
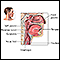
Normal lung anatomy - illustration
Within the respiratory system, air is first inhaled through the nose or mouth into the pharynx. From the pharynx, air is drawn through the larynx and trachea to make its way to the lungs.
Normal lung anatomy
illustration
-
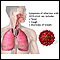
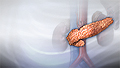
Influenza - illustration
Influenza is a viral infection of the respiratory tract that causes coughing, breathing difficulty, fever, headache, muscle aches and weakness. The virus is spread from person to person by inhaling infected droplets from the air.
Influenza
illustration
-
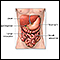
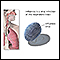
Nasal spray flu vaccine - illustration
The flu vaccine can also be administered as a nasal spray instead of the usual injection method. It can be an alternative for healthy people age 2 to 49 who want to be protected from the flu virus. Pregnant women should get a flu shot, not the nasal spray flu vaccine. Unlike the regular vaccine, it is a live virus. Therefore, it is best if the person receiving it does not have close contact with people who have a weakened immune system.
Nasal spray flu vaccine
illustration
-
Normal lung anatomy - illustration
Within the respiratory system, air is first inhaled through the nose or mouth into the pharynx. From the pharynx, air is drawn through the larynx and trachea to make its way to the lungs.
Normal lung anatomy
illustration
-
Influenza - illustration
Influenza is a viral infection of the respiratory tract that causes coughing, breathing difficulty, fever, headache, muscle aches and weakness. The virus is spread from person to person by inhaling infected droplets from the air.
Influenza
illustration
-
Nasal spray flu vaccine - illustration
The flu vaccine can also be administered as a nasal spray instead of the usual injection method. It can be an alternative for healthy people age 2 to 49 who want to be protected from the flu virus. Pregnant women should get a flu shot, not the nasal spray flu vaccine. Unlike the regular vaccine, it is a live virus. Therefore, it is best if the person receiving it does not have close contact with people who have a weakened immune system.
Nasal spray flu vaccine
illustration
Review Date: 7/23/2024
Reviewed By: Linda J. Vorvick, MD, Clinical Professor, Department of Family Medicine, UW Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 12-24-2024.





