Nasal mucosal biopsy
Biopsy - nasal mucosa; Nose biopsyA nasal mucosal biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue from the lining of the nose so that it can be checked for disease.
How the Test is Performed
A painkiller is sprayed into the nose. In some cases, a numbing shot may be used. A small piece of the tissue that appears abnormal is removed and checked for problems in the laboratory.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed. You may be asked to fast for a few hours before the biopsy.
How the Test will Feel
You may feel pressure or tugging when the tissue is removed. After the numbness wears off, the area may be sore for a few days.
A small to moderate amount of bleeding after the procedure is common. If there is bleeding, the blood vessels may be sealed with an electric current, laser, or chemical.
Why the Test is Performed
Nasal mucosal biopsy is most often done when abnormal tissue is seen during examination of the nose. It may also be done when the health care provider suspects you have a problem affecting the mucosal tissue of the nose or for diagnosis of certain diseases like primary ciliary dyskinesia or granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
Normal Results
The tissue in the nose is normal.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may indicate:
- Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections, such as tuberculosis
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Necrotizing granuloma, a type of non-cancerous tumor
Necrotizing granuloma
A granuloma is a clump of cells that forms when the immune system tries to fight off a harmful substance but cannot remove it from the body. A necrot...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Nasal polyps
Nasal polyps
Nasal polyps are soft, sac-like growths on the lining of the nose or sinuses.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nasal tumors
Nasal tumors
Juvenile angiofibroma is a noncancerous growth that causes bleeding in the nose and sinuses. It is most often seen in boys and young adult men....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and/or other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
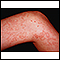
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) is a rare disorder in which blood vessels become inflamed. This leads to damage in major organs of the body. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary ciliary dyskinesia
Risks
Risks involved with this procedure include:
- Bleeding from the biopsy site
- Infection
Considerations
Avoid blowing your nose after the biopsy. Do not pick your nose or put your fingers over the area. Gently squeeze the nostrils shut if there is bleeding, holding the pressure for 10 minutes. If the bleeding doesn't stop after 30 minutes, you may need to see your doctor. The blood vessels may be sealed with an electric current or packing.
References
Batra PS, Wrobel BB, Trimarchi M. Systemic diseases of the nose and sinuses. In: Flint PW, Francis HW, Haughey BH, et al, eds. Cummings Otolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 51.
Bauman JE. Head and neck cancer. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 176.
Judson MA, Koth LL, Baughman RP. Sarcoidosis. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 93.
Sinuses - illustration
The sinuses are hollow cavities within the facial bones. Sinuses are not fully developed until after age 12. When people speak of sinus infections, they are most frequently referring to the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses.
Sinuses
illustration
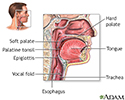
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
Nasal biopsy - illustration
A nasal biopsy is a diagnostic procedure in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the mucosal lining of the nose. The biopsy is most often performed when abnormal tissue is observed during an examination of the nose, or when disorders affecting the nasal mucosal tissue are suspected.
Nasal biopsy
illustration
Sinuses - illustration
The sinuses are hollow cavities within the facial bones. Sinuses are not fully developed until after age 12. When people speak of sinus infections, they are most frequently referring to the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses.
Sinuses
illustration
Throat anatomy - illustration
Structures of the throat include the esophagus, trachea, epiglottis and tonsils.
Throat anatomy
illustration
Nasal biopsy - illustration
A nasal biopsy is a diagnostic procedure in which a small piece of tissue is removed from the mucosal lining of the nose. The biopsy is most often performed when abnormal tissue is observed during an examination of the nose, or when disorders affecting the nasal mucosal tissue are suspected.
Nasal biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 6/4/2023
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.