Foreign object - inhaled
Obstructed airway; Blocked airwayIf you breathe a foreign object into your nose, mouth, or respiratory tract, it may become stuck. This can cause breathing problems or choking. The area around the object also can become inflamed or infected.
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.

Considerations
Children ages 6 months to 3 years are in the age group most likely to breathe in (inhale) a foreign object. These items may include nuts, coins, toys, balloons, or other small items or foods.
Causes
Young children can easily inhale small foods (nuts, seeds, or popcorn) and objects (buttons, beads, or parts of toys) when playing or eating. This may cause a partial or total airway blockage.
Total airway blockage
Blockage of the upper airway occurs when the upper breathing passages become narrowed or blocked, making it hard to breathe. Areas in the upper airw...
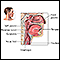
Young children have smaller airways than adults. They also can't move enough air when coughing to dislodge an object. Therefore, a foreign object is more likely to get stuck and block the air passage.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Choking
- Coughing
- Difficulty speaking
- No breathing or breathing trouble (respiratory distress)
- Turning blue, red or white in the face
-
Wheezing
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest, throat or neck pain
Sometimes, only minor symptoms are seen at first. The object may be forgotten until symptoms such as inflammation or infection develop.
First Aid
First aid may be performed on an infant or older child who has inhaled an object. First aid measures include:
Infant
Choking is when someone cannot breathe because food, a toy, or other object is blocking the throat or windpipe (airway). This article discusses cho...

Older child
Choking is when someone is having a very hard time breathing because food, a toy, or other object is blocking the throat or windpipe (airway). A chok...

- Back blows or chest compressions for infants.
- Abdominal thrusts for older children.
- If the infant or child continues to have trouble breathing, they might need emergency cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Be sure you are trained to perform these first aid measures.
Parents of infants and young children should consider taking a Basic Life Support class from the American Heart Association.
Any child who may have inhaled an object should be seen by their health care provider. A child with a total airway blockage requires emergency medical help.
If choking or coughing goes away, and the child does not have any other symptoms, he or she should be watched for signs and symptoms of infection or irritation. X-rays may be needed.
A procedure called bronchoscopy may be needed to confirm the diagnosis and to remove the object. Antibiotics and breathing therapy may be needed if an infection develops.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
Do Not
Do not force feed infants who are crying or breathing rapidly. This may cause the baby to inhale liquid or solid food into their airway.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider or call 911 or the local emergency number if you think a child has inhaled a foreign object.
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Keep small objects out of the reach of young children.
- Discourage talking, laughing, or playing while food is in the mouth.
- Do not give potentially dangerous foods such as hot dogs, whole grapes, nuts, popcorn, food with bones, or hard candy to children under age 3.
- Teach children to avoid placing foreign objects into their noses and other body openings.
References
Gorelik M, Schroeder JW. Foreign bodies in the airway. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 435.
Hairston TK, McNamara L. Emergency and critical care management. In: Kleinman K, Mcdaniel L, Molloy M, eds. Harriet Lane Handbook, The. 23rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 1.
Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM. Upper airway obstruction. In: Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM, eds. Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2023:chap 135.
Shah SR, Little DC. Ingestion of foreign bodies. In: Holcomb GW, Murphy JP, St. Peter SD, eds. Holcomb and Ashcraft's Pediatric Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 11.
-
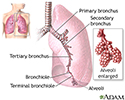
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on adult - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on adult
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on an adult - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on an adult
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on oneself - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique. When no one else is around, the Heimlich maneuver can be performed as shown.
Heimlich maneuver on oneself
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on infant - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on infant
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on infant - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on infant
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child
illustration
-
Lungs - illustration
The major features of the lungs include the bronchi, the bronchioles and the alveoli. The alveoli are the microscopic blood vessel-lined sacks in which oxygen and carbon dioxide gas are exchanged.
Lungs
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on adult - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on adult
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on an adult - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on an adult
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on oneself - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique. When no one else is around, the Heimlich maneuver can be performed as shown.
Heimlich maneuver on oneself
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on infant - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on infant
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on infant - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on infant
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child
illustration
-
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child - illustration
Choking is fairly common. Choking deaths occur most commonly in children less than 3 years old and in senior citizens, but can occur at any age. The Heimlich maneuver has been valuable in saving lives and can be administered by anyone who has learned the technique.
Heimlich maneuver on conscious child
illustration
Review Date: 4/9/2024
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.