Non-small cell lung cancer
Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of lung cancer. It usually grows and spreads more slowly than small cell lung cancer.
Lung cancer
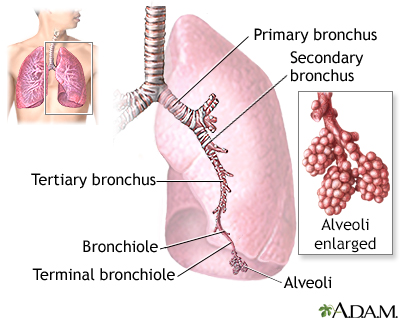
Lung cancer is cancer that starts in the lungs. The lungs are located in the chest. When you breathe, air goes through your nose, down your windpipe...

Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a fast-growing type of lung cancer. It spreads much more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer. There are two typ...
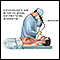
There are three common types of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
- Adenocarcinomas are often found in an outer area of the lung.
- Squamous cell carcinomas are usually found in the center of the lung next to an air tube (bronchus).
- Large cell carcinomas can occur in any part of the lung.
- There are other uncommon types of lung cancer that are also called non-small.
Causes
Lung cancer is the deadliest type of cancer for both men and women. Each year, more people die of lung cancer than of breast, colon, and prostate cancers combined.
Lung cancer is more common in older adults. It is rare in people under age 45.
Smoking causes most cases (around 80%) of non-small cell lung cancer. The risk depends on the number of cigarettes you smoke each day and for how long you have smoked. Being around the smoke from other people (secondhand smoke) also raises your risk of lung cancer. The risk decreases with time after you stop smoking. There is no evidence that smoking low-tar cigarettes lowers the risk. Some people who have never smoked do develop lung cancer.
Smoking
Knowing the serious health risks of using tobacco may help motivate you to quit. Using tobacco over a long time can increase your risk for many heal...
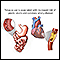
Lung cancer - Animation
Cancer can affect just about any part of the body, from the colon to the pancreas. Some cancers grow quickly, while others grow more slowly and are easier to treat. But of all the different cancers out there, one of the deadliest is lung cancer. Let's talk today about lung cancer. Cancer starts when cells begin to grow uncontrollably and form tumors. In the case of lung cancer, the tumors start in the lungs. Sometimes cancer starts somewhere else in the body and then spreads to the lungs. In that case, it's called metastatic cancer to the lung. Metastatic means disease that has spread. There are two types of lung cancer. The most common, and slower-growing form is non-small cell lung cancer. The other, faster-growing form is called small cell lung cancer. The most common way to get lung cancer is to smoke cigarettes. The more cigarettes you smoke and the earlier you start smoking, the greater your risk is. Even being around someone who smokes and breathing in the secondhand smoke from their cigarettes increases your risk of getting lung cancer. Even though smoking makes you much more likely to get lung cancer, you don't have to smoke or be exposed to smoke to get the disease. Some people who have lung cancer never lit up a cigarette in their life. They have been exposed to cancer-causing substances like asbestos, diesel fumes, arsenic, radiation, or radon gas. Or, they may not have had any known lung cancer risks. The most common signs of lung cancer are a cough that won't go away, chest pain, shortness of breath, weight loss, and fatigue. But just because you have these symptoms it doesn't mean that you have don't have lung cancer. These can also be signs of other conditions, like asthma or a respiratory infection. If you do have these symptoms, see your doctor. A chest x-ray, MRI, or CT scan can view the inside of your lungs to look for signs of cancer or other diseases. What happens if you do have lung cancer? Doctors divide lung cancer into stages. The higher the stage, the more the cancer has spread. For example, a stage 1 cancer is small and hasn't spread outside of the lungs. A stage 4 cancer has spread to the other organs, such as the kidneys or brain. Depending upon the type and stage of your lung cancer, you may need surgery to remove part or all of your lung. Or, your doctor may recommend radiation or chemotherapy to kill cancer cells. If you have lung cancer, how well you do depends upon the stage of your disease and the type of lung cancer that you have. Early-stage cancers have the highest survival and cure rates. Late-stage cancers are harder to treat. Because lung cancer can be so deadly, prevention is key. The most important that thing you can do is to stop smoking, and avoid being around anyone who does smoke.
Research shows that smoking marijuana may help cancer cells grow. But there is no direct link between smoking marijuana and developing lung cancer.
Smoking marijuana
Marijuana comes from a plant called hemp. Its scientific name is Cannabis sativa. The main active ingredient in marijuana is THC (short for delta-9...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleConstant exposure to high levels of air pollution and drinking water that has a high level of arsenic can increase your risk of lung cancer. A history of radiation therapy to the lungs can also increase risk.
Working with or living near cancer-causing chemicals or materials can also increase the risk of developing lung cancer. Such chemicals include:
- Arsenic
- Asbestos
- Radon
- Chemicals such as uranium, beryllium, vinyl chloride, nickel chromates, coal products, mustard gas, chloromethyl ethers, gasoline, and diesel exhaust
- Certain alloys, paints, pigments, and preservatives
- Products using chloride and formaldehyde
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Chest pain
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cough that does not go away
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood
Coughing up blood is the spitting up of blood or bloody mucus from the lungs and throat (respiratory tract). Hemoptysis is the medical term for cough...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
Loss of appetite
A decreased appetite is when your desire to eat is reduced. The medical term for a loss of appetite is anorexia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Losing weight without trying
Losing weight without trying
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Wheezing
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound during breathing. It occurs when air moves through narrowed breathing tubes in the lungs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Early lung cancer may not cause any symptoms.
Other symptoms that may be due to NSCLC, often in the late stages:
- Bone pain or tenderness
Bone pain or tenderness
Bone pain or tenderness is aching or other discomfort in one or more bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Eyelid drooping
Eyelid drooping
Ptosis (eyelid drooping) in infants and children is when the upper eyelid is lower than it should be. This may occur in one or both eyes. Eyelid dr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hoarseness or changing voice
Hoarseness or changing voice
Hoarseness refers to difficulty making sounds when trying to speak. Vocal sounds may be weak, breathy, scratchy, or husky, and the pitch or quality ...
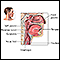 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Joint pain
- Nail problems
Nail problems
Nail abnormalities are problems with the color, shape, texture, or thickness of the fingernails or toenails.
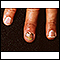 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Shoulder pain or weakness
- Swallowing difficulty
Swallowing difficulty
Difficulty with swallowing is the feeling that food or liquid is stuck in the throat or at any point before the food enters the stomach. This proble...
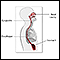 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling of the face
Swelling of the face
Facial swelling is the buildup of fluid in the tissues of the face. Swelling may also affect the neck and upper arms.
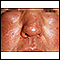 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Weakness
These symptoms can be due to other, less serious conditions. It is important to talk to your health care provider if you have symptoms.
Exams and Tests
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history. You will be asked if you smoke, and if so, how much you smoke and for how long you have smoked. You will also be asked about other things that may have put you at risk of lung cancer, such as exposure to certain chemicals.
When listening to your chest with a stethoscope, your provider may hear fluid around your lungs. This may suggest cancer.
Tests that may be done to diagnose lung cancer or to see if it has spread include:
- Bone scan
Bone scan
A bone scan is an imaging test used to diagnose bone diseases and find out how severe they are.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Comprehensive metabolic panel
- CT scan of the chest and abdomen
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI of the chest
MRI of the chest
A chest MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create pictures of the chest (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
Positron emission tomography
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Sputum test to look for cancer cells
Sputum test
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thoracentesis (sampling of fluid buildup around the lung)
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid from the space between the lining of the outside of the lungs (pleura) and the wall of the chest....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
In most cases, a piece of tissue is removed from your lungs for examination under a microscope. This is called a biopsy. There are several ways to do this:
- Bronchoscopy combined with biopsy
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBiopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT-scan-directed needle biopsy
CT-scan-directed needle biopsy
A lung needle biopsy is a method to remove a piece of lung tissue for examination. If it is done through the wall of your chest, it is called a tran...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Endoscopic bronchoscopy ultrasound (EBUS) with biopsy
- Mediastinoscopy with biopsy
Mediastinoscopy with biopsy
Mediastinoscopy with biopsy is a procedure in which a lighted instrument (mediastinoscope) is inserted in the space in the chest between the lungs (m...
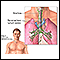 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Open lung biopsy
Open lung biopsy
An open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pleural biopsy
Pleural biopsy
Pleural biopsy is a procedure to remove a sample of the pleura. This is the thin tissue that lines the chest cavity and surrounds the lungs. The bi...
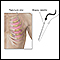 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If the biopsy shows cancer, it may be checked for certain genetic changes that may lead to specific treatment. More imaging tests are done to find out the stage of the cancer. Stage means how big the tumor is and how far it has spread. NSCLC is divided into 5 stages:
Stage of the cancer
Cancer staging is a way to describe how much cancer is in your body and where it is located. Staging helps determine where the original tumor is, ho...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article- Stage 0 -- The cancer has not spread beyond the inner lining of the lung.
- Stage I -- The cancer is small and has not spread to the lymph nodes.
- Stage II -- The cancer has spread to some lymph nodes near the original tumor.
- Stage III -- The cancer has spread to nearby tissue or to far away lymph nodes.
- Stage IV -- The cancer has spread to other organs of the body, such as the other lung, brain, or liver.
Treatment
There are many different types of treatment for NSCLC. Treatment depends on the stage of the cancer and whether the cancer cells have genetic changes that create target molecules in or on the cells.
Surgery is the common treatment for NSCLC that has not spread beyond nearby lymph nodes. The surgeon may remove:
Surgery
Lung surgery is surgery done to repair or remove lung tissue. There are many common lung surgeries, including:Biopsy of an unknown growth in or arou...
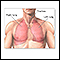
- One of the lobes of the lung (lobectomy)
- Only a small part of the lung (wedge or segment removal)
- The entire lung (pneumonectomy)
Some people need chemotherapy. Chemotherapy uses medicines to kill cancer cells and stop new cells from growing. Treatment may be done in the following ways:
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
- Chemotherapy is often used when the cancer has spread outside the lung (stage IV).
- It may also be given before surgery. This is called neoadjuvant therapy.
- It may be given after surgery to kill any remaining cancer. This is called adjuvant therapy.
- Chemotherapy is usually given through a vein (by IV).
Controlling symptoms and preventing complications during and after chemotherapy is an important part of care.
During and after chemotherapy
You had chemotherapy treatment for your cancer. Your risk for infection, bleeding, and skin problems may be high. To stay healthy after chemotherap...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleImmunotherapy can be given by itself or with chemotherapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that relies on the body's infection-fighting system (immune system). It uses substances made by the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleTargeted therapy may be used to treat NSCLC. Targeted therapy uses medicines to zero in on specific target molecules in or on cancer cells. These targets play a role in how cancer cells grow and survive. Using these targets, the medicine disables the cancer cells so they cannot spread.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses medicines to stop cancer from growing and spreading. It does this with less harm to normal cells than other treatments. Stand...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleRadiation therapy can be used with chemotherapy if surgery is not possible. Radiation therapy uses powerful x-rays or other forms of radiation to kill cancer cells. Radiation may be used to:
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
- Treat the cancer, sometimes along with chemotherapy, if surgery is not possible
- Help relieve symptoms caused by the cancer, such as breathing problems and swelling
- Help relieve cancer pain when the cancer has spread to the bones
Controlling symptoms during and after radiation to the chest is an important part of care.
During and after radiation to the chest
When you have radiation treatment for cancer, your body goes through changes. Follow your health care provider's instructions on how to care for you...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleThe following treatments are mostly used to relieve symptoms caused by NSCLC:
- Laser therapy -- A small beam of light burns and kills cancer cells.
- Photodynamic therapy -- Uses a light to activate a medicine in the body, which then kills cancer cells.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOutlook (Prognosis)
The outlook varies. Most often, NSCLC grows slowly. In some cases, it can grow and spread quickly and cause rapid death. The cancer may spread to other parts of the body, including the bone, liver, small intestine, and brain.
Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy have been shown to prolong life and improve the quality of life in some people with stage IV NSCLC.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...

Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of cancer treatment that relies on the body's infection-fighting system (immune system). It uses substances made by the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleTargeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses medicines to stop cancer from growing and spreading. It does this with less harm to normal cells than other treatments. Stand...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCure rates are related to the stage of disease and whether you are able to have surgery.
- Stage I and II cancers have the highest survival and cure rates.
- Stage III cancer can be cured in some cases.
- Stage IV cancer is almost never cured. The goals of therapy are to extend and improve the quality of life.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of lung cancer, particularly if you smoke.
Prevention
If you smoke, now is the time to quit. If you are having trouble quitting, talk with your provider. There are many methods to help you quit, from support groups to prescription medicines. Also, try to avoid secondhand smoke.
Help you quit
There are many ways to quit smoking. There are also resources to help you. Family members, friends, and co-workers may be supportive. But to be su...
Support groups
It is hard to quit smoking if you are acting alone. Smokers usually have a much better chance of quitting with a support program. Stop smoking prog...

Prescription medicines
Nicotine replacement therapy is a treatment to help people stop smoking. It uses products that supply low doses of nicotine. These products do not ...

If you are age 50 to 80 years and have a 20 pack-year smoking history and currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years, ask your provider about being screened for lung cancer by low-dose CT scan of your chest.
Reviewed By
Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
American Cancer Society website. Lung cancer risk factors. www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html. Updated January 29, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024.
American Lung Association website. Lung cancer trends brief. www.lung.org/research/trends-in-lung-disease/lung-cancer-trends-brief. Accessed June 3, 2024.
Araujo LH, Horn L, Merritt RE, Shilo K, Xu-Welliver M, Carbone DP. Cancer of the lung: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 69.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Health problems caused by secondhand smoke. www.cdc.gov/tobacco/secondhand-smoke/health.html. Updated May 15, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024.
National Cancer Institute website. Non-small cell lung cancer treatment (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/lung/hp/non-small-cell-lung-treatment-pdq. Updated March 8, 2024. Accessed June 3, 2024.
NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology: non-small cell lung cancer, version 6.2024. www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1450. Accessed June 18, 2024.
Rivera MP, Mody GN, Weiner AA. Lung cancer: treatment. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 77.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Lung cancer: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/lung-cancer-screening. Updated March 9, 2021. Accessed June 3, 2024.


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.