Foot drop
Peroneal nerve injury - foot drop; Fibular nerve injury; Foot drop palsy; Fibular neuropathy; Peroneal neuropathy; Drop footFoot drop is when you have difficulty lifting the front part of your foot. This may cause you to drag your foot when you walk. Foot drop, also called drop foot, can be caused by a problem with the muscles, nerves, or anatomy of your foot or leg.
Causes
Foot drop is not a condition by itself. It is a symptom of another disorder. Foot drop can be caused by a number of health conditions.
The most common cause of foot drop is peroneal nerve injury. This nerve is also called the fibular nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. It supplies movement and sensation to the lower leg, foot, and toes.
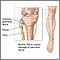
Peroneal nerve injury
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction is due to damage to the peroneal nerve leading to loss of movement or sensation in the foot and leg. This conditio...
Conditions that affect the nerves and muscles in the body can lead to foot drop. They include:
-
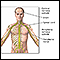
Peripheral neuropathy -- Diabetes is the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a common inherited peripheral neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral nerves carry information to and from the brain. They also carry signals in both directions between the spinal cord and the rest of the bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDiabetes
Nerve damage that occurs in people with diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy. This condition is a complication of diabetes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCharcot-Marie-Tooth
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease is a group of disorders passed down through families that affect the nerves outside the brain and spine. These are calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
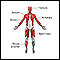
Some muscle diseases cause foot drop, including some forms of muscular dystrophy.
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Polio is caused by a virus, and can cause muscle weakness and paralysis.
Polio
Polio is a viral disease that can affect nerves and can lead to partial or full paralysis. The medical name for polio is poliomyelitis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Crossing the legs at the knees can also damage the peroneal nerve.
Brain and spinal cord disorders can cause muscle weakness and paralysis and include:
-
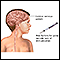
Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, is a disease of the nerve cells in the brain, brain stem and spinal cord that control voluntary muscle movemen...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
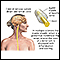
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Foot drop can cause problems walking. Because you can't raise the front of your foot, you need to raise your leg higher than normal to take a step to avoid dragging your toes or tripping. The foot may make a slapping noise as it hits the ground. This is called a steppage gait.
Gait
Walking abnormalities can be caused by many different types of problems. Problems with the joints, (such as arthritis), bones (such as deformities),...
Depending on the cause of foot drop, you may feel numbness or tingling on the top of your foot or shin. Foot drop may occur in one or both feet, depending on the cause.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam, which may show:
- Loss of muscle control in the lower legs and feet
- Atrophy of the foot or leg muscles
- Difficulty lifting up the foot and toes
Your provider may order one or more of the following tests to check your muscles and nerves and to determine the cause:
-
Electromyography (EMG, a test of electrical activity in muscles)
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nerve conduction tests to see how fast electrical signals move through a peripheral nerve)
Nerve conduction tests
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Imaging tests such as MRI, x-rays, CT scans
MRI
A leg MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan of the leg uses strong magnets to create pictures of the leg. This may include the ankle, foot, and surr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scans
Hyperaldosteronism is a disorder in which the adrenal gland releases too much of the hormone aldosterone into the blood. Hyperaldosteronism can be pr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve ultrasound
- Blood tests
Treatment
Treatment of foot drop depends on what is causing it. In some cases, treating the cause will also cure foot drop. If the cause is a chronic or ongoing illness, foot drop may be permanent.
Certain people may benefit from physical and occupational therapy.
Possible treatments include:
- Braces, splints, or shoe inserts to help support the foot and keep it in a more normal position.
- Physical therapy can help stretch and strengthen muscles and help you walk better.
- Nerve stimulation may help retrain the nerves and muscles of the foot.
Surgery may be needed to relieve pressure on the nerve or to try to repair it. For long-term foot drop, your provider may suggest fusing the ankle or foot bones. Or you may have tendon surgery. In this, a working tendon and attached muscle is transferred to a different part of the foot.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you recover depends on what is causing foot drop. Foot drop will often go away completely. If the cause is more severe, such as stroke, you may not recover completely.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have trouble walking or controlling your foot, including:
- Your toes drag on the floor while walking.
- Your foot makes a slapping noise on the ground as you walk (steppage gait).
- You are unable to hold up the front of your foot.
- You have decreased sensation, numbness, or tingling in your foot or toes.
- You have ankle or foot weakness.
References
Del Toro DR, Seslija D, King JC. Fibular (peroneal) neuropathy. In: Frontera WR, Silver JK, Rizzo TD, eds. Essentials of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 75.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 106.
Thompson PD, Nutt JG. Gait disorders. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
-
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction - illustration
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction is a disorder characterized by loss of movement or sensation of the foot and leg caused by damage to the peroneal nerve.
Common peroneal nerve dysfunction
illustration
Review Date: 4/29/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.