Mycobacterial culture
Culture - mycobacterialMycobacterial culture is a test to look for the bacteria that cause tuberculosis and other infections caused by similar bacteria.
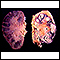
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
How the Test is Performed
A sample of body fluid or tissue is needed. This sample may be taken from the lungs, liver, or bone marrow.
Most often, a sputum sample will be taken. To obtain a sample, you will be asked to cough deeply and spit out the material that comes up from your lungs.
Sputum sample will be taken
Sputum stain for mycobacteria is a test to check for a type of bacteria that cause tuberculosis and other infections.

A biopsy or aspiration may also be done.
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
Aspiration
Aspiration means to draw in or out using a sucking motion. It has two meanings:Breathing in a foreign object (for example, sucking food into the air...
The sample is sent to a laboratory. There it is placed in a special dish (culture). It is then watched for up to 6 weeks to see if the bacteria grow.
How to Prepare for the Test
Preparation depends on how the test is done. Follow your health care provider's instructions.
How the Test will Feel
How the test will feel depends on the specific procedure. Your provider can discuss this with you before the test.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may order this test if you have signs of tuberculosis or a related infection.
Normal Results
If there is no disease present, there will be no growth of bacteria in the culture medium.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Mycobacterium tuberculosis or similar bacteria is present in the culture.
Risks
Risks depend on the specific biopsy or aspiration being performed.
References
Fitzgerald DW, Sterling TR, Haas DW. Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 249.
Rodino KG, Woods GL, Wengenack NL. Mycobacteria. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 59.
-
Liver culture - illustration
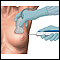
During a liver biopsy, a needle is inserted into the liver and a tissue sample is withdrawn and sent to the laboratory for testing. The test is performed to determine the presence of tuberculosis infection in the liver.
Liver culture
illustration
-
Sputum test - illustration
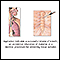
A sputum sample is obtained by coughing deeply and expelling the material that comes from the lungs into a sterile cup. The sample is taken to a laboratory and placed in a medium under conditions that allow the organisms to grow. A positive culture may identify disease-producing organisms that may help diagnose bronchitis, tuberculosis, a lung abscess, or pneumonia.
Sputum test
illustration
-
Liver culture - illustration
During a liver biopsy, a needle is inserted into the liver and a tissue sample is withdrawn and sent to the laboratory for testing. The test is performed to determine the presence of tuberculosis infection in the liver.
Liver culture
illustration
-
Sputum test - illustration
A sputum sample is obtained by coughing deeply and expelling the material that comes from the lungs into a sterile cup. The sample is taken to a laboratory and placed in a medium under conditions that allow the organisms to grow. A positive culture may identify disease-producing organisms that may help diagnose bronchitis, tuberculosis, a lung abscess, or pneumonia.
Sputum test
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.




