Diabetes - keeping active
If you have diabetes, you may think that only vigorous exercise is helpful. But this is not true. Increasing your daily activity by any amount can help improve your health. And there are a lot of ways to add more activity to your day.
Diabetes
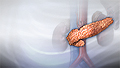
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
Diabetes - Animation
Diabetes is on the rise worldwide, and is a serious, lifelong disease that can lead to heart disease, stroke, and lasting nerve, eye and foot problems. Let's talk about diabetes and the difference between the three types of diabetes. So, what exactly is diabetes and where does it come from? An organ in your body called the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that controls the levels of your blood sugar. When you have too little insulin in your body, or when insulin doesn't work right in your body, you can have diabetes, the condition where you have abnormally high glucose or sugar levels in your blood. Normally when you eat food, glucose enters your bloodstream. Glucose is your body's source of fuel. Your pancreas makes insulin to move glucose from your bloodstream into muscle, fat, and liver cells, where your body turns it into energy. People with diabetes have too much blood sugar because their body cannot move glucose into fat, liver, and muscle cells to be changed into and stored for energy. There are three major types of diabetes. Type 1 diabetes happens when the body makes little or no insulin. It usually is diagnosed in children, teens, or young adults. But about 80% of people with diabetes have what's called Type 2 diabetes. This disease often occurs in middle adulthood, but young adults, teens, and now even children are now being diagnosed with it linked to high obesity rates. In Type 2 diabetes, your fat, liver, and muscle cells do not respond to insulin appropriately. Another type of diabetes is called gestational diabetes. It's when high blood sugar develops during pregnancy in a woman who had not had diabetes beforehand. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after the baby is born. But, still pay attention. These women are at a higher risk of type 2 diabetes over the next 5 years without a change in lifestyle. If you doctor suspects you have diabetes, you will probably have a hemoglobin A1c test. This is an average of your blood sugar levels over 3 months. You have pre-diabetes if your A1c is 5.7% to 6.4%. Anything at 6.5% or higher indicates you have diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is a wake up call to focus on diet and exercise to try to control your blood sugar and prevent problems. If you do not control your blood sugar, you could develop eye problems, have problems with sores and infections in your feet, have high blood pressure and cholesterol problems, and have kidney, heart, and problems with other essential organs. People with Type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day, usually injected under the skin using a needle. Some people may be able to use a pump that delivers insulin to their body all the time. People with Type 2 diabetes may be able to manage their blood sugar through diet and exercise. But if not, they will need to take one or more drugs to lower their blood sugar levels. The good news is, people with any type of diabetes, who maintain good control over their blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure, have a lower risk of kidney disease, eye disease, nervous system problems, heart attack, and stroke, and can live, a long and healthy life.
Introduction
There are many benefits to being active. Staying active can:
- Help control your blood sugar
- Help control your weight
- Keep your heart, lungs, and blood vessels healthy
While the focus of activity is often weight loss, you can benefit and become healthier from activity even without losing weight.
Staying Active at Home
One of the best things you can do is get up and start moving. Any activity is better than no activity.
Clean the house. Walk around when you are on the phone. Take frequent, short breaks at least every 30 minutes to get up and walk around when using the computer.
Get outside of your house and do chores, such as gardening, raking leaves, or washing the car. Play outside with your kids or grandchildren. Take the dog for a walk.
Staying Active Outside the Home
For many people with diabetes, an activity program outside the home is a great option.
- Talk to your health care provider about your plans and discuss what activities are right for you.
- Visit the gym or a fitness facility and have an instructor show you how to use the equipment. Pick a gym that has an atmosphere you enjoy and gives you a number of options in terms of activities and locations.
- When the weather is cold or wet, stay active by walking around in places like a mall.
- Make sure you are using the right shoes and equipment.
- Start slowly. A common mistake is to try and do too much too quickly. This can result in muscle and joint injury.
- Involve friends or family. Activity in a group or with partners is usually more fun and motivating.
Shopping, Running Errands, and Working
When you run errands:
- Walk as much as you can.
- If you do drive, park your car in the farthest part of the parking lot.
- Do not use drive-up windows. Get out of your car and walk inside the restaurant or retailer.
At work:
- Walk over to your co-workers instead of calling, texting, or sending them emails.
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator -- start with 1 floor up or 2 floors down and try to increase over time.
- Stand up and move around while making phone calls.
- Stretch or walk around instead of taking a coffee break or snacking.
- During lunch, walk to the bank or post office, or do other errands that allow you to move around.
At the end of your commute, get off the train or bus one stop earlier and walk the rest of the way to work or home.
If you want to find out how much activity you are getting during the day, use a wearable activity monitor, a smartphone app, or a step counting device, called a pedometer. Once you know how many steps you average in a day, try to take more steps each day. Your goal for better health should be around 10,000 steps a day, or progressively more steps than you took the day before.
Health Risks
There are some health risks to beginning new activity programs. Always check with your provider before getting started.
People with diabetes are at increased risk of having heart problems. They don't always sense the warning signs of a heart attack. Ask your provider if you need to be screened for heart disease, particularly if you:
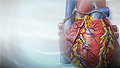
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
- Also have high blood pressure
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Also have high cholesterol
High cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fat (also called a lipid) that your body needs to work properly. Too much bad cholesterol in your blood can increase your chance of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Smoke
- Have a history of heart disease in your family
Heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
People with diabetes who are overweight or obese are at higher risk of having arthritis or other joint problems. Talk to your provider if you have had joint pain with activity in the past.
Overweight
Overweight and obesity mean having a weight than is higher than what is healthy for a given height. A person may be overweight from extra muscle, bo...

Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
Some people who are obese may develop skin rashes when they start new exercises. These can often be prevented by choosing the right clothing. If you develop a skin infection or rash, often in skin folds, talk to your provider and make sure it is treated before you continue being active.
Skin rashes
Rashes involve changes in the color, feeling or texture of your skin.

People with diabetes and nerve damage in their feet need to be extra careful when starting new activities. Check your feet daily for redness, blisters, or calluses that are starting to form. Always wear socks. Check your socks and shoes for rough spots, which can cause blisters or ulcers. Make sure your toenails are trimmed. Let your provider know right away if you have warmth, swelling, or redness across the top of your foot or your ankle.
Nerve damage
Nerve damage that occurs in people with diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy. This condition is a complication of diabetes.
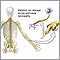
Check your feet
Diabetes can damage the nerves and blood vessels in your feet. This damage can cause numbness and reduce feeling in your feet. As a result, your fe...

Some types of vigorous exercise (mostly heavier weight lifting) can damage your eyes if you already have diabetic eye disease. Be sure to get an eye exam before starting a new exercise program.
Diabetic eye disease
Diabetes can harm the eyes. It can damage the small blood vessels in the retina, the back part of your eye. This condition is called diabetic retin...

Reviewed By
Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 5. Facilitating positive health behaviors and well-being to improve health outcomes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S77-S110. Erratum in: Diabetes Care. 2024;47(4):761-762. PMID: 38078584 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38078584/.
Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e563-e595. PMID: 30879339 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30879339/.
Dhatariya KK, Umpierrez GE, Crandall JP. Diabetes mellitus. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 210.
Lundgren JA, Kirk SE. The athlete with diabetes. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez, & Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 18.


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.