Prediabetes
Impaired fasting glucose - prediabetes; Impaired glucose tolerance - prediabetesPrediabetes occurs when the level of sugar (glucose) in your blood is too high, but not high enough to be called diabetes.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
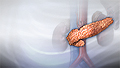
If you have prediabetes, you are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes within 10 years. It also increases your risk for heart disease and stroke.
Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong (chronic) disease in which there is a high level of sugar (glucose) in the blood. Type 2 diabetes is the most common f...

Heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
Losing extra weight and getting regular exercise will reduce the chance of your prediabetes becoming type 2 diabetes.
About Prediabetes
Your body gets energy from the glucose in your blood. A hormone called insulin helps the cells in your body use glucose. If you have prediabetes, this process does not work as well as usual. Glucose builds up in your bloodstream. If the levels get high enough, it means you have developed diabetes.
If you are at risk for diabetes, your health care provider will test your blood sugar using one or more of the following tests. Any of the following test results indicate prediabetes:
- Fasting blood glucose of 100 to 125 mg/dL (called impaired fasting glucose)
- Blood glucose of 140 to 199 mg/dL 2 hours after taking 75 grams of glucose (called impaired glucose tolerance)
- Hemoglobin A1C level of 5.7% to 6.4%
Having diabetes increases the risk for certain health problems. This is because high glucose levels in the blood can damage the blood vessels and nerves. This can lead to heart disease and stroke. If you have prediabetes, damage may already be occurring in your blood vessels.
Having prediabetes is a wake-up call to take action to improve your health.
How to Help Prevent Diabetes
Your provider will talk with you about your condition and your risks from prediabetes. To help you prevent diabetes, your provider will likely suggest certain lifestyle changes:
-
Eat healthy foods. This includes whole grains, lean proteins, low-fat dairy, and plenty of vegetables. Watch portion sizes and avoid sweets, fried foods, and excessive amount of fruits.
Portion sizes
It can be hard to measure out every portion of food you eat. Yet there are some simple ways to know that you are eating the right serving sizes. Fo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lose weight. Just a small weight loss can make a big difference in your health. For example, your provider may suggest that you lose about 7% of your body weight. So, if you weigh 200 pounds (90 kilograms), to lose 7% your goal would be to lose about 14 pounds (6.3 kilograms). Your provider may suggest a diet, or you can join a program to help you lose weight.
- Get more exercise. Aim to get at least 30 to 60 minutes of moderate exercise at least 5 days a week. This can include brisk walking, riding your bike, or swimming. You can also break up exercise into smaller sessions throughout the day. Take the stairs instead of the elevator. Even small amounts of activity count toward your weekly goal.
- Take medicines as directed. Your provider may prescribe metformin or another medicine to reduce the chance that your prediabetes will progress to diabetes. Depending on your other risk factors for heart disease, your provider may also prescribe medicines to lower your blood cholesterol level or blood pressure.
Risk Factors
You can't tell that you have prediabetes because it has no symptoms. The only way to know is through a blood test. Your provider will test your blood sugar if you are at risk for diabetes. The risk factors for prediabetes are the same as those for type 2 diabetes.
You should consider getting tested for prediabetes if you are age 35 or older. If you are younger than 35, ask your provider if you should get tested if you are overweight or obese and have one or more of these risk factors:
- A previous diabetes test showing diabetes risk
- A parent, sibling, or child with a history of diabetes
- Inactive lifestyle and lack of regular exercise
- African American, Hispanic/Latin American, American Indian and Alaska Native or Pacific Islander ethnicity
- Asian-American with body mass index of 23 kg per square meter or more
- High blood pressure (140/90 mm Hg or higher)
-
Low HDL (good) cholesterol or high triglycerides
Low HDL (good) cholesterol
Cholesterol is a soft, wax-like substance found in all parts of the body. Your body needs cholesterol to work properly. But too much cholesterol ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - History of heart disease
- History of diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes)
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleGestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is high blood sugar (glucose) that starts or is first diagnosed during pregnancy.
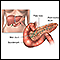 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Health conditions associated with insulin resistance (polycystic ovary syndrome, acanthosis nigricans, severe obesity)
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which a woman has increased levels of male hormones (androgens). Many problems occur as a result ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAcanthosis nigricans
Acanthosis nigricans (AN) is a skin disorder in which there is darker, thick, velvety skin in body folds and creases.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Waist circumference more than 35 inches in women or 40 inches in men
Follow-Up Testing
If your blood test results show that you have prediabetes, your provider may suggest that you be retested once each year. If your results are normal, your provider may suggest getting retested every 3 years.
References
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 3. Prevention or delay of diabetes and associated comorbidities: Standards of medical care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S43-S51. PMID: 38078581 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38078581/.
Kahn CR, Ferris HA, O'Neill BT. Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 34.
US Preventive Services Task Force. Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/screening-for-prediabetes-and-type-2-diabetes#bootstrap-panel--6. Updated August 24, 2021. Accessed May 7, 2024.
-
Diabetes risk factors - illustration
Type 1 diabetes usually begins in childhood, and type 2 diabetes typically begins in adulthood. Type 2 diabetes is becoming more common due to the growing number of older Americans and an increasing trend toward obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. Without proper management of diabetes, long-term health risks such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure can occur.
Diabetes risk factors
illustration
-
Diabetes risk factors - illustration
Type 1 diabetes usually begins in childhood, and type 2 diabetes typically begins in adulthood. Type 2 diabetes is becoming more common due to the growing number of older Americans and an increasing trend toward obesity and a sedentary lifestyle. Without proper management of diabetes, long-term health risks such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure can occur.
Diabetes risk factors
illustration
Review Date: 3/11/2024
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



