Lung disease
Lung disease is any problem in the lungs that prevents the lungs from working properly. There are three main types of lung disease:
- Airway diseases -- These diseases affect the tubes (airways) that carry oxygen and other gases into and out of the lungs. They usually cause a narrowing or blockage of the airways. Airway diseases include asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), bronchiolitis, and bronchiectasis (which also is the main disorder for persons with cystic fibrosis). People with airway diseases often say they feel as if they're "trying to breathe out through a straw."
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleChronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is swelling and mucus buildup in the smallest air passages in the lungs (bronchioles). It is usually due to a viral infection....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become permanently wider. Bronchiectasis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung tissue diseases -- These diseases affect the structure of the lung tissue. Scarring or inflammation of the tissue makes the lungs unable to expand fully (restrictive lung disease). This makes it hard for the lungs to take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide. People with this type of lung disorder often say they feel as if they are "wearing a too-tight sweater or vest." As a result, they can't breathe deeply. Pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis are examples of lung tissue disease.
Pulmonary fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is scarring or thickening of the lungs without a known cause.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and/or other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung circulation diseases -- These diseases affect the blood vessels in the lungs. They are caused by clotting, scarring, or inflammation of the blood vessels. They affect the ability of the lungs to take up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. These diseases may also affect heart function. An example of a lung circulation disease is pulmonary hypertension. People with these conditions often feel very short of breath when they exert themselves.
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lungs. It makes the right side of the heart work harder than normal....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Many lung diseases involve a combination of these three types.
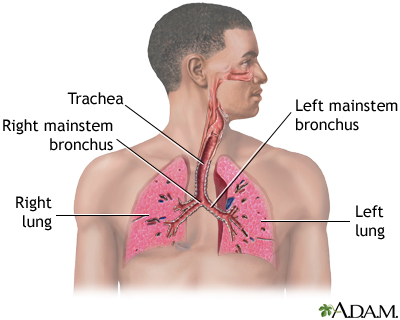
Respiratory system
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
The most common lung diseases include:
- Asthma
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Collapse of part or all of the lung (pneumothorax or atelectasis)
Pneumothorax
A collapsed lung occurs when air escapes from the lung. The air then fills the space outside of the lung between the lung and chest wall. This buil...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAtelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse of part or, much less commonly, all of a lung.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling and inflammation in the main passages (bronchial tubes) that carry air to the lungs (bronchitis)
Bronchitis
Acute bronchitis is swelling and inflamed tissue in the bronchi, the main passages that carry air to the lungs. This swelling narrows the airways, w...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - COPD
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lung infection (pneumonia)
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema)
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blocked lung artery (pulmonary embolus)
Pulmonary embolus
A pulmonary embolus is a blockage of an artery in the lungs. The most common cause of the blockage is a blood clot.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Reviewed By
Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Clifton IJ, Ellames DAB. Respiratory medicine. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 17.
Kraft M. Approach to the patient with respiratory disease. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 71.






 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.