Cologuard
Cologuard; Colon cancer screening - Cologuard; Stool DNA test - Cologuard; FIT-DNA stool test; Colon precancer screening - CologuardCologuard is a screening test for colon and rectal cancer.
The colon sheds cells from its lining every day. These cells pass with the stool through the colon. Colon cancer cells may have DNA changes in certain genes. Cologuard detects the altered DNA. The presence of abnormal cells or blood in the stool may indicate cancer or precancer tumors.
How the Test is Performed
The Cologuard testing kit for colon and rectal cancer must be ordered by your health care provider. It will be sent by mail to your address. You collect the sample at home and send it back to the lab for testing.
Colon and rectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). It is also sometimes simply called colon ca...
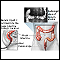
The Cologuard testing kit will contain a sample container, a tube, preserving liquid, labels, and instructions on how to collect the sample. When you are ready to have a bowel movement, use the Cologuard testing kit to collect your stool sample.
Read the instructions that come with the testing kit carefully. Wait until you are ready to have a bowel movement. Collect the sample only when it is possible to ship it within 24 hours. The sample must reach the lab in 72 hours (3 days).
DO NOT collect the sample if:
- You have diarrhea.
- You are menstruating.
- You have rectal bleeding due to hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or lower part of the rectum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Follow these steps to collect the sample:
- Read all instructions that come with the kit.
- Use the brackets provided with the testing kit to fix the sample container on your toilet seat.
- Use the toilet as usual for your bowel movement.
- Try not to let urine get into the sample container.
- Do not put toilet paper into the sample container.
- Once your bowel movement is over, remove the sample container from the brackets and keep it on a flat surface.
- Follow instructions to collect a little sample in the tube provided with the testing kit.
- Pour the preserving liquid in the sample container and close the lid tightly.
- Label the tubes and the sample container according to the instructions, and place them in the box.
- Store the box at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and heat.
- Ship the box within 24 hours to the lab using the label provided.
The results of the test will be sent to your provider in two weeks.
How to Prepare for the Test
The Cologuard test does not require any preparation. You do not need to change your diet or medicines before the test.
How the Test will Feel
The test requires you to have a normal bowel movement. It will not feel any different from your regular bowel movements. You can collect the sample at your home privately.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is done to screen for colon and rectal cancer and abnormal growths (polyps) in the colon or rectum.
Screen for colon and rectal cancer
Colon cancer screening can detect polyps and early cancers in the large intestine. This type of screening can find problems that can be treated befo...
Your provider may suggest Cologuard testing once every 1 to 3 years starting at age 45 years. The test is recommended if you are age 45 to 75 years and have an average risk of colon cancer. This means that you do not have:
- Personal history of colon polyps and colon cancer
- Family history of colon cancer
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis)
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUlcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
The normal result (negative result) will indicate that:
- The test did not detect blood cells or altered DNA in your stool.
- You do not need further testing for colon cancer if you have an average risk of colon or rectal cancer.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal result (positive result) suggests that the test found some pre-cancer or cancer cells in your stool sample. However, the Cologuard test does not diagnose cancer. You will need further tests to make a diagnosis of cancer. Your provider will likely suggest a colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...

Risks
There is no risk involved in taking the sample for Cologuard test.
Screening tests carry a small risk of:
- False-positives (your test results are abnormal, but you do NOT have colon cancer or pre-malignant polyps)
- False-negatives (your test is normal, even when you have colon cancer)
Considerations
It is unclear yet whether the use of Cologuard will lead to better outcomes compared with other methods used to screen for colon and rectal cancer.
References
Bresalier RS. Colorectal cancer. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 127.
Eckmann JD, Ebner DW, Bering J, et al, eds. Multitarget stool DNA screening in clinical practice: high positive predictive value for colorectal neoplasia regardless of exposure to previous colonoscopy. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(4):608-615. PMID: 32068535. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32068535/.
NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN Guidelines) colon cancer, version 2.2023. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colon.pdf. Accessed August 29, 2023.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Davidson KW, Barry MJ, et al. Screening for Colorectal Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2021;325(19):1965-1977. PMID: 34003218 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34003218/.
Large intestine (colon) - illustration
The large intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of water from the indigestible residue of food. The ileocecal valve of the ileum (small intestine) passes material into the large intestine at the cecum. Material passes through the ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid portions of the colon, and finally into the rectum. From the rectum, the waste is expelled from the body.
Large intestine (colon)
illustration
Large intestine (colon) - illustration
The large intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of water from the indigestible residue of food. The ileocecal valve of the ileum (small intestine) passes material into the large intestine at the cecum. Material passes through the ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid portions of the colon, and finally into the rectum. From the rectum, the waste is expelled from the body.
Large intestine (colon)
illustration
Review Date: 5/3/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.