Gram stain of skin lesion
Skin lesion Gram stainA Gram stain of a skin lesion is a lab test that uses special stains to detect and identify bacteria in a sample from the skin. The Gram stain method is one of the most commonly used techniques to quickly diagnose bacterial infections.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider will remove a sample of tissue from the skin sore (lesion). This can be done with a simple swab, a needle or syringe, or with a biopsy. If you have a biopsy, your provider will numb the area of skin so you don't feel anything.
Biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
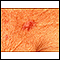
The sample is sent to a lab. There, it is applied in a very thin layer to a glass slide. A series of different colored stains are applied to the sample. The stained slide is examined under a microscope to check for bacteria. The color, size, shape, and organization of the cells help identify the germ causing the infection.
How to Prepare for the Test
No preparation is needed for the lab test.
How the Test will Feel
There will be a sting when the anesthetic is given. You should only feel pressure or discomfort similar to a pinprick during the biopsy.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test if you have signs of an infected skin sore. The test is done to determine which bacteria caused the infection.
Normal Results
A normal result means no bacteria are present on the Gram stain. Other tests may be done to help diagnose the problem.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result means bacteria have been found in the skin lesion. Further tests may be needed to confirm the results. This allows your provider to prescribe the appropriate antibiotic or other treatment.
Risks
Risks of a skin biopsy may include:
- Infection
- Scar
You will bleed slightly during the procedure.
Considerations
A skin or mucosal culture may be done along with this test. Other studies are often done on a skin sample to determine if cancer is present.
Skin or mucosal culture
A skin or nail culture is a laboratory test to look for and identify germs that cause problems with the skin or nails. It is called a mucosal culture...
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleViral skin lesions, such as herpes simplex, are examined by other tests or a viral culture.
Viral culture
Herpes viral culture of a lesion is a laboratory test to check if a skin sore is infected with the herpes virus.

References
Dinulos JGH. Bacterial infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
Wojewoda CM, Stempak LM. Medical bacteriology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 57.
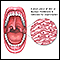
Gram stain - illustration
A Gram stain is a test used to help identify bacteria. The tested sample can be taken from body fluids that do not normally contain bacteria, such as blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid. A sample can also be taken from the site of a suspected infection, such as the throat, lungs, genitals, or skin. Bacteria are classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative, based on how they color in reaction with the Gram stain. The Gram stain is colored purple. When combined with the bacteria in a sample, the stain will either stay purple inside the bacteria (Gram-positive), or it will turn pink (Gram-negative). Examples of Gram-positive bacteria include Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as bacteria that cause anthrax, diphtheria, and toxic shock syndrome. Examples of Gram-negative bacteria include Escherichia coli (E coli), Salmonella, Hemophilus influenzae, as well as many bacteria that cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, or peritonitis. Gram stain can be done within a few hours. The results help providers choose the first antibiotics to use. Cultures of bacteria help identify specific bacteria, but take days to complete.
Gram stain
illustration
Gram stain - illustration
A Gram stain is a test used to help identify bacteria. The tested sample can be taken from body fluids that do not normally contain bacteria, such as blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid. A sample can also be taken from the site of a suspected infection, such as the throat, lungs, genitals, or skin. Bacteria are classified as either Gram-positive or Gram-negative, based on how they color in reaction with the Gram stain. The Gram stain is colored purple. When combined with the bacteria in a sample, the stain will either stay purple inside the bacteria (Gram-positive), or it will turn pink (Gram-negative). Examples of Gram-positive bacteria include Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus, as well as bacteria that cause anthrax, diphtheria, and toxic shock syndrome. Examples of Gram-negative bacteria include Escherichia coli (E coli), Salmonella, Hemophilus influenzae, as well as many bacteria that cause urinary tract infections, pneumonia, or peritonitis. Gram stain can be done within a few hours. The results help providers choose the first antibiotics to use. Cultures of bacteria help identify specific bacteria, but take days to complete.
Gram stain
illustration
Review Date: 10/11/2024
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


