Headaches - danger signs
Migraine headache - danger signs; Tension headache - danger signs; Cluster headache - danger signs; Vascular headache - danger signsA headache is a pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck.
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...

Common types of headaches include tension headaches, migraine or cluster headaches, sinus headaches, and headaches that begin in your neck. You may have a mild headache with a cold, the flu, or other viral illnesses when you also have a low fever.
Tension headaches
A tension headache is the most common type of headache. It is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck, and is often associated with muscle ti...

Migraine
A migraine is a type of headache. It may occur with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. In most people, a throbbi...

Cluster headaches
A cluster headache is an uncommon type of headache. It is one-sided head pain that may involve tearing of the eyes, a droopy eyelid, and a stuffy no...

Cold
The common cold most often causes a runny nose, nasal congestion, and sneezing. You may also have a sore throat, cough, headache, or other symptoms....

Flu
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
Some headaches are a sign of a more serious problem and need medical attention right away.
Emergency Causes of Headaches
Problems with blood vessels and bleeding in the brain can cause a headache. These problems include:
- Abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth. This problem is called an arteriovenous malformation, or AVM.
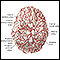
Arteriovenous malformation
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood flow to part of the brain stops. This is called a stroke.
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakening of the wall of a blood vessel that can break open and bleed into the brain. This is known as a brain aneurysm.
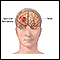
Brain aneurysm
An aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel that causes the blood vessel to bulge or balloon out. When an aneurysm occurs in a blood ve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bleeding in the brain. This is called an intracerebral hematoma.
- Bleeding around the brain. This can be a subarachnoid hemorrhage, a subdural hematoma, or an epidural hematoma.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage is bleeding in the area between the brain and the thin tissues that cover the brain. This area is called the subarachnoid sp...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSubdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma is a collection of blood between the covering of the brain (dura) and the surface of the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleEpidural hematoma
An epidural hematoma (EDH) is bleeding between the inside of the skull and the outer covering of the brain (called the dura mater).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Clots in the veins prevent blood flow from leaving the brain (sinus thrombosis).
Sinus thrombosis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a blood clot in an area at the base of the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other causes of headaches that should be checked by a health care provider right away include:
- Acute hydrocephalus, which results from an interruption of cerebrospinal fluid flow.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is a buildup of fluid inside the skull that leads to the brain pushing against the skull. Hydrocephalus means "water on the brain. "...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood pressure that is very high.
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain tumor.
Brain tumor
A primary brain tumor is a group (mass) of abnormal cells that start in the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Brain swelling (brain edema) from altitude sickness, carbon monoxide poisoning, or acute brain injury.
- Buildup of pressure inside the skull that appears to be, but is not, a tumor (pseudotumor cerebri).
Pseudotumor cerebri
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) is a condition in which the pressure inside the skull is increased. The brain is affected in a way that t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection in the brain or the tissue that surrounds the brain, as well as a brain abscess or meningitis.
Infection in the brain
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleThe tissue that surrounds the brain
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBrain abscess or meningitis
A brain abscess is a collection of pus, immune cells, and other material in the brain, caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
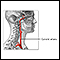
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen, inflamed artery that supplies blood to part of the head, temple, and neck area (temporal arteritis).
Temporal arteritis
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is inflammation and damage to the blood vessels that supply blood to the head, neck, upper body and arms. It is also call...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Call the Doctor
If you cannot see your provider right away, go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if:
- This is the first severe headache you have ever had in your life and it interferes with your daily activities.
- You develop a headache right after activities such as weightlifting, aerobics, jogging, or sex.
- Your headache comes on suddenly and is explosive or violent.
- Your headache is "the worst ever," even if you regularly get headaches.
- You also have slurred speech, a change in vision, problems moving your arms or legs, loss of balance, confusion, or memory loss with your headache.
Slurred speech
Dysarthria is a condition in which you have difficulty saying words because of problems with the muscles that help you talk.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Your headache gets worse over 24 hours.
- You also have fever, stiff neck, nausea, and vomiting with your headache.
- Your headache occurs with a head injury.
- Your headache is severe and just in one eye, with redness in that eye.
- You just started getting headaches, especially if you are older than 50.
- You have headaches along with vision problems and pain while chewing, or weight loss.
- You have a history of cancer and develop a new headache.
- Your immune system is weakened by disease (such as HIV infection) or by medicines (such as chemotherapy drugs and steroids).
See your provider soon if:
- Your headaches wake you up from sleep, or your headaches make it difficult for you to fall asleep.
- A headache lasts more than a few days.
- Headaches are worse in the morning.
- You have a history of headaches but they have changed in pattern or intensity.
- You have headaches often and there is no known cause.
References
Digre KB. Headaches and other head pain. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 367.
Garza I, Robertson CE, Smith JH, Whealy MA. Headache and other craniofacial pain. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 102.
Walker LE. Headache. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 16.
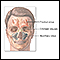
Headache - illustration
Headaches are usually caused by either muscle tension, vascular problems, or both. Migraines are vascular in origin, and may be preceded by visual disturbances, loss of peripheral vision, and fatigue. Most headaches can be relieved or ameliorated by over-the-counter pain medications.
Headache
illustration
Tension-type headache - illustration
The most common cause of tension-type headaches is muscle contraction in the head, neck or shoulders.
Tension-type headache
illustration
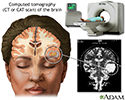
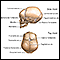
CT scan of the brain - illustration
A CT or CAT scan (computed tomography) is a much more sensitive imaging technique than X-ray, allowing high definition not only of the bony structures, but of the soft tissues. Clear images of organs such as the brain, muscles, joint structures, veins and arteries, as well as anomalies like tumors and hemorrhages may be obtained with or without the injection of contrasting dye.
CT scan of the brain
illustration
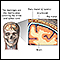
Migraine headache - illustration
Symptoms of a migraine attack may include heightened sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, auras (loss of vision in one eye or tunnel vision), difficulty of speech and intense pain predominating on one side of the head.
Migraine headache
illustration
Headache - illustration
Headaches are usually caused by either muscle tension, vascular problems, or both. Migraines are vascular in origin, and may be preceded by visual disturbances, loss of peripheral vision, and fatigue. Most headaches can be relieved or ameliorated by over-the-counter pain medications.
Headache
illustration
Tension-type headache - illustration
The most common cause of tension-type headaches is muscle contraction in the head, neck or shoulders.
Tension-type headache
illustration
CT scan of the brain - illustration
A CT or CAT scan (computed tomography) is a much more sensitive imaging technique than X-ray, allowing high definition not only of the bony structures, but of the soft tissues. Clear images of organs such as the brain, muscles, joint structures, veins and arteries, as well as anomalies like tumors and hemorrhages may be obtained with or without the injection of contrasting dye.
CT scan of the brain
illustration
Migraine headache - illustration
Symptoms of a migraine attack may include heightened sensitivity to light and sound, nausea, auras (loss of vision in one eye or tunnel vision), difficulty of speech and intense pain predominating on one side of the head.
Migraine headache
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.