Fecal culture
Stool culture; Culture - stool; Gastroenteritis fecal cultureA fecal culture is a lab test to find organisms in the stool (feces) that can cause gastrointestinal symptoms and disease.
How the Test is Performed
A stool sample is needed.
There are many ways to collect the sample.
You can collect the sample:
- On plastic wrap. Place the wrap loosely over the toilet bowl so that it is held in place by the toilet seat. Put the sample in a clean container given to you by your health care provider.
- In a plastic container for the toilet that the lab may give you.
- In a test kit that supplies a special toilet tissue. Put it in a clean container given to you by your provider.
Do not mix urine, water, or toilet tissue with the sample.
For children wearing diapers:
- Line the diaper with plastic wrap.
- Position the plastic wrap so that it will prevent urine and stool from mixing. This will provide a better sample.
Return the sample to the laboratory as soon as possible. Do not include toilet paper or urine in the specimen.
In the lab, a technician places a sample of the specimen in a special dish. The dish is then filled with a gel that boosts the growth of bacteria or other germs. If there is growth, the germs are identified. The lab technician may also do more tests to determine the best treatment.
How to Prepare for the Test
You will get a collection container for the stool specimen. Depending on the stool tests ordered, you may be given multiple collection bottles. They may have different instructions. Read everything ahead of time, and make sure to follow all instructions carefully.
How the Test will Feel
There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
The test is performed when your health care provider suspects that you may have a gastrointestinal infection. It may be done if you have severe diarrhea that does not go away or that keeps coming back.
Normal Results
There are no abnormal bacteria or other organisms in the sample.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Abnormal results may mean you have an intestinal infection. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
Intestinal infection
Bacterial gastroenteritis occurs when there is a bacterial infection of your stomach or intestines.

Risks
There are no risks.
Considerations
Often other stool tests are done in addition to the culture, such as:
- Gram stain of stool
Gram stain of stool
A stool Gram stain is a laboratory test that uses different chemical stains to detect and identify bacteria in a stool sample. The Gram stain method ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fecal smear
Fecal smear
Fecal smear is a laboratory test of a stool sample. This test is done to check for bacteria and parasites. Presence of organisms in stool shows dis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stool ova and parasites exam
Stool ova and parasites exam
Stool ova and parasites exam is a lab test to look for parasites or eggs (ova) in a stool sample. The parasites are associated with intestinal infec...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Fleckenstein JM. Approach to the patient with suspected enteric infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 262.
Melia JMP, Sears CL. Infectious enteritis and proctocolitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease.11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 110.
Siddiqi HA, Rabinowitz S, Axiotis CA. Laboratory diagnosis of gastrointestinal and pancreatic disorders. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Wojewoda CM, Stempak LM. Medical bacteriology. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 57.
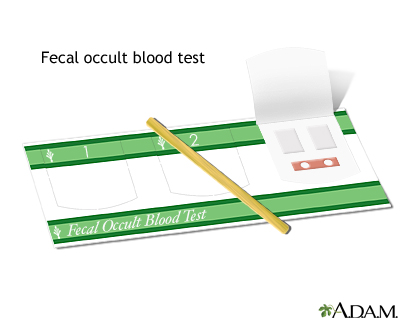
Fecal occult blood test - illustration
A fecal occult blood test is a noninvasive test that detects the presence of hidden blood in the stool. Blood in the stool that is not visible is often the first, and in many cases the only, warning sign that a person has colorectal disease, including colon cancer.
Fecal occult blood test
illustration
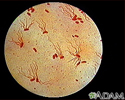
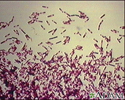
Salmonella typhi organism - illustration
The causative agent of typhoid fever is the bacterium Salmonella typhi. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Salmonella typhi organism
illustration
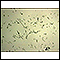
Yersinia enterocolitica organism - illustration
This picture shows the organism Yersinia enterocolitica. Yersinia organisms cause a wide range of disease but are most often associated with diarrhea or gastrointestinal symptoms. Yersinia infection is appearing with increased frequency in immunocompromised individuals. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Yersinia enterocolitica organism
illustration
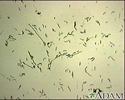
Campylobacter jejuni organism - illustration
Campylobacter jejuni infection causes cramping, diarrhea, abdominal pain and fever within 2 to 5 days after a person has been exposed to the organism. Campylobacter jejuni is one of the most common bacterial causes of diarrhea. Most cases of Campylobacter jejuni come from handling or ingesting raw or undercooked poultry meat. Although poultry and other birds are not affected by the bacterium, other animals can be. Therefore it is possible for a person to acquire the infection from contact with infected stool of an ill cat or dog. This is what Campylobacter organisms look like through a microscope. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Campylobacter jejuni organism
illustration
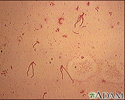
Clostridium difficile organism - illustration
Clostridioides difficile is a bacterium commonly found in the intestinal tract but which, under the right circumstances, such as after or during antibiotics therapy, can be the cause of enterocolitis. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Clostridium difficile organism
illustration
Fecal occult blood test - illustration
A fecal occult blood test is a noninvasive test that detects the presence of hidden blood in the stool. Blood in the stool that is not visible is often the first, and in many cases the only, warning sign that a person has colorectal disease, including colon cancer.
Fecal occult blood test
illustration
Salmonella typhi organism - illustration
The causative agent of typhoid fever is the bacterium Salmonella typhi. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Salmonella typhi organism
illustration
Yersinia enterocolitica organism - illustration
This picture shows the organism Yersinia enterocolitica. Yersinia organisms cause a wide range of disease but are most often associated with diarrhea or gastrointestinal symptoms. Yersinia infection is appearing with increased frequency in immunocompromised individuals. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Yersinia enterocolitica organism
illustration
Campylobacter jejuni organism - illustration
Campylobacter jejuni infection causes cramping, diarrhea, abdominal pain and fever within 2 to 5 days after a person has been exposed to the organism. Campylobacter jejuni is one of the most common bacterial causes of diarrhea. Most cases of Campylobacter jejuni come from handling or ingesting raw or undercooked poultry meat. Although poultry and other birds are not affected by the bacterium, other animals can be. Therefore it is possible for a person to acquire the infection from contact with infected stool of an ill cat or dog. This is what Campylobacter organisms look like through a microscope. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Campylobacter jejuni organism
illustration
Clostridium difficile organism - illustration
Clostridioides difficile is a bacterium commonly found in the intestinal tract but which, under the right circumstances, such as after or during antibiotics therapy, can be the cause of enterocolitis. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Clostridium difficile organism
illustration
Review Date: 6/11/2024
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, MD, Department of Gastroenterology, Aria - Jefferson Health Torresdale, Jefferson Digestive Diseases Network, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.