Health screenings for women ages 40 to 64
Health maintenance visit - women - ages 40 to 64; Physical exam - women - ages 40 to 64; Yearly exam - women - ages 40 to 64; Checkup - women - ages 40 to 64; Women's health - ages 40 to 64; Preventive care - women - ages 40 to 64You should visit your health care provider from time to time, even if you are healthy. The purpose of these visits is to:
- Screen for medical issues
- Assess your risk for future medical problems
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle
- Update vaccinations and other preventive care services
- Help you get to know your provider in case of an illness
Information
Even if you feel fine, you should still see your provider for regular checkups. These visits can help you avoid problems in the future. For example, the only way to find out if you have high blood pressure is to have it checked regularly. High blood sugar and high cholesterol levels also may not have any symptoms in the early stages. A simple blood test can check for these conditions.
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...

High cholesterol
Cholesterol is a fat (also called a lipid) that your body needs to work properly. Too much bad cholesterol in your blood can increase your chance of...

There are specific times when you should see your provider or receive specific health screenings. The US Preventive Services Task Force publishes a list of recommended screenings. Below are screening guidelines for women ages 40 to 64.
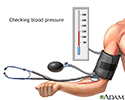
BLOOD PRESSURE SCREENING
Have your blood pressure checked at least once every year. Watch for blood pressure screenings in your area. Ask your provider if you can stop in to have your blood pressure checked. You can also check your blood pressure using the automated machines that are often located at local grocery stores and pharmacies.
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force on the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood through your body. You can measure your blood pr...

Ask your provider if you need your blood pressure checked more often if:
- You have diabetes, heart disease, kidney problems, or are overweight or have certain other health conditions
Heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleKidney problems
Chronic kidney disease is the slow loss of kidney function over time. The main job of the kidneys is to remove wastes and excess water from the body...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - You have a first-degree relative with high blood pressure.
- You are Black.
- Your blood pressure top number is from 120 to 129 mm Hg, or the bottom number is from 70 to 79 mm Hg.
- You had high blood pressure during a pregnancy.
If the top number is 130 mm Hg or greater, but lower than 140 mm Hg or the bottom number is 80 mm Hg or greater but lower than 90 mm Hg, this is considered to be stage 1 hypertension. Readings above these are considered to be stage 2 hypertension. Schedule an appointment with your provider to learn how you can reduce your blood pressure. Record your blood pressure numbers and bring this information to share with your provider.
BREAST CANCER SCREENING
Experts do not agree about the benefits of breast self-exams in finding breast cancer or saving lives. Talk to your provider about what is best for you.
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer:Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (du...
Mammography is performed to screen women to detect early breast cancer when it is more likely to be cured. The recommendations of different expert organizations can differ.
- Mammography is generally recommended for all women starting at age 40, repeated every 1 to 2 years.
- Women with a family history of breast cancer should work with their health care provider to assess their risk of breast cancer. In some situations, additional testing may be considered.
Mammograms work best at finding breast cancer in women ages 40 to 74. It is not clear how well mammograms work at finding cancer in women age 75 and older.
Mammograms
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to evaluate some breast symptoms and to find breast cancer in women with no symptoms (cal...

If you have other risk factors for breast cancer, your provider may recommend an MRI scan for screening.
MRI scan
A breast MRI scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the breast and surrounding tissue. It does not...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCERVICAL CANCER SCREENING
After starting cervical cancer screening:
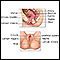
Cervical cancer screening
Cervical cancer is a cancer that starts in the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina. There ...
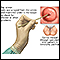
- Women ages 30 through 65 should be screened with either a Pap test every 3 years or the HPV test every 5 years or both tests every 5 years (called "cotesting").
Pap test
The Pap test mainly checks for changes in the cervix that may turn into cervical cancer. Cells scraped from the opening of the cervix are examined u...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHPV test
The HPV test is used to check for infection with HPV types associated with cervical cancer. Typically, the test looks for 14 different HPV types. H...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Women who have been treated for precancer (cervical dysplasia) should continue to have Pap tests for 20 years after treatment or until age 65, whichever is longer.
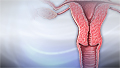
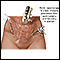
If you have had your uterus and cervix removed (total hysterectomy), and you have not been diagnosed with cervical cancer or precancer (high grade cervical neoplasia), you do not need cervical cancer screening.
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy...
CHOLESTEROL SCREENING
Cholesterol screening should begin at:
Cholesterol screening
Cholesterol is a soft, wax-like substance found in all parts of the body. Your body needs cholesterol to work properly. But too much cholesterol ca...

- Age 45 for women with no known risk factors for coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease
Coronary heart disease is a narrowing of the blood vessels that supply blood and oxygen to the heart. Coronary heart disease (CHD) is also called co...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Age 20 for women with known risk factors for coronary heart disease
Repeat cholesterol screening should take place:
- Every 5 years for women with normal cholesterol levels
- More often if changes occur in lifestyle (including weight gain and diet)
- More often if you have diabetes, heart disease, kidney problems, stroke, or blood flow problems in the legs or feet, or certain other conditions
Your provider may recommend testing more often if you are taking medicines to control high cholesterol.
COLORECTAL CANCER SCREENING
If you are under age 45, talk to your provider about getting screened. You should be screened if you have a strong family history of colon cancer or polyps. Screening may also be considered if you have risk factors such as a history of inflammatory bowel disease or polyps.
Screening
Colon cancer screening can detect polyps and early cancers in the large intestine. This type of screening can find problems that can be treated befo...
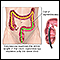
If you are age 45 to 75, you should be screened for colorectal cancer. There are several screening tests available:
Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). It is also sometimes simply called colon ca...
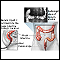
- A stool-based fecal occult blood (FOBT) or fecal immunochemical test (FIT) every year (colonoscopy is needed if results are positive)
FIT
The fecal immunochemical test (FIT) is used as a screening test for colon cancer. It tests for hidden blood in the stool, which can be an early sign...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A stool sDNA-FIT test every 1 to 3 years (colonoscopy is needed if results are positive)
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy every 5 years or every 10 years with stool testing with FOBT or FIT done every year
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy using a flexible scope is a procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum. The sigmoid colon is the area of the large inte...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT colonography (virtual colonoscopy) every 5 years
Virtual colonoscopy
A virtual colonoscopy (VC) is an imaging or x-ray test that looks for cancer, polyps, or other disease in the large intestine (colon). The medical n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
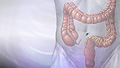
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Colonoscopy every 10 years
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may need a colonoscopy more often if you have risk factors for colorectal cancer, such as:
- Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - A personal or family history of colorectal cancer
- A family history of inherited colorectal cancer syndromes such as familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC)
DENTAL EXAM
- Go to the dentist once or twice every year for an exam and cleaning. Your dentist will evaluate if you have a need for more frequent visits.
PREDIABETES AND TYPE 2 DIABETES SCREENING
You should be screened for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes starting at age 35. Screening should be repeated every 3 years if you are overweight and have obesity.
You should be tested more often if you have other risk factors for diabetes, such as:
- You have a first-degree relative with diabetes.
- You have high blood pressure, prediabetes, or a history of heart disease.
- If you are overweight and have other risk factors, such as high blood pressure, and are planning to become pregnant.
EYE EXAM
- Have an eye exam every 2 to 4 years ages 40 to 54 and every 1 to 3 years ages 55 to 64. Your provider may recommend more frequent eye exams if you have vision problems or glaucoma risk.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Have an eye exam that includes an examination of your retina (back of your eye) at least every year if you have diabetes.
IMMUNIZATIONS
Commonly needed vaccines include:
- Flu shot: get one every year.
Flu
The flu (influenza) is a viral respiratory illness that causes fever, chills, runny nose, body aches, and cough. It spreads easily from person to pe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - COVID-19 vaccine: ask your provider what is best for you.
- Tetanus-diphtheria and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccine: have as one of your tetanus-diphtheria vaccines if you did not receive it as an adolescent.
- Tetanus-diphtheria: have a booster (Td or Tdap) every 10 years.
- Varicella vaccine: receive 2 doses if you never had chickenpox or the varicella vaccine and were born in 1980 or after.
- Hepatitis B vaccine: receive 2, 3, or 4 doses, depending on your exact circumstances, if you did not receive these as a child or adolescent, until age 59.
- Shingles (herpes zoster) vaccine: 2 doses at or after age 50.
Ask your provider if you should receive other immunizations if you have certain health problems that increase your risk for some diseases such as pneumonia.
INFECTIOUS DISEASE SCREENING
Screening for hepatitis C:
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...

- All adults ages 18 to 79 should get a one-time test for hepatitis C.
- Pregnant women should be screened at every pregnancy.
Screening for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): all people ages 15 to 65 should get a one-time test.
HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Depending on your lifestyle and medical history, you may need to be screened for infections such as syphilis, chlamydia, and other infections.
LUNG CANCER SCREENING
You should have an annual screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) if all of the following are present:
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe...

- You are age 50 to 80 years AND
- You have a 20 pack-year smoking history AND
- You currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years
OSTEOPOROSIS SCREENING
If you are age 50 to 64 and have risk factors for osteoporosis, you should discuss screening with your provider.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).

Risk factors can include long-term steroid use, low body weight, smoking, heavy alcohol use, having a fracture after age 50, or a family history of hip fracture or osteoporosis.
PHYSICAL EXAM
All adults should visit their provider from time to time, even if they are healthy. The purpose of these visits is to:
- Screen for diseases
- Assess risk of future medical problems
- Encourage a healthy lifestyle
- Update vaccinations and other preventive care services
- Maintain a relationship with a provider in case of an illness
Your blood pressure, height, weight, and body mass index (BMI) should be checked at each exam.
Body mass index (BMI)
A good way to decide if your weight is healthy for your height is to figure out your body mass index (BMI). You and your health care provider can us...

During your exam, your provider may ask you about:
- Depression and anxiety
Depression
Depression may be described as feeling sad, blue, unhappy, miserable, or down in the dumps. Most of us feel this way at one time or another for shor...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diet and exercise
- Alcohol and tobacco use
- Safety issues, such as using seat belts and smoke detectors and intimate partner violence
- Your medicines and risk for interactions
SKIN EXAM
Your provider may check your skin for signs of skin cancer, especially if you're at high risk. You may be at high risk if you:
Skin cancer
Squamous cell skin cancer is the second most common type of cancer in the United States. Other common types of skin cancer are:Basal cell cancerMelan...

- Have had skin cancer before
- Have close relatives with skin cancer
- Have a weakened immune system
Professional organizations do not recommend for or against performing a skin self-exam.
References
American Academy of Ophthalmology website. Comprehensive adult medical eye examination PPP 2020. www.aao.org/education/preferred-practice-pattern/comprehensive-adult-medical-eye-evaluation-ppp. Updated November 2020. Accessed May 20, 2024.
American Cancer Society website. Breast cancer early detection and diagnosis: American Cancer Society recommendations for the early detection of breast cancer. www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/screening-tests-and-early-detection/american-cancer-society-recommendations-for-the-early-detection-of-breast-cancer.html. Updated December 19, 2023. Accessed May 20, 2024.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) website. FAQ178: Mammography and other screening tests for breast problems. www.acog.org/patient-resources/faqs/gynecologic-problems/mammography-and-other-screening-tests-for-breast-problems. Updated July 2022. Accessed May 20, 2024.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. FAQ163: Cervical cancer. www.acog.org/patient-resources/faqs/gynecologic-problems/cervical-cancer. Updated October 2023. Accessed May 20, 2024.
American Dental Association website. Your top 9 questions about going to the dentist -- answered! www.mouthhealthy.org/en/dental-care-concerns/questions-about-going-to-the-dentist. Accessed May 20, 2024.
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(Suppl 1):S20-S42. PMID: 38078589; PMCID: PMC10725812. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38078589/.
Barton MB, Wolff TA. The preventive health visit. In: Goldman L, Cooney K, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 12.
Brown HL, Warner JJ, Gianos E, et al; American Heart Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Promoting risk identification and reduction of cardiovascular disease in women through collaboration with obstetricians and gynecologists: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Circulation. 2018;137(24):e843-e852. PMID: 29748185 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29748185/.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Recommended Vaccinations for Adults. Recommended Immunizations for adults aged 19 years and older, United States, 2024. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/imz-schedules/adult-easyread.html. Updated August 14, 2024. Accessed September 26, 2024.
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the management of blood cholesterol: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines [published correction appears in J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(24):3237-3241]. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;73(24):e285-e350. PMID: 30423393 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30423393/.
Meschia JF, Bushnell C, Boden-Albala B; American Heart Association Stroke Council; et al. Guidelines for the primary prevention of stroke: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2014;45(12):3754-3832. PMID: 25355838 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25355838/.
Mora S, Libby P, Ridker PM. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 25.
National Cancer Institute website. Breast cancer screening (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/breast/hp/breast-screening-pdq. Updated March 28, 2024. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Breast cancer: medication use to reduce risk. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/breast-cancer-medications-for-risk-reduction. Updated September 3, 2019. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force; Nicholson WK, Silverstein M, Wong JB, Barry MJ, Chelmow D, Coker TR, Davis EM, Jaén CR, Krousel-Wood M, Lee S, Li L, Mangione CM, Rao G, Ruiz JM, Stevermer JJ, Tsevat J, Underwood SM, Wiehe S. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA. 2024 Apr 30. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 38687503. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38687503/.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Cervical cancer: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/cervical-cancer-screening. Published August 21, 2018. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Colorectal cancer: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/colorectal-cancer-screening. Published May 18, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Falls prevention in community-dwelling older adults: Interventions. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/falls-prevention-community-dwelling-older-adults-interventions. Published June 4, 2024. Accessed July 3, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Hepatitis C virus infection in adolescents and adults: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/hepatitis-c-screening. Published March 2, 2020. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/human-immunodeficiency-virus-hiv-infection-screening. Published June 11, 2019. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Hypertension in adults: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/hypertension-in-adults-screening. Published April 27, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement: Lung cancer: Screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening. Updated March 9, 2021. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement: osteoporosis to prevent fractures: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/osteoporosis-screening. Updated June 26, 2018. Accessed May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/screening-for-prediabetes-and-type-2-diabetes. Updated August 24, 2021. May 20, 2024.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Skin cancer: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/skin-cancer-screening. Updated April 18, 2023. Accessed May 20, 2024.
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Mancia G, Kreutz R, Bundy JD, Williams B. Harmonization of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association and European Society of Cardiology/European Society of Hypertension Blood Pressure/Hypertension Guidelines: Comparisons, reflections, and recommendations. Circulation. 2022;146:868-877. pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35950927/.
Mammogram - illustration
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to find tumors and to help tell the difference between noncancerous (benign) and cancerous (malignant) disease. One breast at a time is rested on a flat surface that contains the x-ray plate. A device called a compressor is pressed firmly against the breast to help flatten out the breast tissue. Each breast is compressed horizontally,then obliquely and an x-ray is taken of each position.
Mammogram
illustration
Pap smear - illustration
A Pap test is a simple, relatively inexpensive procedure that can easily detect cancerous or precancerous conditions.
Pap smear
illustration
Effects of age on blood pressure - illustration
Blood vessels become less elastic with age. The average blood pressure increases from 120/70 to 150/90 and may persist slightly high even if treated. The blood vessels respond more slowly to a change in body position.
Effects of age on blood pressure
illustration
Osteoporosis - illustration
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by progressive loss of bone density, thinning of bone tissue and increased vulnerability to fractures. Osteoporosis may result from disease, dietary or hormonal deficiency or advanced age. Regular exercise and vitamin and mineral supplements can reduce and even reverse loss of bone density.
Osteoporosis
illustration
Fecal occult blood test - illustration
A fecal occult blood test is a noninvasive test that detects the presence of hidden blood in the stool. Blood in the stool that is not visible is often the first, and in many cases the only, warning sign that a person has colorectal disease, including colon cancer.
Fecal occult blood test
illustration
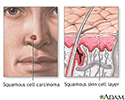
Squamous cell cancer - illustration
Squamous cell cancer involves cancerous changes to the cells of the middle portion of the epidermal skin layer. It is a malignant tumor, and is more aggressive than basal cell cancer, but still may be relatively slow-growing. It is more likely than basal cell cancer to spread (metastasize) to other locations, including internal organs. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the tumor along with some surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer
illustration
Mammogram - illustration
A mammogram is an x-ray picture of the breasts. It is used to find tumors and to help tell the difference between noncancerous (benign) and cancerous (malignant) disease. One breast at a time is rested on a flat surface that contains the x-ray plate. A device called a compressor is pressed firmly against the breast to help flatten out the breast tissue. Each breast is compressed horizontally,then obliquely and an x-ray is taken of each position.
Mammogram
illustration
Pap smear - illustration
A Pap test is a simple, relatively inexpensive procedure that can easily detect cancerous or precancerous conditions.
Pap smear
illustration
Effects of age on blood pressure - illustration
Blood vessels become less elastic with age. The average blood pressure increases from 120/70 to 150/90 and may persist slightly high even if treated. The blood vessels respond more slowly to a change in body position.
Effects of age on blood pressure
illustration
Osteoporosis - illustration
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by progressive loss of bone density, thinning of bone tissue and increased vulnerability to fractures. Osteoporosis may result from disease, dietary or hormonal deficiency or advanced age. Regular exercise and vitamin and mineral supplements can reduce and even reverse loss of bone density.
Osteoporosis
illustration
Fecal occult blood test - illustration
A fecal occult blood test is a noninvasive test that detects the presence of hidden blood in the stool. Blood in the stool that is not visible is often the first, and in many cases the only, warning sign that a person has colorectal disease, including colon cancer.
Fecal occult blood test
illustration
Squamous cell cancer - illustration
Squamous cell cancer involves cancerous changes to the cells of the middle portion of the epidermal skin layer. It is a malignant tumor, and is more aggressive than basal cell cancer, but still may be relatively slow-growing. It is more likely than basal cell cancer to spread (metastasize) to other locations, including internal organs. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the tumor along with some surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer
illustration
Review Date: 5/21/2024
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 02/05/2025.