Sickle cell test
Sickledex; Hgb S testThe sickle cell test looks for the abnormal hemoglobin in the blood that causes the disorder sickle cell disease.
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. The hemoglobin test measures how much hemoglobin is in your blood.

Sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is a disorder passed down through families. The red blood cells that are normally shaped like a disk take on a sickle or crescen...
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to tell if a person has abnormal hemoglobin that causes sickle cell disease and sickle cell trait. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
In sickle cell disease, a person has two abnormal hemoglobin S genes. A person with sickle cell trait has only one of these abnormal genes and no symptoms, or only mild ones.
This test does not tell the difference between these two conditions. Another test, called hemoglobin electrophoresis, will be done to tell which condition someone has.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Hemoglobin is a protein that carries oxygen in the blood. It is present inside the red blood cells. Hemoglobin electrophoresis measures the levels ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleNormal Results
A normal test result is called a negative result.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal test result indicates the person might have one of these:
- Sickle cell disease
- Sickle cell trait
Iron deficiency or blood transfusions within the past 3 months can cause a false negative result. This means the person might have the abnormal hemoglobin for sickle cell, but these other factors are making their test results appear negative (normal).
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another, and from one side of the body to the other. Obtaining a blood sample from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
Fainting
Fainting is a brief loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood flow to the brain. The episode most often lasts less than a couple of minutes and y...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple punctures to locate veins
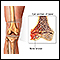
- Hematoma (blood buildup under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Get screened to know your sickle cell status. www.cdc.gov/sickle-cell/sickle-cell-trait/fact-sheet-get-screened-to-know-your-sickle-cell-status.html. Updated May 15, 2024. Accessed May 27, 2024.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) About sickle cell disease. www.cdc.gov/sickle-cell/about/index.html. Updated May 15, 2024. Accessed June 25, 2024.
Menapace LA, Thein SL. Clinical aspects of sickle cell disease. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 43.
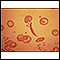
Red blood cells, sickle cell - illustration
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disease in which the red blood cells produce abnormal pigment (hemoglobin). The abnormal hemoglobin causes deformity of the red blood cells into crescent or sickle-shapes, as seen in this photomicrograph.
Red blood cells, sickle cell
illustration
Red blood cells - multiple sickle cells - illustration
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disorder in which abnormal hemoglobin (the red pigment inside red blood cells) is produced. The abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to assume a sickle shape, like the ones seen in this photomicrograph.
Red blood cells - multiple sickle cells
illustration
Red blood cells - sickle cells - illustration
These crescent or sickle-shaped red blood cells (RBCs) are present with Sickle cell anemia, and stand out clearly against the normal round RBCs. These abnormally shaped cells may become entangled and block blood flow in the small blood vessels (capillaries).
Red blood cells - sickle cells
illustration
Red blood cells - sickle and Pappenheimer - illustration
This photomicrograph of red blood cells (RBCs) shows both sickle-shaped and Pappenheimer bodies.
Red blood cells - sickle and Pappenheimer
illustration
Red blood cells, sickle cell - illustration
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited blood disease in which the red blood cells produce abnormal pigment (hemoglobin). The abnormal hemoglobin causes deformity of the red blood cells into crescent or sickle-shapes, as seen in this photomicrograph.
Red blood cells, sickle cell
illustration
Red blood cells - multiple sickle cells - illustration
Sickle cell anemia is an inherited disorder in which abnormal hemoglobin (the red pigment inside red blood cells) is produced. The abnormal hemoglobin causes red blood cells to assume a sickle shape, like the ones seen in this photomicrograph.
Red blood cells - multiple sickle cells
illustration
Red blood cells - sickle cells - illustration
These crescent or sickle-shaped red blood cells (RBCs) are present with Sickle cell anemia, and stand out clearly against the normal round RBCs. These abnormally shaped cells may become entangled and block blood flow in the small blood vessels (capillaries).
Red blood cells - sickle cells
illustration
Red blood cells - sickle and Pappenheimer - illustration
This photomicrograph of red blood cells (RBCs) shows both sickle-shaped and Pappenheimer bodies.
Red blood cells - sickle and Pappenheimer
illustration
- Sickle cell disease - InDepth(In-Depth)
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.





