Digestive diseases
Digestive diseases are disorders of the digestive tract, which is sometimes called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract.
In digestion, food and drink are broken down into small parts (called nutrients) that the body can absorb and use as energy and building blocks for cells.
The digestive tract is made up of the esophagus (food tube), stomach, large and small intestines, liver, pancreas, and the gallbladder.
Information
The first sign of problems in the digestive tract often includes one or more of the following symptoms:
-
Bleeding
Bleeding
Bleeding is the loss of blood. Bleeding may be:Inside the body (internal)Outside the body (external)Bleeding may occur:Inside the body when blood le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bloating
Bloating
Abdominal bloating is a condition in which the belly (abdomen) feels full and tight. Your belly may look swollen (distended).
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Constipation
Constipation
Constipation in infants and children means they have hard stools or have problems passing stools. A child may have pain while passing stools or may ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diarrhea
-
Heartburn
Heartburn
Heartburn is a painful burning feeling just below or behind the breastbone. Most of the time, it comes from the esophagus. The pain often rises in ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Incontinence
-
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
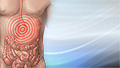
Pain in the belly
Pain in the belly
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swallowing problems
Swallowing problems
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weight gain or loss
Gain
Unintentional weight gain is when you gain weight without trying to do so and you are not eating or drinking more.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLoss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
A digestive disease is any health problem that occurs in the digestive tract. Conditions may range from mild to serious. Some common problems include heartburn, cancer, irritable bowel syndrome, and lactose intolerance.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleIrritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a disorder that leads to pain in abdomen and changes in bowel movements. IBS is not the same as inflammatory bowel...

Lactose intolerance
Lactose is a type of sugar found in milk and other dairy products. An enzyme called lactase is needed by the body to digest lactose. Lactose intoler...
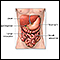
Other digestive diseases include:
-
Gallstones, cholecystitis, and cholangitis
Gallstones
Gallstones are hard deposits that form inside the gallbladder. These may be as small as a grain of sand or as large as a golf ball.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCholecystitis
Chronic cholecystitis is swelling and irritation of the gallbladder that continues over time. The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCholangitis
Cholangitis is an infection of the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver to the gallbladder and intestines. Bile is a liquid made by ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rectal problems, such as anal fissure, hemorrhoids, proctitis, and rectal prolapse
Anal fissure
An anal fissure is a small split or tear in the thin moist tissue (mucosa) lining the lower rectum (anus).
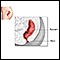 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the anus or lower part of the rectum.
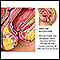 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleProctitis
Proctitis is an inflammation of the rectum. It can cause discomfort, bleeding, and the discharge of mucus or pus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRectal prolapse
Rectal prolapse occurs when the rectum sags and comes through the anal opening.
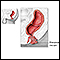 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Esophagus problems, such as stricture (narrowing) and achalasia and esophagitis
Stricture
Benign esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach). It causes swallowing difficulties. Benign mean...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleAchalasia
The tube that carries food from the mouth to the stomach is the esophagus or food pipe. Achalasia makes it harder for the esophagus to move food int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stomach problems, including gastritis, gastric ulcers usually caused by Helicobacter pylori infection and cancer
- Liver problems, such as hepatitis B or hepatitis C, cirrhosis, liver failure, and autoimmune and alcoholic hepatitis
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the liver due to infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV). Other types of viral hepatitis ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHepatitis C
Hepatitis C is a viral disease that leads to swelling (inflammation) of the liver. Other types of viral hepatitis include:Hepatitis AHepatitis BHepat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAlcoholic hepatitis
Alcoholic liver disease is damage to the liver and its function due to alcohol abuse.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pancreatitis and pancreatic pseudocyst
Pancreatic pseudocyst
A pancreatic pseudocyst is a fluid-filled sac in the abdomen that arises from the pancreas. It may also contain tissue from the pancreas, enzymes, a...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intestinal problems, such as polyps and cancer, infections, celiac disease, Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, malabsorption, short bowel syndrome, and intestinal ischemia
Celiac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage comes from a reaction to eating gluten. This ...
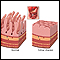 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCrohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUlcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
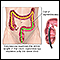 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDiverticulitis
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflame...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMalabsorption
Malabsorption involves problems with the body's ability to take in (absorb) nutrients from food.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleShort bowel syndrome
Short bowel syndrome is a problem that occurs when part of the small intestine is missing or has been removed during surgery. Nutrients are not prop...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleIntestinal ischemia
Intestinal ischemia and infarction occurs when there is a narrowing or blockage of one or more of the arteries that supply the small intestine....
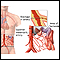 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and hiatal hernia
GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a condition in which the stomach contents leak backward from the stomach into the esophagus (food pipe). F...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePeptic ulcer
A peptic ulcer is an open sore or raw area in the lining of the stomach or intestine. There are two types of peptic ulcers:Gastric ulcer -- occurs in...
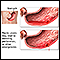 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHiatal hernia
Hiatal hernia is a condition in which part of the stomach extends through an opening of the diaphragm into the chest. The diaphragm is the sheet of ...
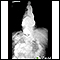 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Tests for digestive problems can include colonoscopy, upper GI endoscopy, capsule endoscopy, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), and endoscopic ultrasound.
Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
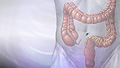
Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a way of looking inside the body using a flexible tube that has a small camera and light on the end of it. This instrument is called an...

Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
Many surgical procedures are performed on the digestive tract. These include procedures done using endoscopy, laparoscopy, and open surgery. Organ transplants can be performed on the liver, pancreas, and small intestine.
Many health care providers can help diagnose and treat digestive problems. A gastroenterologist is a physician specialist who has received extra training in the diagnosis and treatment of the digestive disorders. Other providers involved in the treatment of digestive diseases include:
-
Nurse practitioners (NPs) or physician assistants (PAs)
Nurse practitioners
A nurse practitioner (NP) is a nurse with a graduate degree in advanced practice nursing. This type of provider may also be referred to as an ARNP (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePhysician assistants
HISTORY OF THE PROFESSIONThe first Physician Assistant (PA) training program was founded in 1965 at Duke University by Dr. Eugene Stead. Programs re...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nutritionists or dietitians
- Primary care doctors
- Radiologists
- Surgeons
References
Höegenauer C, Hammer HF. Maldigestion and malabsorption. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 104.
Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM. Digestive system disorders. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 123.
Mayer EA. Functional gastrointestinal disorders: irritable bowel syndrome, dyspepsia, esophageal chest pain, and heartburn. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 128.
-
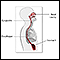
Normal abdominal anatomy - illustration
The abdomen is the area of the body between the diaphragm and pelvis. Most of the organs of digestion are located in the abdomen.
Normal abdominal anatomy
illustration
Review Date: 10/27/2021
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.