Colonoscopy
Colon cancer - colonoscopy; Colorectal cancer - colonoscopy; Colonoscopy - screening; Colon polyps - colonoscopy; Ulcerative colitis - colonoscopy; Crohn disease - colonoscopy; Diverticulitis - colonoscopy; Diarrhea - colonoscopy; Anemia - colonoscopy; Blood in stool - colonoscopyA colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope.
The colonoscope has a small camera attached to a flexible tube that can reach the entire length of the colon.
How the Test is Performed
Colonoscopy is done most often in a procedure room at your health care provider's office. It can also be done in the outpatient department of a hospital or medical center. This procedure is most often done by a specially trained doctor called a gastroenterologist.
- You will be asked to change out of your street clothes and wear a hospital gown for the procedure.
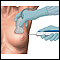
- You will likely be given medicine into a vein (IV) to help you relax. You should not feel any pain. You may be awake during the test and may even be able to speak. You will probably not remember anything.
Medicine into a vein (IV) to help you r...
Conscious sedation uses a combination of medicines to help you relax (a sedative) and to reduce pain (an analgesic) during a medical or dental proced...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - You lie on your left side with your knees drawn up toward your chest.
- The scope is gently inserted through the anus. It is carefully moved into the lowest part of the large intestine. The scope is slowly advanced as far as the lowest part of the small intestine.
- Air is inserted through the scope to provide a better view. Suction may be used to remove fluid or stool.
- The doctor gets a better view as the scope is moved back out. So, a more careful exam is done while the scope is being pulled back.
- Tissue samples (biopsy) or polyps may be removed using tiny tools inserted through the scope. Photos may be taken using the camera at the end of the scope. If needed, procedures, such as laser therapy, are also done.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePolyps
A colorectal polyp is a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLaser therapy
Laser therapy is a medical treatment that uses a strong beam of light to cut, burn, or destroy tissue. The term LASER stands for light amplification...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
How to Prepare for the Test
Your bowel needs to be completely empty and clean for the exam. A problem in your large intestine that needs to be treated may be missed if your intestines are not cleaned out.
Your provider will give you the steps for cleansing your bowel. This is called bowel preparation. Steps may include:
- Using enemas
- Not eating solid foods for 1 to 3 days before the test
- Taking laxatives
You need to drink plenty of clear liquids for 1 to 3 days before the test. Examples of clear liquids are:
- Clear coffee or tea
- Fat-free bouillon or broth
- Gelatin
- Sports drinks without added color
- Strained fruit juices
- Water
You will likely be told to stop taking aspirin, ibuprofen, naproxen, or other blood-thinning medicines for several days before the test. Keep taking your other medicines unless your provider tells you otherwise.
You will need to stop taking iron pills or liquids a few days before the test, unless your provider tells you it is OK to continue. Iron can make your stool dark black. This makes it harder for the doctor to view inside your bowel.
How the Test will Feel
The medicines given for the test will make you sleepy so that you may not feel any discomfort or have any memory of the test.
You may feel pressure as the scope moves inside. You may feel brief cramping and gas pains as air is inserted or the scope advances. Passing gas is necessary and should be expected.
After the exam, you may have mild abdominal cramping and pass a lot of gas. You may also feel bloated and sick to your stomach. These feelings will soon go away.
Abdominal cramping
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
You should be able to go home about one hour after the test. You must plan to have someone take you home after the test because you will be woozy and unable to drive. Your providers will not let you leave until someone arrives to help you.
When you are home, follow instructions on recovering from the procedure. These may include:
Instructions
A colonoscopy is an exam that views the inside of the colon (large intestine) and rectum, using a tool called a colonoscope. The colonoscope has a sm...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article- Drink plenty of liquids. Eat a healthy meal to restore your energy.
- You should be able to return to your regular activities the next day.
- Avoid driving, operating machinery, drinking alcohol, and making important decisions for at least 24 hours after the test.
Why the Test is Performed
Colonoscopy may be done for the following reasons:
- Abdominal pain, changes in bowel movements, or weight loss
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abnormal changes (polyps) found on sigmoidoscopy or x-ray tests (virtual colonoscopy, CT scan, or barium enema)
Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy using a flexible scope is a procedure used to see inside the sigmoid colon and rectum. The sigmoid colon is the area of the large inte...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleVirtual colonoscopy
A virtual colonoscopy (VC) is an imaging or x-ray test that looks for cancer, polyps, or other disease in the large intestine (colon). The medical n...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
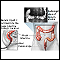
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBarium enema
Barium enema is a special x-ray of the large intestine, which includes the colon and rectum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Anemia due to low iron (usually when no other cause has been found)
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood in the stool, or black, tarry stools
Blood in the stool
Black or tarry stools with a foul smell are a sign of a problem in the upper digestive tract. It most often indicates that there is bleeding in the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Follow-up of a past finding, such as polyps or colon cancer
Polyps
A colorectal polyp is a growth on the lining of the colon or rectum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleColon cancer
Colorectal cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). It is also sometimes simply called colon ca...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease)
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a condition in which the lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum become inflamed. It is a form of inflammatory bowel ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCrohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Screening for colorectal cancer
Screening for colorectal cancer
Colon cancer screening can detect polyps and early cancers in the large intestine. This type of screening can find problems that can be treated befo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Normal Results
Normal findings are healthy intestinal tissues.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal test results may mean any of the following:
- Abnormal pouches on the lining of the intestines, called diverticulosis
Diverticulosis
Diverticula are small, bulging sacs or pouches that form on the inner wall of the intestine. Diverticulitis occurs when these pouches become inflame...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Areas of bleeding
- Cancer in the colon or rectum
- Colitis (a swollen and inflamed intestine) due to Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, infection, or lack of blood flow
Colitis
Colitis is swelling (inflammation) of the large intestine (colon).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Small growths called polyps on the lining of your colon (which can be removed through the colonoscope during the exam)
Risks
Risks of colonoscopy may include any of the following:
- Heavy or ongoing bleeding from biopsy or removal of polyps
- Hole or tear in the wall of the colon that requires surgery to repair
- Infection needing antibiotic therapy (very rare)
- Reaction to the medicine you are given to relax, causing breathing problems or low blood pressure
References
Garber JJ, Chung DC, eds. Colonic polyps and polyposis syndromes. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease: Pathophysiology/Diagnosis/Management. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 126.
National Cancer Institute website. Colorectal cancer prevention (PDQ) - health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/hp/colorectal-prevention-pdq. Updated March 28, 2024. Accessed July 26, 2024.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines): colorectal cancer screening. Version 1.2024 - February 27, 2024. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/colorectal_screening.pdf. Updated February 27, 2024. Accessed July 26, 2024.
Patel SG, May FP, Anderson JC, et al. Updates on age to start and stop colorectal cancer screening: recommendations from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2022;162(1):285-299. PMID: 34794816 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34794816/.
Shaukat A, Kahi CJ, Burke CA, Rabeneck L, Sauer BG, Rex DK. ACG clinical guidelines: colorectal cancer screening 2021. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(3):458-479. PMID: 33657038 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33657038/.
US Preventive Services Task Force website. Final recommendation statement. Colorectal cancer: screening. www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/uspstf/recommendation/colorectal-cancer-screening. Published May 18, 2021. Accessed July 26, 2024.
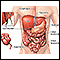
Colonoscopy - illustration
There are 3 basic tests for colon cancer; a stool test (to check for blood), sigmoidoscopy (inspection of the lower colon), and colonoscopy (inspection of the entire colon). All 3 are effective in catching cancers in the early stages, when treatment is most beneficial.
Colonoscopy
illustration
Colonoscopy - illustration
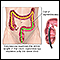
A sample of colon tissue is obtained during a colonoscopy procedure using special instruments. The specimen is sent to the laboratory and fixed with special stains. The specimen is examined under the microscope for abnormal findings, such as cancer or inflammation.
Colonoscopy
illustration
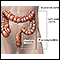
Large intestine (colon) - illustration
The large intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of water from the indigestible residue of food. The ileocecal valve of the ileum (small intestine) passes material into the large intestine at the cecum. Material passes through the ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid portions of the colon, and finally into the rectum. From the rectum, the waste is expelled from the body.
Large intestine (colon)
illustration
Colonoscopy - illustration
There are 3 basic tests for colon cancer; a stool test (to check for blood), sigmoidoscopy (inspection of the lower colon), and colonoscopy (inspection of the entire colon). All 3 are effective in catching cancers in the early stages, when treatment is most beneficial.
Colonoscopy
illustration
Colonoscopy - illustration
A sample of colon tissue is obtained during a colonoscopy procedure using special instruments. The specimen is sent to the laboratory and fixed with special stains. The specimen is examined under the microscope for abnormal findings, such as cancer or inflammation.
Colonoscopy
illustration
Large intestine (colon) - illustration
The large intestine is the portion of the digestive system most responsible for absorption of water from the indigestible residue of food. The ileocecal valve of the ileum (small intestine) passes material into the large intestine at the cecum. Material passes through the ascending, transverse, descending and sigmoid portions of the colon, and finally into the rectum. From the rectum, the waste is expelled from the body.
Large intestine (colon)
illustration
Review Date: 1/31/2023
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Internal review and update on 07/26/2024 by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.




