Total cholesterol
Total cholesterol is a blood test to measure all types of cholesterol in your blood. Cholesterol is a fatty, wax-like substance found in all parts of the body.
The cholesterol test is often done as part of a lipid profile, which measures the fats (lipids) in your blood:
Lipid profile
Lipids are fatty, wax-like substances found in the body. Your body needs lipids for proper body functions, growth, and energy. Two important types ...

- Total cholesterol
- Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL cholesterol)
LDL cholesterol)
The low-density lipoprotein (LDL) test is a blood test to measure the amount of LDL cholesterol in your blood. LDL is a type of fat (lipid) in your ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL cholesterol)
HDL cholesterol
The high-density lipoprotein (HDL) test is a blood test to measure the amount of HDL cholesterol in your blood. HDL is a type of fat (lipid) in your...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Triglycerides (another type of fat in your blood)
Triglycerides
The triglyceride level is a blood test to measure the amount of triglycerides in your blood. Triglycerides are a type of fat. Your body makes some t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Very low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL cholesterol)
VLDL cholesterol
VLDL stands for very low density lipoprotein. Lipoproteins are made up of cholesterol, triglycerides, and proteins. They move cholesterol, triglyce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
How the Test is Performed
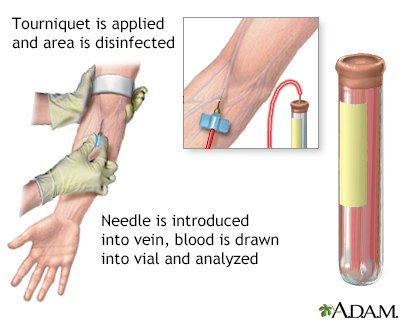
A blood sample is needed. Most of the time, blood is drawn from a vein located on the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand.
Blood is drawn from a vein
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
You should not eat for 9 to 12 hours before the test.
Alcohol and some medicines can interfere with blood test results.
- Make sure your health care provider knows what medicines you take, including over-the-counter medicines and supplements.
- Your provider will tell you if you need to stop taking any medicines before you have this test.
- Do not stop or change your medicines without talking to your provider first.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel slight pain or a sting when the needle is inserted. You may also feel some throbbing at the site after the blood is drawn.
Why the Test is Performed
Total cholesterol is usually measured together with other blood fats as part of a lipid profile. It is done to help determine your risk of developing heart disease.
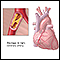
A high total cholesterol level may lead to atherosclerosis. This increases your risk for heart attack and stroke.
Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis, sometimes called "hardening of the arteries," occurs when fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries. ...
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...

Normal Results
Results may indicate:
- Optimal: Less than 200 mg/dL (5.18 mmol/L)
- Borderline high: 200 to 239 mg/dL (5.18 to 6.19 mmol/L)
- High: More than or equal to 240 mg/dL (6.22 mmol/L)
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A high total cholesterol level may be due to:
High total cholesterol level
Cholesterol is a fat (also called a lipid) that your body needs to work properly. Too much bad cholesterol in your blood can increase your chance of...

- Eating a diet high in saturated fats
- Lack of physical activity
- Stress
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Being overweight or having obesity
Being overweight
Overweight and obesity mean having a weight than is higher than what is healthy for a given height. A person may be overweight from extra muscle, bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHaving obesity
Obesity means weighing more than what is healthy for a given height. Obesity is a serious, chronic disease. It can lead to other health problems, i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
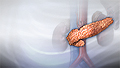
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diabetes
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
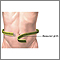
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a name for a group of risk factors that occur together and increase the chance of having coronary artery disease, stroke, and t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disorder passed down through families in which there are high amounts of cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood (familial combined hyperlipidemia)
Familial combined hyperlipidemia
Familial combined hyperlipidemia is a disorder that is passed down through families. It causes high blood cholesterol and triglyceride levels....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Side effect of certain medicines
- Underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism)
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney or liver disease
If your total cholesterol is high, your provider may recommend changes in your lifestyle such as:
Lifestyle
Your body needs cholesterol to work well. But cholesterol levels that are too high can harm you. In the US, blood cholesterol is most often measured...

- Eating a healthy diet
- Losing weight (if you are overweight or have obesity)
- Getting regular exercise
- Quitting smoking
- Avoiding alcohol
You may also need medicine to lower your cholesterol level if you have diabetes or are at risk of heart disease. While taking medicines to lower your cholesterol level, you should continue the lifestyle changes.
Medicine to lower your cholesterol leve
Your body needs cholesterol to work properly. But extra cholesterol in your blood causes deposits to build up on the inside walls of your blood vess...

A low total cholesterol level is usually considered desirable. But, it may be due to serious medical conditions too, in which case it is undesirable:
- Rare genetic disorder that runs in families
- Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism)
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Severe liver disease
- Malabsorption syndrome (conditions in which the small intestine does not absorb fats well)
Malabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Malnutrition
Malnutrition
Malnutrition is the condition that occurs when your body does not get enough nutrients.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
Hematoma
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive bleeding
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Considerations
Certain medicines, pregnancy, infection, and some medical conditions can affect test results.
Reviewed By
Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Bredefeld CL, Lau R, Hussain MM. Lipids and dyslipoproteinemia. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 18.
Genest J, Mora S, Libby P. Lipoprotein disorders and cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli, GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 27.
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;139(25):e1046-e1081. PMID: 30565953 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30565953/.
Mora S, Libby P, Ridker PM. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli, GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
Robinson JG. Disorders of lipid metabolism. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 190.



 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.