Cervical spine CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the cervical spine makes cross-sectional pictures of the neck. It uses x-rays to create the images.
How the Test is Performed
You will lie on a narrow table that slides into the center of the CT scanner.
Once you are inside the scanner, the machine's x-ray beam rotates around you. Modern "spiral" scanners can perform the exam without stopping.
A computer creates separate images of the body area, called slices. These images can be stored, viewed on a monitor, or printed on film. Three-dimensional models of the cervical spine can be created by adding the slices together.
You must be still during the exam. Movement can cause blurred images. You may need to hold your breath for short periods of time.
The scan takes 10 to 15 minutes.

CT scan
CT stands for computerized tomography. In this procedure, a thin X-ray beam is rotated around the area of the body to be visualized. Using very complicated mathematical processes called algorithms, the computer is able to generate a 3-D image of a section through the body. CT scans are very detailed and provide excellent information for the physician.
How to Prepare for the Test
Some exams use a special dye, called contrast that is put into your body before the test starts. Contrast helps certain areas show up better on the x-rays.
Contrast can be given in different ways:
- It may be given through a vein (IV) in your hand or forearm.
- It may be given as an injection into the space around the spinal cord.
If contrast is used, you may also be asked not to eat or drink anything for 4 to 6 hours before the test.
Let your health care provider know if you have ever had a reaction to contrast. You may need to take medicines before the test to avoid this problem.
Before having the contrast, tell your provider if you take the diabetes medicine metformin (Glucophage). You may need to take extra steps before the test if you take this drug.
Too much weight can cause damage to the scanner's working parts. Find out if the CT machine has a weight limit if you weigh more than 300 pounds (135 kilograms).
You will wear a hospital gown during the study. You will need to take off all jewelry as metal can affect the CT images.
How the Test will Feel
Some people may have discomfort from lying on the hard table.
Contrast given through an IV may cause a slight burning feeling, a metal taste in the mouth, and a warm flushing of the body. These feelings are normal and go away in a few seconds.
Why the Test is Performed
CT makes detailed pictures of the body very quickly. The test may help look for:
- Birth defects of the cervical spine in children
- Spine problems, when a spine MRI cannot be used
Spine MRI
A cervical MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan uses energy from strong magnets to create pictures of the part of the spine that runs through the ne...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Injury to the upper spine
- Bone tumors or cancers
- Fracture of a spine bone
- Disk herniations and compression of the spinal cord
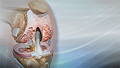
Disk herniations
A herniated (slipped) disk occurs when all or part of a disk is forced through a weakened part of the disk. This may place pressure on nearby nerves...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Healing problems or scar tissue following surgery
Normal Results
Results are considered normal if the cervical spine looks OK.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may be due to:
- Degenerative changes due to age
- Birth defects of the cervical spine
- Bone problems
- Fracture
- Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder. It is due to aging and wear and tear on a joint.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disk herniation
- Healing problems or growth of scar tissue after surgery
- Deformity from previous surgery or injuries
Risks
Risks of CT scans include:
- Being exposed to radiation
- Allergic reaction to contrast dye
- Birth defect if done during pregnancy
CT scans expose you to more radiation than regular x-rays. Having many x-rays or CT scans over time may raise your risk for cancer, but the risk from any one scan is small. Talk to your provider about this risk and how it weighs against the benefits of the test.
x-rays
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

Some people have allergies to contrast dye. Let your provider know if you have ever had an allergic reaction to injected contrast dye.
- The most common type of contrast given into a vein contains iodine. If a person with an iodine allergy is given this type of contrast, nausea or vomiting, sneezing, itching, or hives may occur.
Nausea or vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSneezing
A sneeze is a sudden, forceful, uncontrolled burst of air through the nose and mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleItching
Itching is a tingling or irritation of the skin that makes you want to scratch the area. Itching may occur all over the body or only in one location...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHives
Hives are raised, often itchy, red bumps (welts) on the surface of the skin. They can be an allergic reaction to food or medicine. They can also ap...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - If you must have this type of contrast, you may get antihistamines (such as Benadryl) or steroids before the test.
- The kidneys help remove iodine out of the body. People with kidney disease or diabetes may need to get extra fluids after the test to help flush the iodine out of the body.
Diabetes
Diabetes is a long-term (chronic) disease in which the body cannot regulate the amount of sugar in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Rarely, the dye may cause a life-threatening allergic response called anaphylaxis. If you have any trouble breathing during the test, you should notify the scanner operator immediately. Scanners come with an intercom and speakers, so the operator can hear you at all times.
Anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening type of allergic reaction.

Reviewed By
C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Kapoor G, Toms AP. Current status of imaging of the musculoskeletal system. In: Adam A, Dixon AK, Gillard JH, Schaefer-Prokop CM, eds. Grainger & Allison's Diagnostic Radiology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 38.
Shimer AL, Aghdasi B. Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine in the athlete. In: Miller MD, Thompson SR, eds. DeLee, Drez,& Miller's Orthopaedic Sports Medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 128.
Williams KD. Fractures, dislocations, and fracture-dislocations of the spine. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 41.
 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.