Colposcopy - directed biopsy
Biopsy - colposcopy - directed; Biopsy - cervix - colposcopy; Endocervical curettage; ECC; Cervical punch biopsy; Biopsy - cervical punch; Cervical biopsy; Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - colposcopy; CIN - colposcopy; Precancerous changes of the cervix - colposcopy; Cervical cancer - colposcopy; Squamous intraepithelial lesion - colposcopy; LSIL - colposcopy; HSIL - colposcopy; Low-grade colposcopy; High-grade colposcopy; Carcinoma in situ - colposcopy; CIS - colposcopy; ASCUS - colposcopy; Atypical glandular cells - colposcopy; AGUS - colposcopy; Atypical squamous cells - colposcopy; Pap smear - colposcopy; HPV - colposcopy; Human papilloma virus - colposcopy; Cervix - colposcopy; ColposcopyA colposcopy is a special way of looking at the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina. Abnormal changes in the cells on the surface of your cervix is called cervical dysplasia.
Colposcopy uses a light and a low-powered microscope to make the cervix appear much larger. This helps your health care provider find and then biopsy abnormal areas in your cervix.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
How the Test is Performed
You will lie on a table and place your feet in stirrups, to position your pelvis for exam. The provider will place an instrument (called a speculum) into your vagina to see the cervix clearly.
Vagina
The vagina is the female body part that connects the womb (uterus) and cervix to the outside of the body.
The cervix and vagina are gently cleaned with a vinegar or iodine solution. This removes the mucus that covers the surface and highlights abnormal areas.
The provider will place the colposcope at the opening of your vagina and examine the area. Photographs may be taken. The colposcope does not touch you.
If any areas look abnormal, a small sample of the tissue will be removed using small biopsy tools. Several samples may be taken. Sometimes a tissue sample from inside the cervix is removed. This is called endocervical curettage (ECC).
How to Prepare for the Test
There is no special preparation. You may be more comfortable if you empty your bladder and bowel before the procedure.
Before the exam:
- Do not douche (this is never recommended).
- Do not place any products into the vagina.
- Do not have sex for 24 hours before the exam.
- Tell your provider if you are pregnant or could be pregnant.
This test should not be done during a heavy period, unless it is abnormal. Keep your appointment if you are:
- At the very end or beginning of your regular period
- Having abnormal bleeding
You may be able to take ibuprofen or acetaminophen (Tylenol) before the colposcopy. Ask your provider if this is OK, and when and how much you should take.
How the Test will Feel
You may have some discomfort when the speculum is placed inside your vagina. It may be more uncomfortable than a regular Pap test.
Pap test
The Pap test mainly checks for changes in the cervix that may turn into cervical cancer. Cells scraped from the opening of the cervix are examined u...

- Some women feel a slight sting from the cleansing solution.
- You may feel a pinch or cramp each time a tissue sample is taken.
- You may have some cramping or slight bleeding after the biopsy.
- Do not use tampons or put anything in your vagina for several days after a biopsy.
Some women may hold their breath during pelvic procedures because they expect pain. Slow, regular breathing will help you relax and relieve pain. Ask your provider about bringing a support person with you if that will help.
You may have some bleeding after the biopsy, for about 2 days.
- You should not douche, place tampons or creams into your vagina, or have sex for up to a week afterward. Ask your provider how long you should wait.
- You can use sanitary pads.
Why the Test is Performed
Colposcopy is done to detect cervical cancer and changes that may lead to cervical cancer.
It is most often done when you have had an abnormal Pap smear or HPV test. It may also be recommended if you have bleeding after sexual intercourse.
Colposcopy may also be done when your provider sees abnormal areas on your cervix during a pelvic exam. These may include:
- Any abnormal growth on the cervix, or elsewhere in the vagina
- Genital warts or HPV
Genital warts
Genital warts are soft growths on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals. They may be found on the penis, vulva, urethra, vagina, cervix, and...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Irritation or inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis)
Cervicitis
Cervicitis is swelling or inflamed tissue of the end of the uterus (cervix).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The colposcopy may be used to keep track of HPV, and to look for abnormal changes that can come back after treatment.
Normal Results
A smooth, pink surface of the cervix is normal.
A specialist called a pathologist will examine the tissue sample from the cervical biopsy and send a report to your provider. Biopsy results most often take 1 to 2 weeks. A normal result means there is no cancer and no abnormal changes were seen.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Your provider should be able to tell you if anything abnormal was seen during the test, including:
- Abnormal patterns in the blood vessels
- Areas that are swollen, worn away, or wasted away (atrophic)
- Cervical polyps
Cervical polyps
Cervical polyps are fingerlike growths on the lower part of the uterus that connects with the vagina (cervix).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Genital warts
- Whitish patches on the cervix
Abnormal biopsy results may be due to changes that can lead to cervical cancer. These changes are called dysplasia, or cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
- CIN I is mild dysplasia
- CIN II is moderate dysplasia
- CIN III is severe dysplasia or very early cervical cancer called carcinoma in situ
Abnormal biopsy results may be due to:
- Cervical cancer
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) -- precancerous tissue changes that are also called cervical dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Cervical dysplasia refers to abnormal changes in the cells on the surface of the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that open...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cervical warts (infection with human papilloma virus, or HPV)
Human papilloma virus
Genital warts are soft growths on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals. They may be found on the penis, vulva, urethra, vagina, cervix, and...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
If the biopsy does not determine the cause of abnormal results, you may need a procedure called a cold knife cone biopsy.
Risks
After the biopsy, you may have some bleeding for up to a week. You may have mild cramping, your vagina may feel sore, and you may have a dark discharge for 1 to 3 days.
A colposcopy and biopsy will not make it more difficult for you to become pregnant, or cause problems during pregnancy.
Contact your provider right away if:
- Bleeding is very heavy or lasts for longer than 2 weeks.
- You have pain in your belly or in the pelvic area.
- You notice any signs of infection (fever, foul odor, or discharge).
References
Bixel K, Ramaswamy B, Christian B, Cohn DE. Malignancy and pregnancy. In: Lockwood CJ, Copel JA, Dugoff L, et al, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 56.
Khan MJ, Werner CL, Darragh TM, et al. ASCCP colposcopy standards: role of colposcopy, benefits, potential harms and terminology for colposcopic practice. Journal of Lower Genital Tract Disease. 2017;21(4):223-229. PMID: 28953110 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28953110/.
Newkirk GR. Colposcopic examination. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 124.
Salcedo MP, Phoolcharoen N, Schmeler KM. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the lower genital tract (cervix, vagina, vulva): etiology, screening, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
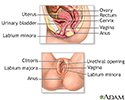
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
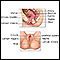
Colposcopy-directed biopsy - illustration
A colposcopy-directed biopsy is a procedure in which the cervix is examined with a colposcope for abnormalities and a tissue sample is taken.
Colposcopy-directed biopsy
illustration
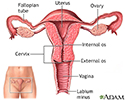
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
Colposcopy-directed biopsy - illustration
A colposcopy-directed biopsy is a procedure in which the cervix is examined with a colposcope for abnormalities and a tissue sample is taken.
Colposcopy-directed biopsy
illustration
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.